Clonixin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
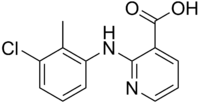
| IUPAC name
2-(3-chloro-2-methylanilino)pyridine-3-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Clonixic acid; CBA 93626[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| 17737-65-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:76200 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1332971 |
| ChemSpider | 26711 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.037.921 |
| KEGG | D03555 |
| PubChem | 28718 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H11ClN2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 262.69 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| Legal status |
|
| per os | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| Glucuronidation via UGT2B7 | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Clonixin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. It also has analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. It is used primarily in the treatment of chronic arthritic conditions and certain soft tissue disorders associated with pain and inflammation.
Synthesis
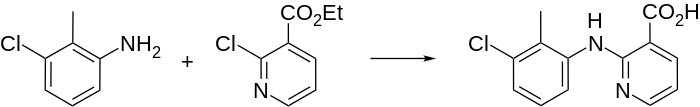
Clonixin synthesis: M. H. Sherlock, N. Sperber, BE 679271; eidem, U.S. Patent 3,337,570 (1966, 1967 both to Schering).
Clonixeril
The glyceryl ester of clonixin, clonixeril, is also a NSAID. It was prepared by a somewhat roundabout method.
Clonixin was reacted with chloroacetonitrile and triethylamine to give 2. Heating with potassium carbonate and glycerol actonide displaced the activating group to produce ester 3, which was deblocked in acetic acid to produce clonixeril (4).
See also
- Flunixin
- Clonixeril
References
- ↑ The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 11(5) (1971). "Clonixin: A Clinical Evaluation of a New Oral Analgesic". Retrieved 2015-05-21.
- ↑ M. H. Sherlock, ZA 6802185 (1968); Chem. Abstr., 70: 96640c (1969).
- ↑ CH 534129 (1973); Chem. Abstr., 79: 18582g (1973).
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/19/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
