South African Class ME 2-6-6-2
|
Class ME no. 1618, c. 1912 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The South African Railways Class ME 2-6-6-2 of 1912 was a steam locomotive.
In January 1912, the South African Railways placed a single Class ME Mallet articulated steam locomotive with a 2-6-6-2 wheel arrangement in service.[1][2][3][4]
Manufacturer
During 1911, the Central South African Railways (CSAR) placed an order for an experimental simple expansion Mallet articulated steam locomotive with the North British Locomotive Company (NBL). The locomotive was intended for test purposes on branchlines with light 45 pounds per yard (22 kilograms per metre) rail.[1][2][3][5]
By the time it was delivered in January 1912, the CSAR had already become part of the newly established South African Railways (SAR). The locomotive was therefore classified as the sole Class ME and numbered 1618 on the SAR roster.[1][2][3][4]
Characteristics
Having been built for branchline working, the engine's maximum axle load was 9 long tons 18 hundredweight (10,060 kilograms) and it was delivered with the 6 long tons (6.1 tonnes) coal capacity version of the Type XF tender. Its Belpaire firebox extended over the second and third coupled wheels of the rear engine unit.[2][6][7]
Compared to other Mallet locomotives which were placed in service during the first decade of the SAR’s existence, the Class ME was unique in being arranged as a simple expansion (simplex) locomotive with four high pressure cylinders, instead of the more usual compound expansion arrangement of two high pressure and two low pressure cylinders.[1][3][8]
The cylinders were arranged outside the plate frames and the 6 inches (152 millimetres) diameter trick-ported piston valves, designed for inside admission, were actuated by Walschaerts valve gear. Each engine unit was equipped with an independent Wakefield mechanical lubricator to supply oil to the valves and pistons.[2]
The comparatively low boiler pressure of 170 pounds per square inch (1,172 kilopascals) is indicative of the opinion held at the time, that the economies to be gained from superheating did not require high boiler pressure. The boiler was equipped with a Schmidt superheater. Steam distribution to the four cylinders was rather unique, being led from the superheater header in the smokebox to a steam collector box, which was arranged between the two cylinders of the rear engine unit, from where a branch was led to the cylinders of the front engine unit by a central steam pipe with flexible joints, since this engine unit could move sideways in relation to the boiler barrel. This pipe took the place of the usual receiver pipe on compound Mallets.[2]
The blast pipe had separate outlets for the exhaust steam from each engine unit, with the rear engine unit's exhaust feeding through an annulus, arranged around the exhaust from the front engine unit. A device was installed by which either engine unit could be cut out whilst running, so that steam could be admitted to one pair of cylinders only, when running light.[2]
Service
The Class ME proved to be successful in operation and, even though it was acquired as an experimental locomotive, remained in service for twenty-five years. It spent its last years working on the line from Nelspruit to Sabie in the Eastern Transvaal Lowveld, until it was withdrawn and scrapped in 1937.[1]
Illustration
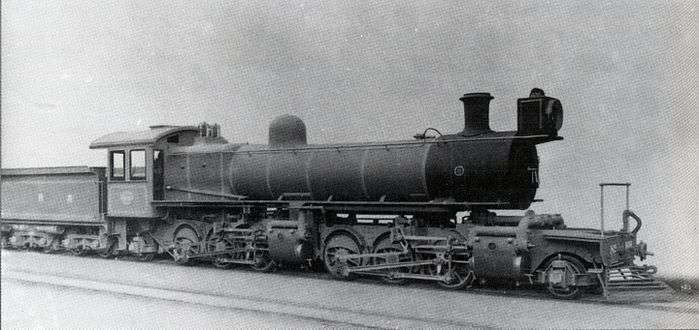 Builder's works picture of no. 1618
Builder's works picture of no. 1618
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Holland, D.F. (1972). Steam Locomotives of the South African Railways, Volume 2: 1910-1955 (1st ed.). Newton Abbott, Devon: David & Charles. pp. 21–22. ISBN 978-0-7153-5427-8.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Espitalier, T.J.; Day, W.A.J. (1945). The Locomotive in South Africa - A Brief History of Railway Development. Chapter VII - South African Railways (Continued). South African Railways and Harbours Magazine, May 1945. pp. 347-348.
- 1 2 3 4 Paxton, Leith; Bourne, David (1985). Locomotives of the South African Railways (1st ed.). Cape Town: Struik. p. 86. ISBN 0869772112.
- 1 2 Classification of S.A.R. Engines with Renumbering Lists, issued by the Chief Mechanical Engineer’s Office, Pretoria, January 1912, pp. 9, 12, 15, 46 (Reprinted in April 1987 by SATS Museum, R.3125-6/9/11-1000)
- ↑ North British Locomotive Company works list, compiled by Austrian locomotive historian Bernhard Schmeiser
- ↑ South African Railways & Harbours/Suid Afrikaanse Spoorweë en Hawens (15 Aug 1941). Locomotive Diagram Book/Lokomotiefdiagramboek, 3'6" Gauge/Spoorwydte. SAR/SAS Mechanical Department/Werktuigkundige Dept. Drawing Office/Tekenkantoor, Pretoria. p. 43.
- ↑ South African Railways & Harbours/Suid Afrikaanse Spoorweë en Hawens (15 Aug 1941). Locomotive Diagram Book/Lokomotiefdiagramboek, 2'0" & 3'6" Gauge/Spoorwydte, Steam Locomotives/Stoomlokomotiewe. SAR/SAS Mechanical Department/Werktuigkundige Dept. Drawing Office/Tekenkantoor, Pretoria. pp. 6a-7a, 41, 43.
- ↑ Holland, D.F. (1971). Steam Locomotives of the South African Railways, Volume 1: 1859-1910 (1st ed.). Newton Abbott, Devon: David & Charles. pp. 54, 56. ISBN 978-0-7153-5382-0.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to South African Class ME (2-6-6-2). |
.jpg)