Androgen deprivation therapy
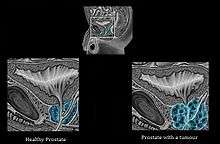
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), also called androgen suppression therapy, is an antihormone therapy whose main use is in treating prostate cancer. Prostate cancer cells usually require androgen hormones, such as testosterone, to grow. ADT reduces the levels of androgen hormones, with drugs or surgery, to prevent the prostate cancer cells from growing.[1] The pharmaceutical approaches include antiandrogens and chemical castration.
Several studies have concluded that ADT has demonstrated benefit in patients with metastatic disease, and as an adjunct to radiation therapy in patients with locally advanced disease. However, in patients with localized prostate cancer, confined to the prostate, ADT has demonstrated no survival advantage, and significant harm, such as impotence, diabetes and bone loss. Even so, 80% of American doctors provide ADT to patients with localized prostate cancer.[2][3][4][5][6]
The therapy can also eliminate cancer cells by inducing androgen deprivation-induced senescence.[7] Lowering androgen levels or stopping them from getting into prostate cancer cells often makes prostate cancer shrink or grow more slowly for a time. However, this treatment needs to be combined with radiation therapy (RT)[8] because ADT itself does not eradicate the cancer; it just decreases its aggressiveness.[9]
Types
Method based on surgery
- Orchiectomy (surgical castration)
- It consists of removing the testicles, the organ where androgens are synthesized, of the cancer sufferers. It is the most radical treatment for ending the production of androgens. Moreover it is the easiest and least expensive one. The main disadvantage is that surgical castration is a permanent method.
Methods based on drugs
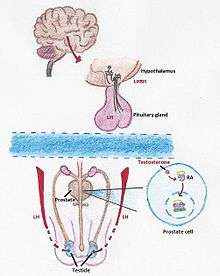
The synthesis of testosterone is mediated by a chain of processes that start in our brain. When our body detects a low level of testosterone, the hypothalamus starts to produce LHRH, an hormone which, once is received by the pituitary gland activates the synthesis of LH (Luteinizing hormone). LH travels to the testicles where induces the formation of testosterone.[10] There are two methods of androgen deprivation therapy based on drugs. One works preventing the pituitary gland from releasing LH and the other one blocks the body’s ability to use androgens.
- There are two different medicines, LHRH agonists and antagonists, which both lower the amount of testosterone made by the testicles. They work inhibiting the formation of LH in the pituitary gland. The LHRH agonists produce a sudden increase on levels of testosterone followed by a huge falling, process called flare, whereas LHRH antagonists decrease directly the amount of testosterone. Some of the most common LHRH agonist and antagonist active substances are leuprolide, goserelin, triptorelin, histrelin and degarelix.
- These drugs are injected under the skin achieving the same result as surgical castration. Although it is much more expensive, men tend to choose this option as they are usually reluctant to have their testicles cut.
- Antiandrogen therapy
- Adrenal glands were discovered as another center of androgen production even after a castration process. Therefore a complementary treatment was developed that uses antiandrogens to block the body’s ability to use any androgens. Prostate cells contain an Androgen Receptor (AR), that when stimulated by androgens like testosterone, promotes growth and maintains prostatic differentiation. These pro-growth signals, however, can be problematic when they occur in a cancer cell. Antiandrogens can enter cells and prevent the binding of testosterone to the receptor proteins, due to their higher affinity for the Androgen Receptor.
- The main antiandrogens are cyproterone acetate, flutamide, nilutamide, bicalutamide, and enzalutamide which are all administered in oral pill form.
- New antiandrogens that target testosterone synthesis (abiraterone acetate and VT-464) or AR nuclear translocation (enzalutamide, apalutamide (ARN-509), and ODM-201), as well as combined therapies (galeterone) have been recently developed and may function to better target androgen-responsive cells in combination with ADT.[11] But these too may have negative adverse roles in the development of CRPC.
Effects on men's sexuality
Normal male sexuality seems to depend upon very specific and complicated hormonal patterns that are not completely understood.[12] One study suggests that ADT can alter the hormonal balance necessary for male sexual activity. As men age, testosterone levels decrease by about 1% a year after age 30; however, it is important to determine whether low testosterone is due to normal aging, or to a disease, such as hypogonadism.[13] Testosterone plays a significant role in sexual functioning; therefore, naturally declining levels of testosterone can lead to reduction in normal sexual functioning. Further decreases in serum testosterone can have a negative impact on normal sexual function, leading to a decline in quality of life.[14]
Erectile dysfunction is not uncommon after radical prostatectomy and men who undergo ADT in addition to this are likely to show further decline in their ability to engage in penetrative intercourse, as well as their desire to do so.[13] A study looking at the differences of using GnRH-A (and androgen suppressant) or an orchiectomy report differences in sexual interest, the experience of erections, and the prevalence of participating in sexual activity. Men reporting no sexual interest increased from 27.6% to 63.6% after orchiectomy, and from 31.7% to 58.0% after GnRH-A; men who experienced no erections increased from 35.0% to 78.6%; and men who did not report engaging in sexual activity increased from 47.9% to 82.8% after orchiectomy and 45.0% to 80.2%.[14] This study suggests that the GnRH-A and orchiectomy had similar effects on sexual functioning. A vicious cycle whereby lowering testosterone levels leads to decreased sexual activity, which in turn cause both free and total testosterone levels to decline even further.[12] This demonstrates the importance of androgens for maintaining sexual structures and functions.[12][15]
Adverse effects
Although targeting the androgen axis has clear therapeutic benefit, its effectiveness is temporary, as prostate tumor cells adapt to survive and grow. The removal of androgens has been shown to activate both epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and neuroendocrine transdifferentiation (NEtD) programs.
- - EMT has established roles in promoting biological phenotypes associated with tumor progression (migration/invasion, tumor cell survival, cancer stem cell-like properties, resistance to radiation and chemotherapy) in multiple human cancer types.
- - NEtD in prostate cancer is associated with resistance to therapy, visceral metastasis, and aggressive disease.
Thus, activation of these programs via inhibition of the androgen axis provides a mechanism by which tumor cells can adapt to promote disease recurrence and progression.[11]
Due to the changes in the levels of sexual hormones (testosterone); Orchiectomy, LHRH analogs and LHRH antagonists can all cause similar side effects:[16]
A program has been developed for patients and their partner to recognize and manage the more burdensome side effects of androgen deprivation therapy. One program is built around the 2014 book "Androgen Deprivation Therapy: An Essential Guide for Prostate Cancer Patients and Their Loved Ones", which is endorsed by the Canadian Urological Association.[17]
One recent study showed ADT may increase the risk of Alzheimer's disease, and the increase in risk may be associated with duration of ADT.[18]
See also
References
- ↑ Perlmutter and Lepor (2007). "Androgen Deprivation Therapy in the Treatment of Advanced Prostate Cancer". Rev Urol. 9 Suppl 1: S3–8. PMC 1831539
 . PMID 17387371.
. PMID 17387371. - ↑ "Prostate Cancer is Focus of 2 Studies, Commentary". JAMA Internal Medicine, Media Releases. July 14, 2014.
- ↑ Grace L. Lu-Yao, Peter C. Albertsen, Dirk F. Moore et al. (July 14, 2014 (online first)). "Fifteen-Year Survival Outcomes Following Primary Androgen-Deprivation Therapy for Localized Prostate Cancer". JAMA Intern Med. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.302. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Quoc-Dien Trinh, Deborah Schrag (July 14, 2014 (online first)). "Measuring the Effectiveness of Androgen-Deprivation Therapy for Prostate Cancer in the Medicare PopulationAdequate Data Are Neither the Same as Nor the Enemy of Perfect Data". JAMA Intern Med. 174: 1468. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.1107. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ Karen E. Hoffman, Jiangong Niu, Yu Shen et al. (July 14, 2014 (online first)). "Physician Variation in Management of Low-Risk Prostate CancerA Population-Based Cohort Study". JAMA Intern Med. 174: 1450. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.3021. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ ANAHAD O'CONNOR (July 14, 2014). "Study Discounts Testosterone Therapy for Early Prostate Cancer". New York Times.
“There are so many side effects associated with this therapy, and really little evidence to support its use,” said Dr. Grace L. Lu-Yao, a researcher at the Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey and the lead author of the report, published on Monday in JAMA Internal Medicine. “I would say that for the majority of patients with localized prostate cancer, this is not a good option.”
- ↑ Burton, Dominick G. A.; Giribaldi, Maria G.; Munoz, Anisleidys; Halvorsen, Katherine; Patel, Asmita; Jorda, Merce; Perez-Stable, Carlos; Rai, Priyamvada; Agoulnik, Irina U. (27 June 2013). Agoulnik, Irina U, ed. "Androgen Deprivation-Induced Senescence Promotes Outgrowth of Androgen-Refractory Prostate Cancer Cells". PLoS ONE. 8 (6): e68003. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0068003. PMC 3695935
 . PMID 23840802.
. PMID 23840802. - ↑ "Combined androgen deprivation therapy and radiation therapy for locally advanced prostate cancer: a randomised, phase 3 trial". The Lancet. 378 (9809): S2104–2111. 2011. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(11)61095-7."Combined androgen deprivation therapy and radiation therapy for locally advanced prostate cancer: a randomised, phase 3"
- ↑ Science Daily
- ↑ Prostate Cancer Guide
- 1 2 Nouri, M; Ratther, E; Stylianou, N; Nelson, CC; Hollier, BG; Williams, ED (2014). "Androgen-targeted therapy-induced epithelial mesenchymal plasticity and neuroendocrine transdifferentiation in prostate cancer: an opportunity for intervention". Front Oncol. 4: 370. doi:10.3389/fonc.2014.00370. PMC 4274903
 . PMID 25566507.
. PMID 25566507. - 1 2 3 Mazzola, C.R.; Mulhall, J.P. (2012). "Impact of androgen deprivation therapy on sexual function". Asian Journal of Andrology. 14: 198–203. doi:10.1038/aja.2011.106.
- 1 2 (2012). Testosterone therapy: Key to male vitality? Retrieved from: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/testosterone-therapy/MC00030
- 1 2 Sharifi, N.; Gulley, J.L.; Dahut, W.L. (2005). "Androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer.". The Journal of the American Medical Association. 294 (2): 238–244. doi:10.1001/jama.294.2.238.
- ↑ "Testosterone Deficiency". Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ↑ Medline Abstract
- ↑ LIFEonADT
- ↑ Nead, Kevin T.; Gaskin, Greg; Chester, Cariad; Swisher-McClure, Samuel; Dudley, Joel T.; Leeper, Nicholas J.; Shah, Nigam H. (2016-02-20). "Androgen Deprivation Therapy and Future Alzheimer's Disease Risk". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 34 (6): 566–571. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.63.6266. ISSN 1527-7755. PMID 26644522.
