1q21.1 copy number variations
1q21.1 copy number variations (CNVs)[1] are rare aberrations of human chromosome 1.
In a common situation a human cell has one pair of identical chromosomes on chromosome 1. With the 1q21.1 CNVs one chromosome of the pair is not complete because a part of the sequence of the chromosome is missing, or overcomplete, because some parts of the sequence are duplicated. The result is that one chromosome is of normal length and the other one is too long or too short.
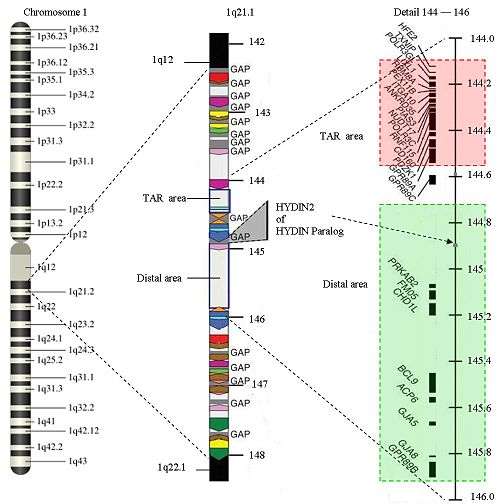
The structure of 1q21.1
The structure of 1q21.1 is complex. The area has a size of approximately 6 Megabase (Mb) (from 141.5 Mb to 147.9 Mb). Within 1q21.1 there are two areas where the CNVs can be found: the proximal area or TAR area (144.1 to 144.5) and the distal area (144.7 to 145.9). A 1q21.1 CNV will commonly be found in one of these areas, but an overlap with the other area or parts that are outside these areas are possible. 1q21.1 has multiple repetitions of the same structure (areas with the same color in the picture have equal structures) Only 25% of the structure is not duplicated. There are several gaps in the sequence. There is no further information available about the DNA-sequence in those areas up till now. The gaps represent approximately 700 Kilobase. New genes are expected in the gaps. The area of 1q21.1 is one of the most difficult parts of the human genome to map.
CNVs occur due to non-allelic homologous recombination mediated by low copy repeats (sequentially similar regions).
Forms of 1q21.1 CNVs
Four separate forms of 1q21.1 CNVs are mentioned in literature.
- the 1q21.1 proximal deletions and duplications
- the TAR syndrome
- the distal deletion, known as the 1q21.1 deletion syndrome
- the distal duplication, known as the 1q21.1 duplication syndrome
The CNVs lead to a very variable phenotype and the manifestations in individuals are quite variable. Some people who have a CNV can function in a normal way, while others have symptoms of mental retardation and various physical anomalies.
Cause of the syndrome
Meiosis is the process of dividing cells in humans. In meiosis, the chromosome pairs splits and a representative of each pair goes to one daughter cell. In this way the number of chromosomes will be halved in each cell, while all the parts on the chromosome (genes) remain, after being randomized. Which information of the parent cell ends up in the daughter cell is purely decided by chance. Besides this random process, there is a second random process. In this second random process the DNA will be scrambled in a way that pieces are omitted (deletion), added (duplication), moved from one place to another (translocation) and inverted (inversion). This is a common process, which leads to about 0,4% variation in the DNA. It explains why even identical twins are not genetically 100% identical.
Problem of the second random process is that genetic mistakes can occur. Especially due to the deletion and duplication process, the chromosomes that come together in a new cell may be shorter or longer. The result of this spontaneous change in the structure of DNA is a so-called copy number variation. Due to the CNV chromosomes of different sizes can be combined in a new cell. If this occurs around conception, the result will be a first cell of a human with a genetic variation. This can be either positive or negative. In positive cases this new human will be capable of a special skill that is assessed positively, for example, in sports or science. In negative cases, you have to deal with a syndrome or a severe disability, as in this case the 1q21.1 CNVs.
Based on the meiotic process, the syndrome may occur in two ways.
- 1. a spontaneous deviation (a 'de novo' situation): two chromosomes come together of which one has a copy number variation as a result of the meiosis process.
- 2. a parent is unknowingly carrier of a chromosome with a copy number variation and passes it through at conception to the child, with different consequences for the child.
Due to this genetic misprint the embryo may experience problems in the development during the first months of pregnancy. Approximately 20 to 40 days after fertilization, something goes wrong in the construction of the body parts and brain, which leads to a chain reaction.
Because of the repetitions in 1q21.1, there is a larger chance on an unequal crossing-over during meiosis.
Related genes
Genes related to the proximal area are HFE2, TXNIP, POLR3GL, LIX1L, RBM8A, PEX11B, ITGA10, ANKRD35, PIAS3, NUDT17, POLR3C, RNF115, CD160, PDZK1, and GPR89A
Genes related to the distal area are PDE4DIP, HYDIN2, PRKAB2, PDIA3P, FMO5, CHD1L, BCL9, ACP6, GJA5, GJA8, NBPF10, GPR89B, GPR89C, PDZK1P1 and NBPF11.
References
- ↑ Understanding the impact of 1q21.1 Copy Number Variant; C. Harvard et al; Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2011, 6:54; doi:10.1186/1750-1172-6-54