UBE1L2
| UBA6 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | ||||||
| Aliases | UBA6, E1-L2, MOP-4, UBE1L2, ubiquitin like modifier activating enzyme 6 | |||||
| External IDs | MGI: 1913894 HomoloGene: 10080 GeneCards: UBA6 | |||||
| RNA expression pattern | ||||||
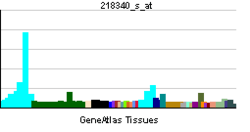 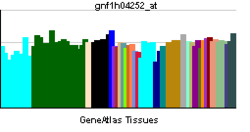 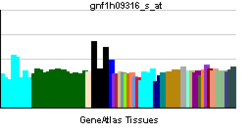 | ||||||
| More reference expression data | ||||||
| Orthologs | ||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | ||||
| Entrez | ||||||
| Ensembl | ||||||
| UniProt | ||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | ||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | ||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 4: 67.61 – 67.7 Mb | Chr 5: 86.11 – 86.17 Mb | ||||
| PubMed search | [1] | [2] | ||||
| Wikidata | ||||||
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBA6 gene.[3][4]
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Pelzer C, Kassner I, Matentzoglu K, Singh RK, Wollscheid HP, Scheffner M, Schmidtke G, Groettrup M (Aug 2007). "UBE1L2, a novel E1 enzyme specific for ubiquitin". J Biol Chem. 282 (32): 23010–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.C700111200. PMID 17580310.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: UBE1L2 ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1-like 2".
Further reading
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (2001). "DNA Cloning Using In Vitro Site-Specific Recombination". Genome Res. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948
 . PMID 11076863.
. PMID 11076863. - Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, et al. (2001). "Toward a Catalog of Human Genes and Proteins: Sequencing and Analysis of 500 Novel Complete Protein Coding Human cDNAs". Genome Res. 11 (3): 422–35. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072
 . PMID 11230166.
. PMID 11230166. - Simpson JC, Wellenreuther R, Poustka A, et al. (2001). "Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing". EMBO Rep. 1 (3): 287–92. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058. PMC 1083732
 . PMID 11256614.
. PMID 11256614. - Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932. - Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Zhu H, Zhou ZM, Huo R, et al. (2004). "Identification and characteristics of a novel E1 like gene nUBE1L in human testis". Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai). 36 (3): 227–34. doi:10.1093/abbs/36.3.227. PMID 15202508.
- Colland F, Jacq X, Trouplin V, et al. (2004). "Functional Proteomics Mapping of a Human Signaling Pathway". Genome Res. 14 (7): 1324–32. doi:10.1101/gr.2334104. PMC 442148
 . PMID 15231748.
. PMID 15231748. - Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928
 . PMID 15489334.
. PMID 15489334. - Wiemann S, Arlt D, Huber W, et al. (2004). "From ORFeome to Biology: A Functional Genomics Pipeline". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2136–44. doi:10.1101/gr.2576704. PMC 528930
 . PMID 15489336.
. PMID 15489336. - Hillier LW, Graves TA, Fulton RS, et al. (2005). "Generation and annotation of the DNA sequences of human chromosomes 2 and 4". Nature. 434 (7034): 724–31. doi:10.1038/nature03466. PMID 15815621.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Mehrle A, Rosenfelder H, Schupp I, et al. (2006). "The LIFEdb database in 2006". Nucleic Acids Res. 34 (Database issue): D415–8. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj139. PMC 1347501
 . PMID 16381901.
. PMID 16381901. - Jin J, Li X, Gygi SP, Harper JW (2007). "Dual E1 activation systems for ubiquitin differentially regulate E2 enzyme charging". Nature. 447 (7148): 1135–8. doi:10.1038/nature05902. PMID 17597759.
- Chiu YH, Sun Q, Chen ZJ (2007). "E1-L2 activates both ubiquitin and FAT10". Mol. Cell. 27 (6): 1014–23. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.08.020. PMID 17889673.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/6/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.