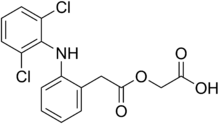
Aceclofenac
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Hifenac, Cincofen, Nacsiv, Acenac |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | oral, topical |
| ATC code | M01AB16 (WHO) M02AA25 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
89796-99-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 71771 |
| ChemSpider |
64809 |
| UNII |
RPK779R03H |
| KEGG |
D01545 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:31159 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL93645 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H13Cl2NO4 |
| Molar mass | 353.02161 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Aceclofenac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) analog of Diclofenac. It is used for the relief of pain and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
It should not be given to people with porphyria or breast-feeding mothers, and is not recommended for children. It should be avoided near term in a pregnant woman because of the risk of having a patent ductus arteriosus in the neonate.
The drug works by inhibiting the action of cyclooxygenase (COX) that is involved in the production of prostaglandins (PG) which is accountable for pain, swelling, inflammation and fever. The incidence of gastric ulcerogenicity of aceclofenac has been reported to be significantly lower than that of the other frequently prescribed NSAIDs, for instance, 2-folds lesser than naproxen, 4-folds lesser than diclofenac, and 7-folds lesser than indomethacin. Aceclofenac (C16H13Cl2NO4), chemically [(2-{2, 6-dichlorophenyl) amino} phenylacetooxyacetic acid], is a crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 354.19. It is practically insoluble in water with good permeability. It is metabolized in human hepatocytes and human microsomes to form [2-(2',6'-dichloro-4'-hydroxy- phenylamino) phenyl] acetoxyacetic acid as the major metabolite, which is then further conjugated. According to the Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) drug substances are classified to four classes upon their solubility and permeability. Aceclofenac falls under the BCS Class II, poorly soluble and highly permeable drug. [1]
References
- ↑ Karmoker, J.R.; Sarkar, S.; Joydhar, P.; Chowdhury, S.F. (2016). "Comparative in vitro equivalence evaluation of some Aceclofenac generic tablets marketed in Bangladesh" (PDF). The Pharma Innovation Journal. 5: 03–07. Retrieved 2016-09-01.
- Sources
- British National Formulary 55, March 2008; ISBN 978-0-85369-776-3 p. 537