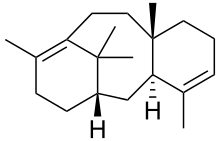
Taxadiene
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Taxa-4,11-diene | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 391697 |
| PubChem | 443484 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H32 | |
| Molar mass | 272.48 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Taxadiene (taxa-4,11-diene) is a diterpene. Taxadiene is the first committed intermediate in the synthesis of taxol. [1] Six hydroxylation reactions, and a few others, are needed to convert taxadiene to baccatin III.
Enzymatically, taxadiene is produced from geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate by taxadiene synthase. A biochemical gram-scale production of taxadiene has been reported in 2010 using genetically engineered Escherichia coli. [2]
References
- ↑ Lin, Xiaoyan; Hezari, Mehri; Koepp, Alfred E.; Floss, Heinz G.; Croteau, Rodney (1996). "Mechanism of Taxadiene Synthase, a Diterpene Cyclase That Catalyzes the First Step of Taxol Biosynthesis in Pacific Yew†". Biochemistry. 35 (9): 2968–77. doi:10.1021/bi9526239. PMID 8608134.
- ↑ Ajikumar PK, Xiao WH, Tyo KE, Wang Y, Simeon F, Leonard E, et al. (2010). "Isoprenoid pathway optimization for Taxol precursor overproduction in Escherichia coli.". Science. 330 (6000): 70–4. doi:10.1126/science.1191652. PMC 3034138
 . PMID 20929806.
. PMID 20929806.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/15/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.