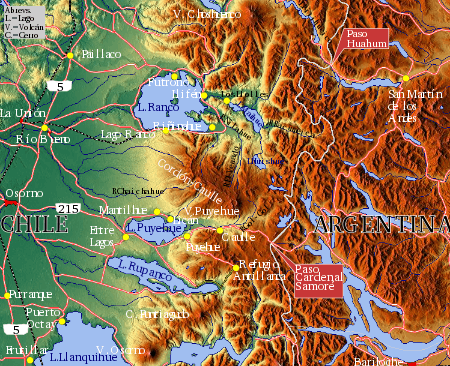
Puyehue Lake
| Puyehue Lake | |
|---|---|
 View of the lake with Puyehue volcano in the background | |
| Coordinates | 40°41′01″S 72°27′46″W / 40.68361°S 72.46278°WCoordinates: 40°41′01″S 72°27′46″W / 40.68361°S 72.46278°W |
| Primary inflows | Gol-Gol River |
| Primary outflows | Pilmaiquén River |
| Catchment area | 1267 km3 |
| Basin countries | Chile |
| Max. length | 23 km |
| Max. width | 11.5 km |
| Surface area | 157 km²[1] |
| Max. depth | 123 m[2] |
| Water volume | 12.6 km[2] |
| Surface elevation | 212 m[1] |
| Islands | Fresia Island, Cuicui Islands |
| Settlements | Entre Lagos |
| References | [1] |
Puyehue Lake (Spanish pronunciation: [puˈjewe]), Mapudungun: puye, small fish and hue, place is an Andean piedmont lake located in the border of Los Lagos Region with Los Ríos Region of Chile. Puyehue is a lake of glacial origin, several times during the pleistocene glaciations the lake depression was occupied by a large glacier lobe of the Patagonian Ice Sheet forming thus a series of moraines along its western shores. The lake has an east-west elongated shape with Fresia Island in the middle and two minor peninsulas pointing toward the island, one from the north and one from the south. The lake has remarkably smooth coasts with only one inlet of significance; the Futacullín Bay on the south.[1]
As most other lakes of southern Chile, Puyehue Lake acts as a sediment trap for material from the Andes. Sediment cores taken from Puyehue Lake in 2001 and 2002 have been interpreted as supporting the existence of the Little Ice Age in the Southern Hemisphere.[3] A longer sediment core from the same site was used to reconstruct the evolution of the lake and its drainage basin during the last 18,000 years.[4][5][6]
The 2011 Puyehue eruption polluted the waters of Nilahue and Golgol rivers, killing fishes. Pyroclastic material reached Puyehue Lake through river transport, which resulted in the deposition of a layer of volcanic ash at the bottom of the lake.[7][8]
References
- 1 2 3 4 Cuenca del río Bueno
- 1 2 Campos, H., Steffen, W., Agüero, G., Parra, O., Zúñiga, L., 1989. Estudios limnologicos en el Lago Puyehue (Chile): morfometria, factores fisicos y quimicos, plancton y productividad primaria. Medio Ambiente 10, 36–53.
- ↑ Bertrand, Sebastien; Boes Xavier, Castiaux, Julie; Charlet, Francois; Urrutia, Roberto; Espinoza, Cristian; Lepoint, Gilles; Charlier, Bernard; Fagel, Nathalie (2005). Temporal evolution of sediment supply in Lago Puyehue (Southern Chile) during the last 600 yr and its climatic significance. Quaternary Research 64, 163-175
- ↑ Bertrand et al., A 17,900-year multi-proxy lacustrine record of Lago Puyehue
- ↑ Bertrand et al., 2010 Bulk organic geochemistry of sediments from Puyehue Lake and its watershed (Chile, 40°S): Implications for paleoenvironmental reconstructions
- ↑ Moernaut et al. Giant earthquakes in South-Central Chile revealed by Holocene mass-wasting events in Lake Puyehue
- ↑ Lago Puyehue tiene 10 centímetros de piedra pómez en el fondo tras erupción, Austral de Osorno, 2 de diciembre de 2014.
- ↑ Bertrand et al. (2014) Deposition of the 2011–2012 Cordón Caulle tephra (Chile, 40°S) in lake sediments: Implications for tephrochronology and volcanology, Journal of Geophysical Research - Earth Surface