Antonio Sicurezza
| Antonio Sicurezza | |
|---|---|
 Photo of young Antonio Sicurezza, date unknown | |
| Born |
Antonio Sicurezza February 25, 1905 Santa Maria Capua Vetere, Italy |
| Died |
August 29, 1979 (aged 74) Formia, Italy |
| Nationality | Italian |
| Known for | Painting |
| Movement | Figurative art |
Antonio Sicurezza (Santa Maria Capua Vetere, February 25, 1905 – Formia, August 29, 1979) was an Italian painter. His work is representative of the Italian figurative art of that period. His artistic production includes still lives, portraits, landscapes, nudes, and altar pieces.
Biography (1)
Sicurezza studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Naples, winning a scholarship to fund his studies. He obtained a diploma in painting training under masters such as Carlo Siviero, Vincenzo Volpe, Vincenzo Migliaro and Paolo Vetri.
He moved to Formia in 1933–1934, when he was called to paint the chapel of St. Anthony in the church of Maranola. Here he met Virginia Mastrogiovanni whom he married in 1934.
In the hardest times of World War II he, his wife, and their four children, fled first into the mountainous caves in Coreno Ausonio, then through the warfront to Calabria. After the war, the family returned to Formia.
The war had destroyed and damaged the churches in the area, which held many of Sicurezzi's work. Among them were Angeli musicanti (Angels Playing Music), a fresco he painted for the chapel of Our Lady of Pompei and two oval portraits of Pope Leo XIII and Blessed Bartolo Longo.
The search for new altar pieces, replacing the ones destroyed, it is not easy for both the difficult economic situation and the clergy that requires religious representations in line with the traditional iconography, which the artist sometimes agrees not to foreclose future commissions.
Artistic maturity

When Antonio Sicurezza can finally express himself more freely, he has artistically valuable results, such as the works of the apse of St. John, St. Albina in the church of Saint Erasmus, and then, above all, the paintings of St. Francis and of the Announced at the church of Our Lady of Carmine and that of Saint Roch in Pico. It is valuable to note that in the landscape behind the figures the painter represents in a deliberately simple manner, so that the faithful can recognize immediately the local sights and monuments, as in St. Albina and in St. Francis, in which it is particularly significant the view of the large Gaeta gulf.

In the summertime he works outside to paint landscapes and alleys, while during the rest of year he works in his studio mainly with charcoal and watercolors or tempera. He produces sketches and studies for religious themes or he paints still lives with immediacy and lightness.
After the summer of 1965 he left teaching and set up the large study that, among carob trees and prickly pears, he had built on the land of Santa Maria la Noce. It is now easier to prepare sketches and large cartoons for religious works and then - limiting the charcoal and pastel studies - he can systematically focus on oil painting, especially of the human figures and still lives.
In fact the style change, which makes him prefer oil painting and sees the use of systematic and almost exclusive spatula instead of a brush, occurs in the late Fifties. Part of the paintings exhibited in Rome in July 1961, including two paintings that were awarded to the contemporary art exhibition held in Turin in the context of the events of Italy '61, already put in evidence the use of the spatula to illustrate the human figure and objects.
In the following years he devoted a greater commitment to personal and collective exhibitions, with a lack of direction, but without referring to a gallery or an agent and tied to a provincial reality. Despite this, there are several distinctions and awards, and news about him with reproductions of his works are found in various catalogs of contemporary artists.
Final years

With the advancing age, Antonio Sicurezza and his wife moved to the center of Formia. The last house is more chaotic for the desire of finding the proper light for each painting. Yet, despite his age and disorder, the work is intense. To complete a painting he takes around five sessions, which means at least two new works every week. He works both mornings and afternoons, often devoting first energies to harder works as the naked human figures. In the living room the walls are covered with framed paintings, while others are simply placed in the corners. It is here that are received friends and admirers. It is of this period the groups of young people with musical instruments that the artist calls concerts, many nudes, vigorous still lives and some outside scenes.
Exceptionally, in August 1978 Antonio Sicurezza does not go to Santa Maria Capua Vetere for the annual meeting of the Assumption. It is the beginning of the sickness that, a year later, August 29, 1979, will bring the artist to die at the age of 74 years.
(1) The biographical data, also for the following chapters, originate from: Anna Luce Sicurezza, "La sala "Antonio Sicurezza" nel palazzo municipale di Formia", Palombi Editori, Roma 2007, pages 17-21; Alessandra Lanzoni, "La pittura di Antonio Sicurezza", De Luca Editori d'Arte, Roma 2011, pages 133-137.
Critical analysis (2)


The background assumptions of Sicurezza's painting are based on values indispensable for him: the respect of human dignity and the sacredness of work. The artist continued to explore and experiment with constant application for many years to reach its capacity of synthesis in painting.
His style reaches maturity based on two fundamental elements: the physical construction of the subject, with increasing use of the spatula to distribute and overlay color, and the mention of the deliberately unfinished around the main theme. The result of all this is a subjective realism. Through the filter of the artist, the performance is careful and accurate for its main theme and the parties to which are assigned a significant role. The same performance is tempered and sometimes only mentioned in the rest of the composition.
Two other considerations must be made: color and atmosphere. Sicurezza manifests for the color a particular passion and he accepts difficult challenges. The atmosphere should be clarified as a physical fact: the atmosphere of the corner of the world where the painter lived and characterized by an extraordinary transparency and brightness, and in which the subjects of his paintings systematically lie, receiving security and serenity.
Antonio Sicurezza, in a century that profoundly transforms reality, puts himself stubbornly in the vein of realism. The artist, at once humble and stubborn, finds his formula of expression in ancient heritage but with original and modern execution.
"The result reached by Antonio Sicurezza is the result of his research, where the responsiveness of more accurate technical means resolves the discovery of the deeper meaning of reality. Therefore, an understanding that surpasses all interpretations animates his painting, to respect it in its entirety. For this reason, in its naked flesh, the more flesh it is, the more chaste" (Luigi Volpicelli).
Elio Marciano for the female nude observes that "the earthly reality of the fine figures of young girls is filled with love of classical perfection of chaste nudity." Guido Bernardi instead puts its focus on humble objects represented in the paintings of the painter, who, "with a wonderful insight figured object, is able to convey continuous points of joy and reflection".
Mario Lepore ascribes to the works of Antonio Sicurezza "the solidity of a job not only well known but also rich in resources and, most importantly, that shows a genuine temperament, from the narrative paintings skills. The quality of design and composition, sensitivity to color and light, reality probated but also poetically observed, often allow him to achieve beautiful accents".
Other critical interventions are often united by a thin thread that identifies values early in the artist and natural attachment to popular traditions, moral honesty, humility and frank simplicity.
(2) The critical comments originate from: Anna Luce Sicurezza, "La sala "antonio Sicurezza" nel palazzo municipale di Formia", Palombi Editori, Roma 2007, chapter "Una breve analisi critica"; Alessandra Lanzoni, "La pittura di Antonio Sicurezza", De Luca Editori d'Arte, Roma 2011, chapter "La maturità artistica".
Gallery
- Still life
-

Still Life With Pitchers, 1969, private collection
-

Still life in white, 1971, private collection
-
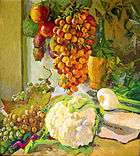
Still live with cauliflower, 1971, private collection
-
Yellow Peppers, 1974, private collection
- Landscape
-

Alley of Itri, 1970, private collection
-

Towards sunset, 1963, private collection
-

Quay in the lagoon of Grado, 1973, private collection
-

Castellonorato, 1974, private collection
- Nudes
-

Susanna, about 1975, private collection
-

Nude Shoulders, 1970, private collection
-

Female Torso, 1973, private collection
-

Nude, 1971, private collection
- Religious themes
-
Pilgrims at Civita's Sanctuary, about 1960, ″Antonio Sicurezza″ hall, City Hall of Formia
-

Saint Albina, 1964, Formia - Church of Saint Erasmus
-

Announced, 1967, Formia - Church of Carmine
-

The Nazarene, 1977, private collection
References
Bibliography
- Grimaldo Casalnuovo and Antonio Sicurezza, Colori e poesia, 1961, Rome
- Studio Fotografico Immagine, Opere di Antonio Sicurezza nelle chiese del Basso Lazio, 1981, Rome
- Massimiliano Vittori (edited by), Maestri storici della provincia di Latina nelle raccolte camerali, 1998, Latina
- Pier Giacomo Sottoriva(edited by), Storia illustrata di Formia - volume V: Formia in età contemporanea, dagli anni Quaranta alla fine del Novecento, 2003, Avellino
- Pier Giacomo Sottoriva (edited by), Antonio Sicurezza, pittore. Cent'anni dalla nascita, 1905–2005, 2005, Cisterna di Latina
- Anna Luce Sicurezza, La Sala Antonio Sicurezza nel palazzo municipale di Formia, Palombi, 2007, ISBN 978-88-6060-081-3, 2007, Rome
- Anna Luce Sicurezza, La produzione pittorica di Antonio Sicurezza negli edifici di culto, Palombi, ISBN 978-88-6060-149-0, 2008,Rome
- Gerardo De Meo, Maranola nella pittura di Antonio Sicurezza, Palombi, ISBN 978-88-6060-289-3, 2010, Rome
- Alessandra Lanzoni, La pittura di Antonio Sicurezza, De Luca Editori d'Arte, ISBN 978-88-6557-041-8, 2011, Rome
- Mario Rizzi, I dipinti minturnesi di Antonio Sicurezza, Palombi Editori, ISBN 978-88-6060-380-7, 2011, Rome
- Giuseppe La Mastra, Antonio Sicurezza - Paesaggi, De Luca Editori d'Arte, ISBN 978-88-6557-092-0, 2012, Rome
- Ferdinando Buranelli, Antonio Sicurezza - Temi Sacri e Religiosi, De Luca Editori d'Arte, ISBN 978-88-6557-115-6, 2013, Rome
- Sabrina Zizzi, Antonio Sicurezza - Nudi, De Luca Editori d'Arte, ISBN 978-88-6557-140-8,2013, Rome
- Teresa Sacchi Lodispoto, Antonio Sicurezza - Nature Morte, De Luca Editori d'Arte, ISBN 978-88-6557-153-8, 2014, Rome.
- Sabrina Spinazzè, Antonio Sicurezza - Ritratti , De Luca Editori d'Arte, ISBN 978-88-6557-188-0, 2014, Rome.
- Teresa Sacchi Lodispoto, Antonio Sicurezza a Formia , De Luca Editori d'Arte, ISBN 978-88-6557-249-8, 2015, Rome.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Antonio Sicurezza. |
