Virginia Conventions

A convention of three generations, the last gathering of Revolutionary era giants[1]
| History of Virginia |
|---|
|
|
|
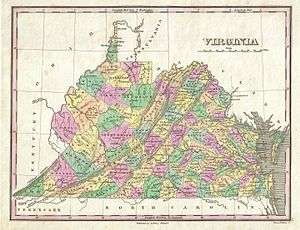

Tidewater is the eastern three, Piedmont is the middle three, the Valley between the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Appalachians is pink and blue.
The orange "Heart of Appalachia" and modern West Virginia were the 19th century "transmontane" western Virginia represented in four Virginia Conventions.
Virginia Conventions have been the assemblies of delegates elected for the purpose of establishing fundamental law for the Commonwealth of Virginia. Their Constitutions and subsequent amendments span four centuries across territory of modern-day Virginia, West Virginia and Kentucky.
The first Virginia Conventions assumed authority from elected delegates in a series of five self-governing political meetings administering the legislative, executive and judicial functions of government in the Colony of Virginia during the American Revolution. They replaced British colonial government and served as a revolutionary provisional government until the Fifth Virginia Convention established a republic for the Commonwealth of Virginia in its Constitution of June 1776.
Subsequent to joining the union of the United States, Virginia's five unlimited state Constitutional Conventions took place in 1829–30, 1850, around the time of the Civil War in 1864, 1868, and finally in 1902. These were primarily concerned with voting rights and representation in the General Assembly. The Conventions of 1861 were called in Richmond for secession and in Wheeling for government loyal to the U.S. Constitution.
In the 20th century, limited state Conventions were used in 1945 to expand suffrage to members of the armed forces in wartime, and in 1955 to implement "massive resistance" to Supreme Court attempts to desegregate public schools. Alternatives to the conventions used Commissions for Constitutional Reform in 1927 for restructuring state government and in 1969 to conform the state Constitution with Congressional statutes of the Voting Rights Act and U.S. Constitutional law. Constitutional provisions for special attention in the 1969 Commission related to the 14th Amendment's provisions for Due Process and Equal Protection as they related to education, voting rights and representation. Each of these 20th century recommendations was placed before the people for ratification in a referendum.
First through fourth Revolutionary conventions
The First Convention was organized after Lord Dunmore dissolved the House of Burgesses when that body called for a day of prayer as a show of solidarity with Boston, Massachusetts, following the Boston Port Act. The Burgesses who had been elected by propertied freeholders throughout the colony, moved to Raleigh Tavern to continue meeting. The Burgesses declared support for Massachusetts and called for a congress of all the colonies, the Continental Congress. The Burgesses, convened as the First Convention, met on August 1, 1774, and elected officers, banned commerce and payment of debts with Britain, and pledged supplies. They elected Peyton Randolph, the Speaker of the House of Burgesses, as the President of the Convention (a position he held for subsequent conventions until his death in October 1775).[2]
.jpg)
The Second Convention opened in Richmond and met at St. John's Episcopal Church on March 20, 1775. Peyton Randolph served again as the President of the Convention and they elected delegates to the Continental Congress. At the convention, Patrick Henry proposed arming the Virginia militia and delivered his "give me liberty or give me death" speech to rally support for the measure. It was resolved that the colony be "put into a posture of defence: and that Patrick Henry, Richard Henry Lee, Robert Carter Nicholas, Benjamin Harrison, Lemuel Riddick, George Washington, Adam Stephen, Andrew Lewis, William Christian, Edmund Pendleton, Thomas Jefferson and Isaac Zane, Esquires, be a committee to prepare a plan for the embodying arming and disciplining such a number of men as may be sufficient for that purpose."[3]

Between conventions in April 1775, Randolph, who was the Speaker of the House of Burgesses and President of the Virginia Conventions, negotiated with Lord Dunmore for gunpowder removed from the Williamsburg arsenal during the Gunpowder Incident, which was a confrontation between the Governor's forces and Virginia militia, led by Patrick Henry. The House of Burgesses was called back by Lord Dunmore one last time in June 1775 to address British Prime Minister Lord North's Conciliatory Resolution. Randolph, who was a delegate to the Continental Congress, returned to Williamsburg to take his place as Speaker. Randolph indicated that the resolution had not been sent to the Congress (it had instead been sent to each colony individually in an attempt to divide them and bypass the Continental Congress). The House of Burgesses rejected the proposal, which was also later rejected by the Continental Congress.[4]
The Third Convention met on July 17, 1775, also at St. John's Church, after Dunmore had fled the capital (following the rejection of North's resolution) and taken refuge on a British warship. Peyton Randolph continued to serve as the President of the Convention.[5] The convention created a Committee of Safety to govern as an executive body in the absence of the governor (Dunmore). Members of the committee were Edmund Pendleton, George Mason, John Page, Richard Bland, Thomas Ludwell Lee, Paul Carrington, Dudley Digges, William Cabell, Carter Braxton, James Mercer, and John Tabb.[6] The convention also divided Virginia into 16 military districts and resolved to raise regular regiments. The convention ended August 26, 1775, while the Committee of Safety would continue to meet and govern between Convention sessions.[7]
The Fourth Convention in Williamsburg met in December 1775 following November's declaration that the colony was in revolt by royal Governor Dunmore's and his battling militia forces in the Hampton Roads area.[8] Edmond Pendleton served as President of the Convention, succeeding Peyton Randolph who had died in Oct 1775. The Convention declared that Virginians were ready to defend themselves "against every species of despotism." The convention passed another ordinance for raising additional troops.[9]
Back in England in December 1775, the King's Proclamation of Rebellion had declared the colonies outside his protection,[10] but throughout the first four Virginia state Conventions, there was no adopted expression in favor of independence from the British Empire.[11]
Gallery of Virginia Constitutional conventions
-

Peyton Randolph
1774, 1775 -

Edmund Pendleton
1776, 1788 -

Philip P. Barbour
1830 -

John Y. Mason
1850 -

John Janney
1861 Richmond -

Arthur I. Boreman
1861 Wheeling -

Francis Pierpont, Loyalist Governor called 1864 Convention
-

John C. Underwood
1868 -

John Goode, Jr.
1902 -

Harry F. Byrd, Sr.
Governor called 1927 Commission -

Thomas B. Stanley Governor called 1956 Limited Convention
-

Mills E. Godwin, Jr.
Governor called 1969 Commission
Fifth Revolutionary convention
By the new year of 1776, George Washington, a delegate in the Virginia Convention and in the Continental Congress, had been appointed in Philadelphia from the First Continental Congress as commander of Continental troops surrounding Boston. Virginia patriots had defeated an advancing British expeditionary force at the Battle of Great Bridge southeast of Norfolk in December.[12]
The newly elected delegates to the Fifth Virginia Convention again met in Williams burg, and re-elected Edmund Pendleton as its president on his return from Philadelphia as presiding officer of the First Continental Congress. The membership could be thought of as belonging to one of three groups: radicals from western Virginia, who had agitated for independence from Britain even before 1775; philosophers of the American Enlightenment; and wealthy planters, largely from the east. A malapportionment of delegates granted disproportionate influence to this latter group.[13]

where the Fourth and Fifth Conventions met
The newly elected Fifth Convention began May 6 to July 5, 1776, and met in Williamsburg. It elected Edmund Pendleton its presiding officer after his return as president of the First Continental Congress in Philadelphia. There were three parties in the Fifth Convention. The first was mainly made up of wealthy planters, including Robert Carter Nicholas Sr..[14] It ensured the continued self-perpetuating gentry rule of county government with a franchise limited by property requirements underpinning the republican form of state government.[15] The second party was made up of the intellectuals of the Enlightenment. These included the older generation of George Mason, George Wythe, Edmund Pendleton, and the younger Thomas Jefferson and James Madison.[16] The third party was a minority of young men mainly from western Virginia. This party was led by Patrick Henry and included "radicals" who had supported independence earlier than 1775.[17]
On May 15, the Convention declared that the government of Virginia as "formerly exercised" by King George in Parliament was "totally dissolved".[18] The Convention adopted a set of three resolutions: one calling for a declaration of rights for Virginia, one calling for the establishment of a republican constitution, and a third calling for federal relations with whichever other colonies would have them and alliances with whichever foreign countries would have them. It also instructed its delegates to the Continental Congress in Philadelphia to declare independence.[19]
On June 7, Richard Henry Lee, one of Virginia's delegates to Congress, carried out the instructions to propose independence in the language the convention had commanded him to use: that "these colonies are, and of right ought to be, free and independent states." The resolution was followed in Congress by the adoption of the American Declaration of Independence, which reflected its ideas.[20]
The convention amended, and on June 12 adopted, George Mason's Declaration of Rights, a precursor to the United States Bill of Rights. On June 29, the convention approved the first Constitution of Virginia. The convention chose Patrick Henry as the first governor of the new Commonwealth of Virginia, and he was inaugurated on June 29, 1776. Thus, Virginia had a functioning republican constitution before July 4, 1776.[21]
Ratifying (Federal) Convention of 1788
The Constitutional Convention convened by the Articles of Confederation Congress in 1787 provided for a ratification process in the states that was duly transmitted by Congress to each state. As Virginian's went to the polls to elect delegates to its state convention, six states had ratified including the two other largest states of Pennsylvania and Massachusetts. But Virginia bisected the new nation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Mississippi River; its admission into the prospective union was critical if the United States as a nation-state were to have contiguous continental territory.[22]
The Convention met from June 2–27, 1788, in the wooden "Old Capitol" building at Richmond VA, and elected Edmund Pendleton its presiding officer.[23] The Virginia Ratifying Convention narrowly approved joining the proposed United States under a Constitution of supreme national law as authorized by "We, the people" of the United States. James Madison led those in favor, Patrick Henry, delegate to the First Continental Convention and Revolutionary wartime governor, led those opposed. Governor Edmund Randolph, who had refused to sign the Constitution in the Philadelphia Convention, chose in Virginia's Ratifying Convention to support adoption. George Mason had refused to sign due to the lack of a Bill of Rights in Philadelphia would continue in his opposition.[24] The Virginia ratification included a recommendation for a Bill of Rights, and Madison subsequently led the First Congress to send the Bill of Rights to the states for ratification.[25]
_in_1858.jpg)
Patrick Henry questioned the authority of the Philadelphia Convention to presume to speak for "We, the people" instead of "We, the states". In his view, delegates should have only recommended amendments to the Articles of Confederation. Edmund Randolph had changed from his opposition in the Philadelphia Convention to now supporting adoption for the sake of preserving the Union. He noted that the Confederation was "totally inadequate".[27] George Mason countered that a national, consolidated government would overburden Virginians with direct taxes in addition to state taxes, and that government of an extensive territory must necessarily destroy liberty.[28] Madison pointed out that the history of Confederations like that provided in the Articles of Confederation government were inadequate in the long run, both with the ancients and with the modern (1700s) Germans, Dutch and Swiss. They brought "anarchy and confusion", disharmony and foreign invasion. Efficient government can only come from direct operation on individuals, it can never flow from negotiations among a confederation's constituent states.[29]
The Virginia Ratification (Federal) Convention narrowly ratified the U.S. Constitution 89 to 79. Virginians reserved the right to withdraw from the new government as "the People of the United States", "whenever the powers granted unto it should be perverted to their injury or oppression," but it also held that failings in the Constitution should be remedied by amendment.[30] Unlike the Pennsylvania Convention where the Federalists railroaded the Anti-federalists in an all or nothing choice, in the Virginia Convention the Federalists made efforts to reconcile with the Anti-federalists by recommending amendments to the federal Constitution like that of Virginia's Bill of Rights preamble to its 1776 Constitution.[31]
Constitutional Convention of 1829–1830
Almost immediately, the Constitution of 1776 was recognized as flawed both for its restriction of the suffrage by property requirements, and for its malapportionment favoring the smaller eastern counties. Between 1801 and 1813, petitioners called on the Assembly to initiate a constitutional convention ten times.[32] Malapportionment in the Assembly was seen by reformers as "an usurpation of the minority over the majority" by the slave owning eastern aristocracy. Partisans argued for apportionment by white population, versus "federal numbers" combining white population with three-fifths slaves, versus the existing system counting whites and slaves equally to favor the slave-holding eastern counties.[33]

The Convention met from October 5, 1829 – January 15, 1830, and elected Philip Pendleton Barbour its presiding officer. The last "gathering of giants"[34] from the Revolutionary generation included former presidents James Madison and James Monroe, and sitting Chief Justice John Marshall. But three generations were represented among those who would serve in public office including three presidents, seven U.S. Senators, fifteen U.S. Representatives and four governors. The other delegates to the Convention were sitting judges or members of the Virginia General Assembly.[35]
Conservatives among the Old Republicans such as John Randolph of Roanoke feared any change from the Founders' 1776 Constitution would lead to an ideological anarchy of "wild abstractions" imposed by egalitarian "French Jacobins" through "this maggot of innovation". In answer, sitting U.S. Chief Justice and convention delegate John Marshall advanced his view with a petition from the freeholders of Richmond which observed that, "Virtue, intelligence, are not among the products of the soil. Attachment to [slave] property, often a sordid sentiment, is not to be confounded with the sacred flame of patriots." Any white male who had served in the War of 1812 or who would serve in the militia in there future defense of the country deserved the right to vote.[36]
Reformers' efforts to adopt direct popular election of the Governor were defeated in favor of continuing election by the General Assembly.[37] Thomas Jefferson Randolph, Thomas Jefferson's grandson, proposed gradual emancipation, a suggestion which never made it out of committee onto the Convention floor.[38] The reformers lost on almost every issue. Nevertheless, even with the exaggerated Virginia Senate representation apportioning the delegates, the three most important roll calls were close. The "white" population basis of apportioning the General Assembly failed by two votes. The extension of the vote to all free white males failed by two votes. When the popular election of governor passed on its first vote, it failed on reconsideration. The divisions which would lead to West Virginia's split were evident. Regardless of the various ideologies represented or delegate political affiliation, the final vote 55 for the proposed Constitution to 40 against was along an east-west divide. Only one delegate voted yes from west of the Blue Ridge Mountains.[39]
Constitutional Convention of 1850
Following the 1830 Constitution, Virginia began to change politically under the pressure of party competition. Though the planter elite and their representatives in the ruling Democratic "Richmond Junto" continued to resist any change. Western Democrats and Whigs were more inclined to a white population basis in their determination to expand suffrage and find a more equitable reapportionment between east and west sections.[40]

The Convention delegates were a younger generation raised in the Second American Party System of Democrat Jefferson Davis and Whig Henry Clay. Unlike the three generation Convention of 1829–30, the delegates were primarily in their twenties and thirties at the beginning of their careers in the professions and industry, without large land holdings, and without gentry family ties.[41]
The Convention met from October 14, 1850 – August 1, 1851, and elected John Y. Mason its presiding officer. The Convention featured fierce debates; the arguments raged throughout Virginia in the press and they were widely reported nationally. Direct popular election of governor was supported by Whig Congressman John Minor Botts. He was opposed by Richmond Junto Democrat Richard L.T. Beale who argued against the natural equality of all men, and the "plundering propensities" of the multitude seeking a "majority of mere numbers".[42] Although he was for direct election of Governor, Henry A. Wise was more fearful of the eastern slave-holders loss of control in the General Assembly. He believed that "protection of slavery, not the liberalizing of Virginia's Constitution, was the most significant business before the convention."[43]
After almost six months of wrangling, the question of apportionment was brought up for a vote. The House of Delegates to be on the white population basis, giving the western counties a majority, and for the Senate to be on a modified mixed basis of population and property including slaves, giving the eastern counties a majority. In the remaining two months of the Convention, it was agreed to allow direct popular election of the governor, but each office holder would be limited to one term. Constitutional provision for public education was voted down.[44] Voting by secret ballot was rejected, perpetuating vive voce voting.[45]
Secession Convention of 1861
Abraham Lincoln's constitutional election reflected the nation's sectional divide, though 82% of the nation had split among the Unionists, Lincoln, Stephen A. Douglas and John Bell. Even before Lincoln's inauguration, the Deep South states that had cast Electoral College votes for John C. Breckinridge resolved to secede from the United States and form the Confederate States of America. The Virginia Assembly called a special convention for the sole purpose of considering secession from the United States. Virginia was deeply divided, returning a convention of delegates amounting to about one-third for secession and two thirds Unionist. But the Unionists would prove to be further divided between those who would be labelled Conditional Unionists who would favor Virginia in the Union only if Lincoln made no move at "coercion", and those who would later be called Unconditional Unionists who would be unwavering in their loyalty to the Constitutional government of the United States.[46]

The Convention met from February 3 – December 6, 1861, and elected John Janney its presiding officer. The majority at first voted to remain in the Union, but stayed in session awaiting events. At first, the speeches were mixed between Secessionists advocating leaving the Union, Conditional Unionists holding onto the patriotism of earlier times, and Unconditional Unionists insisting that secession was bad policy and unlawful.[47] On March 4, Abraham Lincoln's inauguration day, Jefferson Davis called up 100,000 militia to serve a year and sent besieging troops to surround Fort Sumter in South Carolina and Fort Pickens in Florida. That same day Waitman T. Willey from trans-Alleghany Monongalia County answered secessionists with a Unionist speech. He defended Virginia's institutions from Northern attacks against slavery, but "there is no constitutional right of secession ..." He warned that secession would bring about war, taxes and the abolition of slavery in Virginia.[48]
John S. Barbour Jr. of the Piedmont's Culpeper County was the first Unionist to break away into the secessionist camp. While "resolutely protecting slave labor" he was for encouraging manufacturing and commercial interests in Virginia against those of the North. He asked what would do more to promote Virginia's growth, participation "in a hostile confederacy in which your [legislative] power will be but 11 out of 150 [with he North], or in a friendly confederacy where it will be 21 out of 89 [with the South]?" In the South was a government to join "in full working order, strong, powerful and efficient ..." Henry A. Wise tried to move the Convention into a "Spontaneous Southern Rights Convention" to immediately install a secessionist government in Virginia, but on April 4, almost two-thirds of the Convention voted against secession, and a three-man delegation was sent to consult with Lincoln who had resolved to protect Federal property in the South.[49]
With the fall of Fort Sumter, Lincoln matched Jefferson Davis's call up of 100,000 men for a year with a call for 75,000 for three months, including 3,500 Virginians to restore Federal property taken in the South by force.[50] But the Unionist bloc lost its Conditional Unionist faction with the Lincoln requisition of troops.[51] The next day, former Governor Henry Wise announced that he had set the "wheels of revolution" against the U.S. Government in motion with loyal Virginians seizing both the Harper's Ferry federal armory and the Gosport Navy Yard at Norfolk. His exhortation produced a resolution to secede 88 for, 55 against.[52]
The Virginia Secession Ordinance was to "repeal the ratification of the Constitution of the United States of America, by the State of Virginia."[53] Two days after the secession resolution and a month before the referendum, the Confederate flag was raised over Virginia's capitol building, a delegation was sent to vote in the Confederate Congress, state militias were activated and a Confederate army was invited to occupy Richmond. Though the ballots from Unionist counties were lost, the total referendum votes counted numbered more than that of the 1860 presidential election by including men voting viva voce aloud in Confederate army camps, approving secession by 128,884 to 32,134.[54]
Wheeling (Virginia) Convention of 1861
Virginia's second Convention of 1861 was a Unionist response to the secessionist movement in Virginia. The First Wheeling Convention meeting at Wheeling, Virginia (1863 WV), sat on May 13–15. It called for elections to another meeting if Virginia's Ordinance of Secession were to pass referendum. After the vote was taken on May 23, the First Session of the Second Wheeling Convention met from June 11 June 25 to establish the Restored Government of Virginia, electing Arthur I. Boreman its presiding officer.[55] The Second Session of the Second Wheeling Convention met from August 6 to August 21 to call for a new state from the territory of Virginia to be named Kanawha.[56]

The Second Wheeling Convention included 32 western counties, Alexandria and Fairfax County.[57] Twenty-nine of the convention delegates were members of the Virginia General Assembly as state Delegates or state Senators, such as John J.Davis of Harrison County and Lewis Ruffner of Kanawha County.[58]
John S. Carlile who had represented transmontane Harrison County as an Unconditional Unionist at the Richmond Secession Convention, was the floor leader at the Second Wheeling Convention who shepherded in the creation of the Restored Virginia Government. On June 14 he expanded on his view of state and federal relations, " the people of Virginia in establishing government for themselves deemed it best to create two agents. The Federal Government is one, and the State Government is the other ..." Referencing Article VI of the U.S. Constitution, Carlile observed, "Any act done or performed by the State agent in conflict with the powers conferred upon the Federal agent is to be null and void ... [the Constitution] provides for its own alteration, amendment or change ... But [the right of secession] was never intended ..."[59]
On June 17, Carlile attacked the rebellion as treason, he then accounted events at the Richmond Secession Convention in which he had been an Unconditional Unionist. "For several days before the Convention passed the Ordinance of Secession, it was absolutely besieged; members were threatened with being hung to the lamp posts; their lives were jeopardized; the mob was marching up and down the streets, and surrounding the Capitol, and everything was terror and dismay."[60] Carlile continued to impeach the legitimacy of Virginia's referendum on secession.[61]
Republican Francis H. Pierpont of Marion County was elected by the Convention as Governor of the Restored Government of Virginia which was recognized by the Lincoln Administration. Unlike in Kentucky and Missouri, Federal arms were unable to reclaim Virginia counties for incorporation into the Restored Government by 1863, and West Virginia was made its own state.[62]
Loyalist Convention of 1864
Following the creation of West Virginia, the remnant of Restored Virginian government held a Convention of delegates from a few periphery counties occupied by Union forces. The Convention met in Alexandria's U.S. District Court Room from February 13 – April 11, 1864, and elected LeRoy G. Edwards, a slaveholder with three sons in the Confederacy as its presiding officer. The Convention sought direction from President Lincoln whether the General Government would sustain the civil authority, or "whether the civil is to become, as it is now, subordinate to the military", so that the convened delegates could support the Administration's war effort in the midst of Grant's Wilderness Campaign. Debate ensued over whether to seek to disenfranchise all supporters of the rebellion, but with an eye to governing after cessation of hostilities, it limited disenfranchisement only to those who had held office in rebel state or Confederate governments.[63]
After debating whether abolition of slavery would best proceed gradually or at once, with compensation to loyal Union men or without, the Convention resolved to abolish slavery immediately without compensation on April 10, 1864. It abolished the viva voce voting and called for secret balloting for electing state officials. Immediately on its proclamation, the Constitution of 1864 was enforceable only in areas under Union control, but it would serve as Virginia's fundamental law until the Constitution of 1870 went into force.[64]
A fifty-two-page journal of convention proceedings was published, but the debates were not formally recorded. W. J. Cowing, secretary of the convention and editor of the pro-Union Alexandria, Virginia State Journal, featured accounts of some debate, but only one edition of the Journal remains covering the convention.[65]
Constitutional Convention of 1868
During Congressional Reconstruction, U.S. General John Schofield administered Virginia as Military District One. After 1866, according to the Radical Reconstruction Acts, a rebelling state which had vacated its delegation in the U.S. Congress was required to incorporate the 14th Amendment into its state constitution before it was allowed to participate again.[66] By the time Schofield called a new state constitutional convention for 1868, three distinct parties had coalesced in Virginia. Radical Republicans, including most ex-slave freedmen, organized to advocate full political and social equality for blacks, but they wanted to exclude ex-Confederates from political participation either in government or at the ballot box. Moderate Unionists including many pre-war Whigs, sought political equality for blacks, but believed that ex-Confederates had to be included in the political community because of their majority in the white population. Conservatives wanted to ensure white control of the state without Radical influence on issues such as public education.[67]
The Convention met from December 3, 1867 to April 17, 1868, at Richmond in the Capitol Building, and elected John C. Underwood its presiding officer. A convention of enfranchised Unionists, freedmen and ex-Confederates was dominated by Radical Republicans. The Convention proposed two "obnoxious clauses" that provoked widespread opposition, meant to restrict suffrage among ex-Confederates. Negotiations with President Grant resulted in separating the two more controversial proposals, and the remaining Constitution was ratified by referendum. It provided for the vote for African-Americans and public education.[68]

The Convention concerned itself with federal-state relations, with the Convention's Committee on the Preamble and Bill of Rights initially stating that, ""the General Government of the United States is paramount to that of an individual state, except as to rights guaranteed to each State by the Constitution of the United States." But Jacob N. Liggett of Rockingham County voiced the ex-Confederate doctrine that "the Federal Government is the creature of the acts of the States." Christopher Y. Thomas of Henry County proposed a compromise, to simply assert Article VI. of the U.S. Constitution for Virginia's Bill of Rights, Section 2, that "the Constitution of the United States, and the laws of Congress passed in pursuance thereof, constitute the supreme law of the land, to which paramount allegiance and obedience are due from every citizen ..." That was not enough for the Radical majority. Linus M. Nickerson of Fairfax County who had served in a New York infantry regiment successfully added "this State shall ever remain a member of the United States of America ... and that all attempts from whatever source, or upon whatever pretext, to dissolve said Union ... are unauthorized, and ought to be resisted with the whole power of the State."[69]
The Radicals in Convention, against the protests of General Schofield, were able to martial an uncompromised majority in their desire to disenfranchise the white ex-Confederate majority in the state. Instead of the moderate Republican position limiting voter restrictions to former U.S. officeholders who had supported rebellion, they sought to guarantee a future government of Union men only. The Convention wrote two "obnoxious clauses" as they were widely known, that went beyond federal requirements to deny the vote to any office holder in rebel government and an "iron-clad oath" testifying that a prospective voter had never "voluntarily borne arms against the United States."[70] Following the Convention, General Schofield successfully negotiated with President Ulysses S. Grant to propose the referendum on the Radical "Underwood" Constitution, but separating its two disenfranchisement "obnoxious clauses", allowing voters to decide on them apart from the Constitution.[71] While the referendum on the main body of the Constitution was overwhelmingly approved, the two "obnoxious clauses" were defeated by a narrower margin.[72]
Constitutional Convention of 1902
Following Reconstruction of the 1870s, Virginia and other states of the former Confederacy restricted the suffrage by segregationist Jim Crow laws, and by 1890 there began a phase of Southern states Constitutionally removing large numbers of whites and most blacks from voter registration. Reformers among the Progressive Democrats seeking to expand the influence of the "better sort" of voters gained a majority by appealing to the electorate to overthrow the 1868 Underwood Constitution, which the Richmond Dispatch characterized as "that miserable apology to organic law which was forced upon Virginians by carpetbaggers, scalawags and Negroes supported by Federal bayonets".[73]

In May 1900, the increasing public dismay over the electoral fraud and corruption of the Martin political machine manipulating poor white and black voters led to a narrow victory over the entrenched "court house crowd" in a referendum to call a constitutional convention.[74]
The Convention met from June 12, 1901 to June 26, 1902, at Richmond in the Capitol Building and elected John Goode, Jr. its presiding officer, a former delegate to the 1861 Secessionist Convention. Progressives sought to reform corrupt political practices of the ruling Democratic machine under the control of U.S. Senator Thomas S. Martin and to regulate railroads and big corporations. Martin delegates agreed to restrict suffrage of African-Americans and illiterate whites, and a State Corporation Commission was established.[75]
The Convention imposed a system of poll taxes along with literacy and understanding requirements to vote that had the effect of restricting the electorate. The outcome was almost immediate disenfranchising of blacks and half the previous number of whites voting.[76] The Convention instituted a State Corporation Commission to regulate railroads, and it was upheld in the Virginia Supreme Court of Appeals.[77]
Twentieth century milestones
Following the unlimited Convention of 1901–02, twentieth century constitutional activity turned to a mixture of Governor-appointed constitutional commissions in 1927 and 1968, and limited constitutional conventions called by the General Assembly for very specific purpose. After the century's earliest Convention disenfranchising voters in a Constitution that was proclaimed, each modification of the Virginia Constitution has been sent to the voters for referendum approval. Virginia's women suffrage movement was unsuccessful until the national ratification of the Twenty-first Amendment, and the General Assembly did not ratify until 1952, but women could vote beginning in 1920.[78]
Constitutional Commission of 1927

The Commission met from July 7, 1926 – February 16, 1927, and was appointed Virginia Chief Justice Robert R. Prentis its chair. Governor Harry F. Byrd, Sr., the successor boss of the Democratic Organization in Virginia, sought and gained governmental reform streamlining local government and increasing the power of the governor over the executive, as well as implementing constitutional restrictions on the General Assembly's ability to incur debt.[79]
Limited Constitutional Convention of 1945
The Convention met from April 30 – May 1, 2, 22, 1945, and elected John J. Wicker, Jr., its presiding officer. During World War II, Virginia held a Constitutional Convention called for the limited purpose of expanding the franchise to members of the armed forces during wartime. Efforts by some delegates to expand the scope of the convention to reduce the voting age below 21 failed.[80]
Limited Constitutional Convention of 1956
The Convention met from March 5–7, 1956, and elected John C. Parker its presiding officer. When the Supreme Court ruled segregated public schools unconstitutional, proponents of "massive resistance" to racial integration in schools secured a Limited Constitutional Convention for the purpose of state financing of non-sectarian private schools, resulting in segregation academies supported by public funds.[81]
Constitutional Commission of 1969
The Commission met from April 1968 – January 1, 1969, and former Governor Albertis S. Harrison, Jr. was appointed its chair. After seven decades since the previous unlimited Convention, a Constitutional Commission was called by Governor Mills E. Godwin, Jr. to consolidate piecemeal amendments and to conform with U.S. statutory and constitutional law, especially in the areas of education, voter rights and representation in Congressional and General Assembly districts.[82]
Subsequent amendments
After the Convention of 1901–02, the General Assembly did not call another general Convention in the twentieth century. Two proposals for Constitutional Amendment since the 1960s that might have been passed by the General Assembly and sent to the voters for ratification referendum have failed to be enacted, but both remain current topics of periodic political discussion. Virginia remains the only state to ban governors serving consecutive terms, and it is only one of two states still selecting both trial and appellate judges by the state legislature.[83]
Since 1971, additional piecemeal amendments have been added in response to federal developments. Amendments ratified by the voters reduced the voting age to eighteen to conform with the Twenty-sixth Amendment, removed residency requirements for voting, and conformed voter registration to the Motor Voter Act. A legislative session now may be called after a Governor's veto. Virginia has also followed the lead of other states. Virginia joined thirty-two other states in in 1996 by amending its Constitution to provide for rights of victims of crime. Since 1996 Virginia and other states have adopted a provision protecting the right of the people to hunt, fish and harvest game.[84]
In 2006, Virginians aligned with twenty-nine other states seeking to ban homosexual marriage by Constitutional Amendment. The amendment limited marriage to "unions between one man and one woman".[85] This Virginian Constitutional provision ran afoul of the U.S. Supreme Court's interpretation of the Fourteenth Amendment in both its due process and equal protections clauses in Obergefell v. Hodges (2015).
Chart of Virginia Conventions
| Convention/Commission | Dates | Place | Presiding officer | Occasion | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Revolutionary convention | August 1, 1774 | Williamsburg | Peyton Randolph | Governor dissolves House of Burgesses | Call for Continental Congress |
| Second Revolutionary convention | March 20, 1775 | Richmond | Peyton Randolph | withdrawal for physical safety | Militia called up |
| Third Revolutionary convention | July 17, 1775 | Richmond | Peyton Randolph | Dunmore fled Williamsburg | Committees of Safety |
| Fourth Revolutionary Convention | December 1775 | Williamsburg | Edmund Pendleton | safety at Williamsburg | additional troops |
| Constitutional Conventions | |||||
| Fifth Revolutionary Convention | May 6 - July 5, 1776 | Williamsburg | Edmund Pendleton | move to independence | republican constitution |
| Ratifying (Federal) Convention | June 2–27, 1788 | Richmond | Edmund Pendleton | ratification of U.S. Constitution | ratification |
| Constitutional Convention of 1829–30 | Oct 5 1829 - Jan 1830 | Richmond | Philip P. Barbour | regional malapportionment | triumph of traditionalism |
| Constitutional Convention of 1850 | Oct 14 1850 - Aug 1, 1851 | Richmond | John Y. Mason | regional malapportionment | popularly elected governor |
| Secession Convention of 1861 | February 3 - December 16, 1861 | Richmond | John Janney | question of secession | resolution for secession to referendum |
| Wheeling (Virginia) Convention of 1861 | May 13–15, 1861 | Wheeling | Arthur I. Boreman | secession movement | Restored Government loyal to U.S. |
| Loyalist Convention of 1864 | February 13 - April 11, 1864 | Alexandria | LeRoy G. Edwards | separation of West Virginia | abolition of slavery |
| Constitutional Convention of 1868 | Dec 3 1867 - Apr 17, 1868 | Richmond | John C. Underwood | ratifying 14th Amendment | freedmen enfranchised |
| Constitutional Convention of 1902 | Jun 12, 1901 - Jun 26, 1902 | Richmond | John Goode, Jr. | Progressive movementt | 50% white and 90% black disenfranchisement |
| 20th century activity | |||||
| Constitutional Commission of 1927 | Jul 7, 1926 - Feb 16, 1927 | Richmond | Robert R. Prentis | Progressive movementt | Byrd Organization entrenchment |
| Limited Constitutional Convention of 1945 | Apr 30 - May 1,2,22, 1945 | Richmond | John J. Wicker, Jr. | disenfranchised servicemen | enfranchising servicemen |
| Limited Constitutional Convention of 1956 | March 5–7, 1561 | Richmond | John C. Parker | Massive Resistance | segregated academies |
| Constitutional Commission of 1969 | Apr 1968 - Jan 1, 1969 | Richmond | Albertis S. Harrison, Jr. | misalignment with U.S. courts and laws | alignment to U.S. courts and laws |
See also
References
- ↑ Grigsby 1891 p.34
- ↑ Gottlieb "House of Burgesses"
- ↑ Resolutions 23 Mar 1775
- ↑ Resolutions 10 June 1775
- ↑ Proceedings July 17, 1775
- ↑ Virginia in the Revolutionary War
- ↑ Virginia Committee of Safety 1774
- ↑ WPA Guide to Virginia History
- ↑ Virginia in the Revolutionary War
- ↑ Gutzman 2007, p.22
- ↑ Grigsby 1891 p.7
- ↑ Mapp 2006, p. 214
- ↑ Grigsby 1855, p.110, 67
- ↑ Grigsby 1891, p.110, 67
- ↑ Tartar 2013, p. 115
- ↑ Grigsby 1855, p.110, 6
- ↑ Grigsby 1855, p.110, 148
- ↑ The Avalon Project at Yale Law School, "Constitution of Virginia; June 29, 1776" viewed April 14, 2016.
- ↑ Andrews 1937, p. 327.
- ↑ Heinemann 2007, p. 124, 126
- ↑ Heinemann 2007, p. 124, 126
- ↑ Maier 2010, p.260
- ↑ Grigsby 1891, p.67.
- ↑ Grigsby 1891 p. 346
- ↑ Heinemann 2007, p. 145–147
- ↑ Grigsby 1891, p.67. Initially built as the New Academy by the Chevalier Quesnay, subsequently the Richmond Theater
- ↑ Maier 2010, p. 260–261
- ↑ Maier 2010, p. 261–262
- ↑ Maier 2010, p. 268–270
- ↑ Maier 2010, p. 306
- ↑ Maier 2010, p. 308
- ↑ Shade 1996, pp. 57–61
- ↑ Shade 1996, pp. 62–64
- ↑ Gutzman 2007, p. 163, 165
- ↑ Gutzman 2007, p. 163, 165
- ↑ Shade 1996, pp. 65–66
- ↑ Gutzman 2007, p. 188
- ↑ Andrews 1937, p. 430
- ↑ Heinemann 2007, p. 173–174
- ↑ Shade 1996, pp. 262–263
- ↑ Shade 1996, p. 169–272
- ↑ Heinemann 2007, p. 189–190
- ↑ Shade 1996, p. 276–277
- ↑ Shade 1996, p. 280–282
- ↑ Heinemann 2007, p. 190
- ↑ Freehling, pp. 3–10.
- ↑ Freehling, pp. 3–10.
- ↑ Freehling 2010, pp. 12–21.
- ↑ Heinemann 2007, p. 219
- ↑ Freehling 2010, pp. 165–166
- ↑ Freehling 2010, pp. 169–176
- ↑ Heinemann 2007, p. 219–221
- ↑ Wallenstein 2007, p. 190
- ↑ Dabney 1989, p. 294–296
- ↑ 1st Sess. of Second Wheeling Convention
- ↑ 2nd Sess. of Second Wheeling Convention
- ↑ "Second Wheeling Convention", the WV Encyclopedia
- ↑ Delegates to the Second Wheeling Convention, the WV Encyclopedia
- ↑ Second Wheeling Proceedings, 14 Jun 1861
- ↑ Second Wheeling Proceedings, 17 Jun 1861
- ↑ Second Wheeling Proceedings, 17 Jun 1861
- ↑ Heinemann 2007, p. 225
- ↑ Alexandria Gazette, 21, 24 March 1864
- ↑ Virginia Convention of 1864, Encyclopedia Virginia
- ↑ Virginia Convention of 1864, Encyclopedia Virginia
- ↑ Wallenstein 2007, p. 221–222
- ↑ Wallenstein 2007, p. 221
- ↑ Dinan 2006, p. 13–14
- ↑ Dinan 2006, p. 14
- ↑ Dabney 1989, p. 368
- ↑ Dabney 1989, p. 368
- ↑ Wallenstein 2007, p. 223
- ↑ Heinemann 2007, p. 276
- ↑ Dabney 1989, p. 430
- ↑ Dinan 2006, p. 16–17
- ↑ Heinemann 2007, p. 277
- ↑ Dinan 2006, p. 42
- ↑ Heinemann 2007, p. 295–296
- ↑ Dinan 2006, p. 18–20
- ↑ Dinan 2006, p. 20–21
- ↑ Dinan 2006, p. 22–23
- ↑ Dinan 2006, p. 23–24
- ↑ Dinan 2006, p.24.
- ↑ Dinan 2006, p.24, 51, 216.
- ↑ Peaslee 2014, p. 19.
Bibliography
Books
- Andrews, Matthew Page (1937). Virginia, the Old Dominion. Doubleday, Doran & Company. ASIN B0006E942K.
- Dabney, Virginius (1989). Virginia: the New Dominion, a history from 1607 to the present. University of Virginia Press. ISBN 978-0-8139-1015-4.
- Dinan, John (2014). The Virginia State Constitution: a reference guide. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-935574-7.
- Freehling, William; Simpson (eds.), Craig M. (2010). Showdown in Virginia: the 1861 Convention and the fate of the Union. University of Virginia Press. ISBN 978-0-8139-2964-4.
- Grigsby, Hugh Blair (1855). The Virginia Convention of 1776. Da Capo Press, NY. ISBN 978-1-4290-1760-2.
- —— (1891). The Virginia Convention of 1788. Da Capo Press, NY,. ISBN 978-1-4589-2204-5.
- Gutzman, Kevin R.C. (2007). Virginia's American Revolution: from Dominion to Republic, 1776–1840. Lexington Books. ISBN 978-0-7391-2131-3.
- Heinemann, Ronald L. (2008). Old Dominion, New Commonwealth: a history of Virginia, 1607–2007. University of Virginia Press. ISBN 978-0-8139-2769-5.
- Lowe, Richard G. (1991). Republicans and Reconstruction in Virginia, 1856–70. University of Virginia Press. ISBN 978-0-8139-1306-3.
- Maier, Pauline (2010). Ratification: the people debate the Constitution, 1778–1788. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 978-0-684-86855-4.
- Mapp, Alf J., Jr. (2006). The Virginia Experiment: the Old Dominion's role in the making of America 1607–1781. Backinprint.com. ISBN 978-0-595-38809-7.
- Peaslee, Liliokanaio; Swartz, Nicholas J. (2014). Virginia Government: institutions and policy. Congressional Quarterly Press. ISBN 978-1-4522-0589-2.
- Shade, William G. (1996). Democratizing the Old Dominion: Virginia and the Second Party System, 1824–1861. University of Virginia Press. ISBN 978-0-8139-1654-5.
- Tartar, Brent (2013). The Grandees of Government: the origins and persistence of undemocratic politics in Virginia. University of Virginia Press. ISBN 978-0-8139-3431-0.
- Wallenstein, Peter (2007). Cradle of America: a history of Virginia. University Press of Kansas. ISBN 978-0-7006-1994-8.
Web
- Gottlieb, Matthew S. "House of Burgesses". Virginia Foundation of the Humanities. Retrieved 22 October 2016.
- "Resolutions of the Provincial Congress of Virginia; March 23, 1775". The Avalon Project, Yale Law School. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- "Virginia Resolutions on Lord North's Conciliatory Proposal, 10 June 1775". Founders Online, National Archives. Retrieved 10 April 2016.
- "The Proceedings of the Convention of Delegates for the Counties and Corporations in the Colony of Virginia". Wythepedia: The George Wythe Encyclopedia, William & Mary Law Library. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- "Virginia in the Revolutionary War". Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- "JULY 1775 – INTERREGNUM CHAP. III.". Virginia1774.org. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- "WPA Guide to Virginia: Virginia History". American Studies at the University of Virginia. Retrieved 10 April 2016.
- "First Session of the Second Wheeling Convention". wvculture. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- "Second Session of the Second Wheeling Convention". wvculture.org. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- "Second Wheeling Convention". e-WV. the West Virginia Encyclopedia. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- "Delegates to the Second Wheeling Convention". A State of Convenience: the creation of West Virginia. e-WV: the West Virginia Encyclopedia. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- "Proceedings of the Second Wheeling Convention". A State of Convenience: the creation of West Virginia. Wheeling Intelligencer. June 14, 1861. Retrieved October 1, 2016.
- "Proceedings of the Second Wheeling Convention". A State of Convenience: the creation of West Virginia. Wheeling Intelligencer. June 17, 1861. Retrieved October 1, 2016.
- "Virginia Convention of 1864". Virginia Chronicle. Alexandria Gazette. March 22, 1864. Retrieved November 24, 2016.
- Bearss, Sara B. "Virginia Convention of 1864". Encyclopedia Virginia. Library of Virginia. Retrieved November 24, 2016.
External links
1774–76
- Dunaway, W. F. (1904). The Virginia Conventions of the Revolution. The Virginia Law Register.
1788
- Debates and other proceedings of the Convention of Virginia ... 1788 Hunter and Prentis, Petersburg, ebook free online.
1829–30
- Proceedings and Debates of the Virginia State Convention of 1829–30. Samuel Shepherd & Co. for Ritchie & Cook 1830 Richmond online from the archives of the University of Virginia at archive.org
1850
- Register of the Debates and Proceedings of the Virginia Reform Convention of 1850 William G. Bishop, official reporter, Richmond Republican Extras. 1851, from the Duke University Libraries at archive.org
1861
- Journal of the acts and proceedings of a general Convention of the State of Virginia ... 1861 ebook free online.
1868
- The Debates and proceedings of the Constitutional convention of the state of Virginia, assembled at the city of Richmond, tuesday, December 3, 1867 New Nation, Richmond 1868 on line at Hathi Trust Digital Library
1901–02
- Report of the Proceedings and Debates of the Constitutional Convention, State of Virginia ... 1901–1902 from the Duke University Libraries at archive.org