Treaty of Washington (1836)
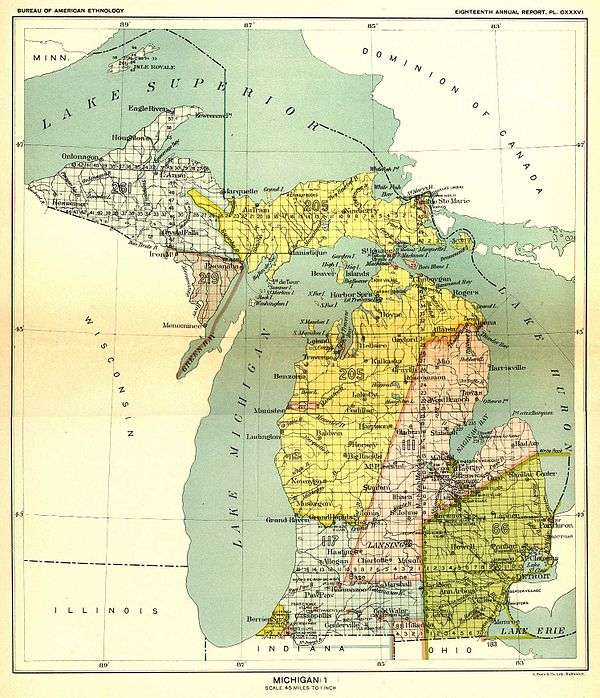
The Treaty of Washington is a treaty between the United States and representatives of the Ottawa and Chippewa nations of Native Americans. With this treaty, the tribes ceded an area of approximately 13,837,207 acres (55,997 km²) in the northwest portion of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan and the eastern portion of the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. This area represents approximately 37% of the current land area of the state of Michigan.
The treaty was concluded and signed on March 28, 1836 in Washington D.C. by Henry Schoolcraft, Indian Commissioner for the United States and several representatives of the Native American nations. The treaty was proclaimed on May 27, 1836.
The boundaries of the treaty begin at the mouth of the Grand River on the north side and follow the river east until it intersected boundaries described in previous treaties (the 1821 Treaty of Chicago and the 1819 Treaty of Saginaw. This point is in present-day Boston Township, Ionia County between Saranac and Lowell. From this point the boundary ran in a direct line to the headwaters of the Thunder Bay River in Albert Township in the southern portion of Montmorency County between Lewiston and Atlanta. The boundary followed the river to its mouth on Lake Huron and then northeast to the international boundary between the United States and Canada. It followed the international boundary through the St. Mary's River to a point in Lake Superior north of Gitchy Seebing, or the Chocolay River (named as the "Chocolate river" in the treaty) in the northeast corner of Chocolay Township in Marquette County, just southeast of Marquette, Michigan. The boundary followed the river to its headwaters in the northeast corner of Forsyth Township a few miles northeast of Gwinn. The boundary continued in a direct line to the headwaters of the Escanaba River (named as the "Skonawba river of Green bay" in the treaty) and then along the south bank of the river to its mouth north of Escanaba on the Little Bay de Noc. The boundary ran through the shipping channel into Green Bay and then through Lake Michigan to a point west of the mouth of the Grand River and then due east to the starting point.
A number of the Native Americans who had signed the treaty were later killed by other Native Americans, allegedly because of their participation.
External links
- Text of the treaty
- PDF illustrating the area of land ceded in treaty
- 2000 Consent agreement regarding Great Lakes fishing rights resolving disagreements arising out of implementation of the 1836 treaty
- The Chippewa Ottawa Resource Authority who manages exercising of rights protected in the 1836 Treaty of Washington.