Triuret
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Carbonyldiurea 1,3-Dicarbamylurea Dicarbamylurea Diimidotricarbonic diamide 2,4-diimidotricarbonic diamide Tricarbonodiimidic diamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 556-99-0 | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.317 |
| PubChem | 68400 |
| Properties | |
| C3H6N4O3 | |
| Molar mass | 146.11 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
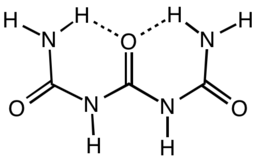
Triuret is an organic compound with the formula (H2NC(O)NH)2CO. It is a product from the pyrolysis of urea. Triuret is a colorless, crystalline, hygroscopic solid, slightly soluble in cold water or ether, and more soluble in hot water. It is a planar molecule. The central carbonyl is hydrogen-bonded to both terminal amino groups.[1]
Synthesis
The compound is typically prepared by heating thin layers of urea, the thin layers facilitating escape of ammonia:
- 3 (H2N)2CO → [H2NC(O)NH]2CO + 2 NH3
It can also prepared by treatment of urea with phosgene:[2]
- 2 (H2N)2CO + COCl2 → [H2NC(O)NH]2CO + 2 HCl
The original synthesis entailed oxidation of uric acid with hydrogen peroxide.[3]
Triuret is a complicating by-product in the industrial synthesis of melamine from urea.
Related compounds
References
- ↑ D. Carlström and H. Ringertz "The molecular and crystal structure of triuret" Acta Crystallogr. (1965. vol. 18, 307-313. doi:10.1107/S0365110X65000737
- ↑ C. Nitschke, G. Scherr (2005), "Urea Derivatives", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.o27_o04
- ↑ Alfred Schittenhelm, Karl Wiener "Carbonyldiharnstoff als Oxydationsprodukt der Harnsäure" Zeitschrift für Physiologische Chemie 1909, volume 62, 100 ff..
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/14/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.