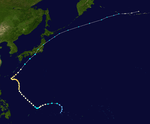
1967 Pacific typhoon season
| |
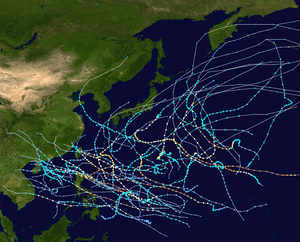
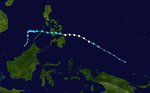
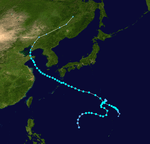
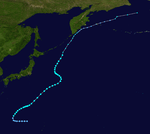
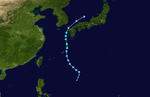
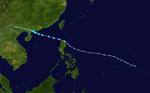
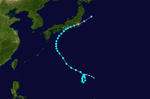
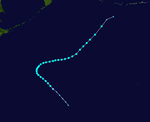
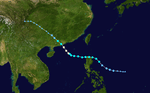
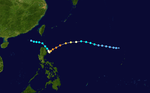
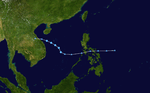
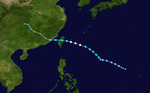
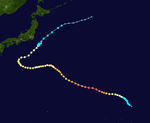
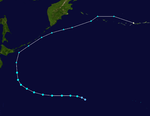
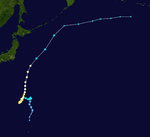
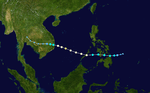
| Season summary map |
| First system formed |
January 28, 1967 |
| Last system dissipated |
December 21, 1967 |
| Strongest storm1 |
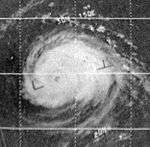
Carla – 900 hPa (mbar), 295 km/h (185 mph) |
| Total depressions |
40 |
| Total storms |
35 |
| Typhoons |
20 |
| Super typhoons |
5 |
| Total fatalities |
Unknown |
| Total damage |
Unknown |
| 1Strongest storm is determined by lowest pressure |
Pacific typhoon seasons
1965, 1966, 1967, 1968, 1969 |
The 1967 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1967, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the international date line. Storms that form east of the date line and north of the equator are called hurricanes; see 1967 Pacific hurricane season. Tropical Storms formed in the entire west pacific basin were assigned a name by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Tropical depressions in this basin have the "W" suffix added to their number. Tropical depressions that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility are assigned a name by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration or PAGASA. This can often result in the same storm having two names.
Storms
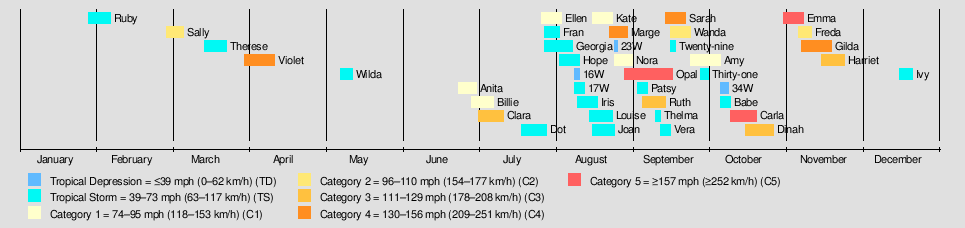
During the 1967 Pacific typhoon season, 40 tropical depressions formed, of which 35 became tropical storms. Twenty tropical storms attained typhoon intensity, and five of the typhoons reached super typhoon intensity.
Tropical Storm Ruby (Auring)
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
January 28 – February 6 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 996 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Sally (Bebeng)
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
February 28 – March 7 |
| Peak intensity |
155 km/h (100 mph) (1-min) 980 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm Therese
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
March 15 – March 24 |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (1-min) 990 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Violet (Karing)
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
March 31 – April 12 |
| Peak intensity |
220 km/h (140 mph) (1-min) 930 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Violet, which formed on April 1, steadily weakened from its peak of 140 mph to directly impact northeastern Luzon as a 115 mph typhoon on the 8th. It dissipated in the South China Sea on April 12 without causing any significant damage.
Tropical Storm Wilda (Diding)
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 8 – May 13 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 1004 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Anita (Gening)
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 24 – July 1 |
| Peak intensity |
150 km/h (90 mph) (1-min) 975 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Billie (Herming)
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 29 – July 8 |
| Peak intensity |
140 km/h (85 mph) (1-min) 980 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Billie, having developed on July 2, reached its peak of 85 mph on July 5. Billie's intensity fluctuated as it headed northward to Japan, and it became extratropical on the 8th; however, Billie's extratropical remnant continued northeastward, and it brought heavy rain to Honshū and Kyūshū, killing 347 people.
Typhoon Clara (Ising)
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 2 – July 12 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 960 hPa (mbar) |
A cold core low developed tropical characteristics and became Tropical Depression 8W on July 6. It tracked westward, becoming a tropical storm later that day and a typhoon on July 7. After briefly weakening to a tropical storm, Clara re-attained typhoon status, and it peaked in intensity on July 10, reaching winds of 115 mph. Clara weakened to a 90 mph typhoon just before hitting Taiwan on the 11th, and it dissipated over China the next day. Clara's heavy rains caused 69 fatalities and a further 32 people to be reported as missing.
Tropical Storm Dot
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 19 – July 29 |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (1-min) 975 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Ellen
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 27 – August 4 |
| Peak intensity |
150 km/h (90 mph) (1-min) 970 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm Fran (Mameng)
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 28 – August 3 |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (1-min) 975 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm Georgia (Luding)
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 28 – August 8 |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (1-min) 982 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm Hope
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 3 – August 11 |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (1-min) 984 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Depression Neneng
| Tropical depression (PAGASA) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 5 – August 8 |
| Peak intensity |
55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min) 999 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Depression 16W
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 9 – August 11 |
| Peak intensity |
55 km/h (35 mph) (1-min) 995 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm 17W
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 9 – August 13 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min) 988 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm Iris (Oniang)
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 10 – August 18 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (1-min) 994 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm Louise
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 15 – August 24 |
| Peak intensity |
100 km/h (65 mph) (1-min) 980 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm Joan
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 16 – August 25 |
| Peak intensity |
100 km/h (65 mph) (1-min) 988 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Kate (Pepang)
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 16 – August 24 |
| Peak intensity |
130 km/h (80 mph) (1-min) 982 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Marge (Rosing)
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 23 – August 30 |
| Peak intensity |
230 km/h (145 mph) (1-min) 940 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Depression 23W
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 25 – August 26 |
| Peak intensity |
45 km/h (30 mph) (1-min) 998 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Nora (Sisang)
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 25 – September 1 |
| Peak intensity |
130 km/h (80 mph) (1-min) 990 hPa (mbar) |
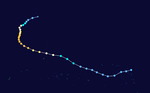
Super Typhoon Opal
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 29 – September 17 |
| Peak intensity |
285 km/h (180 mph) (1-min) 920 hPa (mbar) |
Super Typhoon Opal was a powerful system that peaked in winds of 180 miles per hour (mph), the equivalent of a Category 5 hurricane.
Tropical Storm Patsy
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 3 – September 7 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min) 995 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Ruth
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 5 – September 14 |
| Peak intensity |
205 km/h (125 mph) (1-min) 940 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm Thelma
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 10 – September 12 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min) 990 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm Vera
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 12 – September 16 |
| Peak intensity |
85 km/h (50 mph) (1-min) 994 hPa (mbar) |
Super Typhoon Sarah
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 14 (Entered Basin) – September 22 |
| Peak intensity |
240 km/h (150 mph) (1-min) 930 hPa (mbar) |
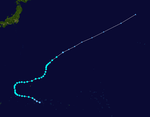
On September 14, Tropical Storm Sarah, which formed across the International Date Line, entered the Western Pacific. Immediately after the first advisory following Sarah's entrance into the West Pacific, it was upgraded to a minimal typhoon. Typhoon Sarah continued to intensify, and late on September 15, it was upgraded to a Category 4 typhoon. The next day, Sarah reached its peak intensity, attaining 150 mph winds and a 932 millibar (mbar) pressure reading (this was the only pressure measurement retrieved from the typhoon), making the system a super typhoon. Sarah began gradually weakening afterwards, and late on September 21, it became extratropical; it was still an 80 mph Category 1 typhoon at the time.
On September 16, Sarah made landfall on Wake Island at peak intensity, causing widespread damage. This typhoon was the third tropical cyclone since the beginning of observations in 1935 to bring typhoon-force winds to Wake Island, following an unnamed typhoon which struck on October 19, 1940 (Tomita, 1968), which brought 120 knot winds to the island, and Typhoon Olive in 1952, which lashed the island with 150 knot winds. Coincidentally, Olive's attack on the island occurred on September 16, exactly 15 years prior to Sarah's direct hit.[1]
Typhoon Wanda
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 16 – September 24 |
| Peak intensity |
175 km/h (110 mph) (1-min) 962 hPa (mbar) |
JMA Tropical Storm Twenty-nine
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 16 – September 18 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min) 998 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Amy
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 24 – October 6 |
| Peak intensity |
150 km/h (90 mph) (1-min) 962 hPa (mbar) |
JMA Tropical Storm Thirty-one
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 28 – October 1 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (1-min) 992 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Depression 34W
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 6 – October 9 |
| Peak intensity |
55 km/h (35 mph) (1-min) 1004 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm Babe
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 6 – October 10 |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (1-min) 980 hPa (mbar) |
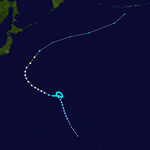
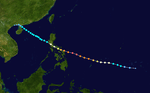
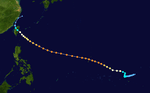
Super Typhoon Carla (Trining)
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 10 – October 20 |
| Peak intensity |
295 km/h (185 mph) (1-min) 900 hPa (mbar) |
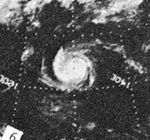
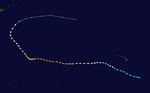
Carla became an intense typhoon while located in the Philippine Sea on October 15.[2] During its weakening stage, the typhoon dumped extreme rainfall around its circulation. Baguio, Philippines recorded 47.86 inches (1,216 mm) of rainfall in a 24‑hour period between October 17 and October 18; however, Carla's precipitation was significantly more extreme in China, where 108.21 inches (2,749 mm) fell in a 48‑hour period between October 17 and October 19.[3]
The worst typhoon to hit the country during the year killing 250 people and leaving 30 others missing
Typhoon Dinah (Uring)
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 16 – October 27 |
| Peak intensity |
185 km/h (115 mph) (1-min) 950 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Dinah struck the southern island of Kyūshū in Japan, killing thirty-seven people and resulting in ten others being reported as missing.[4]
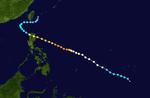
Super Typhoon Emma (Welming)
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 31 – November 8 |
| Peak intensity |
260 km/h (160 mph) (1-min) 908 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Emma was the second super Typhoon to hit the Philippines in just weeks after Typhoon Carla. Typhoon Emma left 300 people dead and 60 others missing
Typhoon Freda (Yayang)
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 6 – November 11 |
| Peak intensity |
155 km/h (100 mph) (1-min) 972 hPa (mbar) |
Super Typhoon Gilda (Ading)
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 7 – November 19 |
| Peak intensity |
240 km/h (150 mph) (1-min) 910 hPa (mbar) |
Typhoon Harriet
| Category 3 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 15 – November 24 |
| Peak intensity |
205 km/h (125 mph) (1-min) 950 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Storm Ivy (Barang)
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
December 16 – December 21 |
| Peak intensity |
110 km/h (70 mph) (1-min) 980 hPa (mbar) |
1967 storm names
-
Agnes
-
Bess
-
Carmen
-
Della
-
Elaine
-
Faye
-
Gloria
-
Hester
-
Irma
-
Judy
-
Kit
-
Lola
-
Mamie
-
Nina
-
Ora
-
Phyllis
-
Rita
-
Susan
-
Tess
-
Viola
-
Winnie
|
-
Alice
-
Betty
-
Cora
-
Doris
-
Elsie
-
Flossie
-
Grace
-
Helen
-
Ida
-
June
-
Kathy
-
Lorna
-
Marie
-
Nancy
-
Olga
-
Pamela
- Ruby 1W
- Sally 2W
- Therese 3W
- Violet 4W
- Wilda 5W
|
- Anita 6W
- Billie 7W
- Clara 8W
- Dot 9W
- Ellen 10W
- Fran 11W
- Georgia 12W
- Hope 13W
- Iris 14W
- Joan 15W
- Kate 16W
- Louise 17W
- Marge 18W
- Nora 19W
- Opal 20W
- Patsy 21W
- Ruth 22W
- Sarah 23W
- Thelma 24W
- Vera 25W
- Wanda 26W
|
- Amy 27W
- Babe 28W
- Carla 29W
- Dinah 30W
- Emma 31W
- Freda 32W
- Gilda 33W
- Harriet 34W
- Ivy 35W
-
Jean
-
Kim
-
Lucy
-
Mary
-
Nadine
-
Olive
-
Polly
-
Rose
-
Shirley
-
Trix
-
Virginia
-
Wendy
|
See also
References
- ↑ "1967 Central Pacific Tropical Cyclone season".
- ↑ Kitamoto Asanobu (2012). "Digital Typhoon: Typhoon 196733 (CARLA) - General Information (Pressure and Track Charts)". Retrieved 2012-02-23.
- ↑ J. L. H. Paulhaus (1973). World Meteorological Organization Operational Hydrology Report No. 1: Manual For Estimation of Probable Maximum Precipitation. World Meteorological Organization. p. 178.
- ↑ Digital Typhoon: Disaster Information
External links