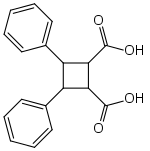
Truxinic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3,4-Diphenyl-1,2-cyclobutanedicarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 528-35-8 | |
| Properties | |
| C18H16O4 | |
| Molar mass | 296.32 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Truxinic acids are any of several stereoisomeric cyclic dicarboxylic acids with the formula (C6H5)2C4H4(COOH)2, found in various plants.[1][2] They are obtained by a photochemical cycloaddition from cinnamic acid,[3] where the two trans alkenes react head-to-head.
Isomers
These compounds have four chiral carbon atoms, which looks like there should be 16 (24) stereoisomers. However, the symmetry of the molecule allows for only ten possibilities, of which six have been described in literature:[4][5]
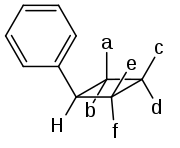
| Isomer | a | b | c | d | e | f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ω-truxinic acid | C6H5 | H | COOH | H | COOH | H |
| β-truxinic acid | C6H5 | H | H | COOH | H | COOH |
| neo-truxinic acid | C6H5 | H | COOH | H | H | COOH |
| ζ-truxinic acid | H | C6H5 | COOH | H | COOH | H |
| μ-truxinic acid | H | C6H5 | H | COOH | COOH | H |
| δ-truxinic acid | H | C6H5 | COOH | H | H | COOH |
See also
- Truxillic acids, which are isomers of the truxinic acids
References
- ↑ Liebermann (1888). "Cinnamic acid polymers obtained from the minor alkaloids of cocaine". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 21.
- ↑ Krauze-Baranowska, Miroslawa (2002). "Truxillic and truxinic acids-occurrence in plant kingdom". Acta poliniae Pharmaceutica-Drug research. 59 (5): 403–410.
- ↑ Hein, Sara M. (2006). "An Exploration of a Photochemical Pericyclic Reaction Using NMR Data". Journal of Chemical Education. 83: 940–942.
- ↑ Agarwai, O. P. (2011). Organic Chemistry Reactions and Reagents. Krishna Prakashan Media. ISBN 8187224657.
- ↑ M. Freedmana, Y. Mohadgera, J. Rennerta, S. Solowaya, I. Waltchera (1969). "β- and δ-truxinic acids". Organic Preparations and Procedures. 1 (4): 267–269. doi:10.1080/00304946909458397.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/16/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.