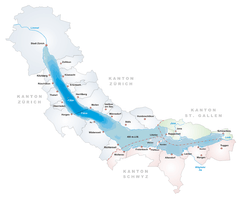
Seedamm
Seedamm is the partially artificial causeway and bridge at the most narrow area of Lake Zurich, between Hurden (SZ) and Rapperswil (SG). The Seedamm carries a road and a railway across the lake, with the railway being used by the S5 and S40 lines of the S-Bahn Zürich and by the Südostbahn Voralpen Express.


Geography and location
The Seedam is based on an ice age moraine located between the three Swiss cantons of Schwyz, St. Gallen and Zürich. This morain formed a peninsula protruding from the south shore of the lake and containing the village of Hurden, a small island to the Rapperswil side of the lake, and a section of shallow water dividing Lake Zürich and its upper part (so-called Obersee). The causeway and bridges span this area of shallow water, are 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) in length and carry a road and a railway line. To the east of the modern causeway and bridge, there is the Holzbrücke Rapperswil-Hurden (wooden bridge for pedestrians), built in 2001 as a reconstruction of the first bridge between eastern and western lakesides around 1650 B.C. Situated to the southwest, Frauenwinkel is a mire landscape situated at the Seedamm' area on the easternly Zürichsee lakeshore between Hurden and Pfäffikon, respectively the Lützelau and Ufenau islands.
History
Around 1650 BC a first wooden footbridge led across Lake Zurich followed by several reconstructions at least until the late 2nd century AD when the Roman Empire built a 6 metres (20 ft) wide wooden bridge under Empire Marcus Aurelius (161-180).[2][3] At Kempraten's Lake Zurich bay, the Roman transshipment harbour for goods was located that have been transported on the Roman streets, on the wooden bridge Rapperswil-Hurden and on the waterway Zürichsee-Obersee–Linth–Walensee. Historians mention a 10th-century ferry station assumably at the so-called Einsiedlerhaus in Rapperswil – in 981 AD as well as the vineyard on the Lindenhof hill – between Kempraten on lake shore, Lützelau and Ufenau island and assumably present Hurden, which allowed the pilgrims towards Einsiedeln to cross the lake before the prehistoric bridge at the Seedamm isthmus was re-built.[4] By 1358, ferry services between Rapperswil and Hurden are mentioned. Between 1358 and 1360, Rudolf IV, Duke of Austria, built a wooden bridge across the lake that has been used to 1878 – measuring approximately 1,450 metres (4,760 ft) in length and 4 metres (13 ft) wide; 546 oak piles have been installed. A small wooden bridge from Ufenau island to Hurden is mentioned around 1430, so-called Kilchweg in die Ufenau.[5][6] In 1873 the Swiss federal parliament approved the construction of the today's stone causeway and bridge. Construction works have been begun in 1875 and finished in 1878 (in the same year the wooden bridge was broken). The construction costs the sum of 1,462,000 Swiss Francs, of which 1,100,000 have been paid by the city of Rapperswil. In 1878 the Zürichsee-Gotthardbahn established the railway line from Rapperswil railway station via Seedamm. In 1939 and 1951 the now called Seedamm causeway was reinforced to meet the growing demands. Whilst the bridge sections of the Seedamm allow smaller vessels to pass under them, the main shipping channel between the lower and upper halves of Lake Zürich now passes through the Hurden ship canal, which was cut through the base of the Hurden peninsular in 1942/43, thus placing the village of Hurden on an artificial island. This canal is spanned by the Sternenbrücke, which also carries both road and railway. This bridge was renewed between March and November 2010 to allow 40 ton trucks to cross the Seedamm.[7][8]
In 2001 a new wooden footbridge was opened alongside the causeway for the first 840 metres (2,760 ft) of the crossing. It was built in quite the same place as the historical lake bridge linking Rapperswil with the nearby Heilig Hüsli bridge chapel that was built in 1551. This connection for centuries has been part of old pilgrimage routes, the so-called Jakobsweg to the Einsiedeln Abbey.
At the beginning of the 21st-century, about 75 passenger trains and 24,000 vehicles crossed the causeway and the town of Rapperswil-Jona every day, and as of 2016, an average of 26,000 vehicles.[9] In order to relieve the traffic on road and rail during rush hours, Rapperswil-Jona is expected to participate as the first Swiss city in a pilot project for so-called Mobility pricing.[9]
Cultural heritage
Located on Obersee lakeshore at the Seedamm isthmus between the Zürichsee and the Obersee lake area, the area was in close vicinity to the Prehistoric lake crossings, neighbored by four Prehistoric pile dwelling settlements: Freienbach–Hurden Rosshorn,[10] Freienbach–Hurden Seefeld,[11] Seegubel[12] and Rapperswil-Jona–Technikum.[13] Because the lake has grown in size over time, the original piles are now around 4 metres (13 ft) to 7 metres (23 ft) under the water level of 406 metres (1,332 ft).
As well as being part of the 56 Swiss sites of the UNESCO Worl Heritage Site Prehistoric pile dwellings around the Alps, the settlements are also listed in the Swiss inventory of cultural property of national and regional significance as Class A objects of national importance.[14][15]
Literature
- Geneviève Lüscher: Brücken und Wege der Bronzezeit. Schweizerischer Nationalfonds. In: Horizonte, März 2005.
- Beat Eberschweiler: Ur- und frühgeschichtliche Verkehrswege über den Zürichsee: Erste Ergebnisse aus den Taucharchäologischen Untersuchungen beim Seedamm. In: Mitteilungen des Historischen Vereins des Kantons Schwyz, No. 96, Schwyz 2004.
- Hans Rathgeb: Brücken über den See. Arbeitsgemeinschaft Fussgänger-Holzsteg Rapperswil-Hurden, Rapperswil 2001. ISBN 3-9522511-1-9
See also
References
- ↑ Alwina Gossauer's claimed "1879" (in fact 1878) photograph was supplemented with graphic elements: ships, waves and grass in the foreground, as wells as the causeway with steam railway, carriages and pedestrians were added. First published in the 1879 book "Geschichte der Stadt Rapperswil" (literally: History of the city of Rapperswil), the photograph was predated because the railway causeway was still under construction in 1878.
- ↑ Unterwasserarchäologische Projekte Kanton St. Gallen. (in German). Retrieved on 10 March 2010.
- ↑ Neue Zürcher Zeitung (20/21 January 2001): Die Brücke auf dem Grund des Zürichsees. (in German). Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- ↑ "Das Einsiedlerhaus in Rapperswil wechselt den Besitzer" (in German). Kapuzinerkloster Rapperswil, published by Markus Turnherr, Stadtarchivar, in Obersee Nachrichten. Retrieved 2015-09-12.
- ↑ Hurden: History. (in German). Retrieved on 10 March 2010.
- ↑ Website Holzsteg Rapperswil (in German). Retrieved on 10 March 2010.
- ↑ "Die Geschichte von Hurden" [The history of Hurden] (in German). uch.ch. Retrieved 18 August 2014.
- ↑ "Seedamm wird saniert" [Causeway is being renovated] (in German). Tages-Anzeiger. 9 March 2010. Retrieved 18 August 2014.
- 1 2 "FOKUS: Mobility Pricing soll Pendlerverkehr entlasten" (in German). 10vor10. 2016-06-30. Retrieved 2016-06-30.
- ↑ "Sites Switzerland: Freienbach–Hurden Rosshorn (CH-SZ-01)". palafittes.org. Retrieved 2014-12-08.
- ↑ "Sites Switzerland: Freienbach–Hurden Rosshorn (CH-SZ-02)". palafittes.org. Retrieved 2014-12-08.
- ↑ "Sites Switzerland: Rapperswil-Jona/Hombrechtikon–Feldbach (CH-SG-01)". palafittes.org. Retrieved 2014-12-08.
- ↑ "Sites Switzerland: Rapperswil-Jona–Technikum (CH-SG-02)". palafittes.org. Retrieved 2014-12-08.
- ↑ "A-Objekte KGS-Inventar (Kanton Schwyz)" (PDF). Schweizerische Eidgenossenschaft, Amt für Bevölkerungsschutz. 2015-01-01. Retrieved 2015-09-14.
- ↑ "A-Objekte KGS-Inventar (Kanton St. Gallen)" (PDF). Schweizerische Eidgenossenschaft, Amt für Bevölkerungsschutz. 2015-01-01. Retrieved 2015-09-14.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Seedamm. |
Coordinates: 47°13′16″N 8°48′40″E / 47.22111°N 8.81111°E