Battle of Taegu
Coordinates: 35°52′N 128°36′E / 35.867°N 128.600°E
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Battle of Taegu was an engagement between UN and North Korean forces early in the Korean War, with fighting continuing from August 5–20, 1950 around the city of Taegu, South Korea. It was a part of the Battle of Pusan Perimeter, and was one of several large engagements fought simultaneously. The battle ended in a victory for the United Nations after their forces were able to drive off an offensive by North Korean divisions attempting to cross the Naktong River and assault the city.
Five North Korean Army (KPA) divisions massed around the city preparing to cross the Naktong River and assault it from the north and west. Defending the city were the 1st Cavalry Division and the ROK II Corps. In a series of engagements, each of the North Korean divisions attempted to cross the Naktong and attack the defending forces. The success of these attacks varied by region, but attacks in the 1st Cavalry Division sector were repulsed and the attacks in the South Korean sector were more successful.
During the battle, however, North Korean troops were able to surprise US troops on Hill 303 and capture them. Late in the battle, these troops were machine gunned in the Hill 303 massacre. Despite these setbacks, the UN forces were successful in driving most of the North Koreans off, but the decisive battle to secure the city would occur during the Battle of the Bowling Alley.
Background
Outbreak of war
Following the invasion of the Republic of Korea (South Korea) by its northern neighbor, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) and the outbreak of the Korean War on June 25, 1950, the United Nations Security Council voted to send armed forces to defend South Korea. The United States, a permanent member of the Security Council, immediately deployed armed forces (U.S. Army, U.S. Navy, and U.S. Air Force units) to southeastern South Korea because of their immediate availability from their bases in Japan and Okinawa, where the military occupation of Japan was still in effect (through 1952). (Reinforcements from such countries as Australia, Canada, Greece, New Zealand, Turkey, and the United Kingdom took much longer to arrive from overseas.)
The goal of American armed forces was to reinforce the remnants of the South Korean Army (ROK) in fighting back the North Korean invasion (but only in the southeastern part of South Korea, around the major seaport of Pusan) to prevent the complete collapse of the South Korean Army and of the South Korean Government. However, the American armed forces in the Orient had been decreasing steadily since the end of World War II, by mid-1950, there were no American troops in South Korea, and the American force in Japan had dwindled drastically.
At the time of the North Korean invasion, the closest American ground force was the 24th Infantry Division, which was based in Japan. This division had fewer than its normal contingent of soldiers, and most of its equipment was rather old due to the U.S. Congress's reductions in military spending. In any case, the 24th Infantry Division was the only part of the U.S. Army that was available to quickly reinforce South Korea.[1]

Thus, the 24th Infantry Division was the first American armed force sent to South Korea with the mission to blunt the advance of the North Korean Army and to set up a defensive perimeter around Pusan (the Pusan Perimeter) with the aid of Air Force, U.S. Navy, and Marine Corps aviation forces. The Supreme United Nations military commander in the area, General Douglas MacArthur, decided to have his American and South Korean troops to dig in around Pusan and hold on until he could assemble a powerful force (the American 10th Corps) to make an amphibious counterattack at Inchon on the northwestern coast of South Korea, near Seoul, later on in 1950.[2] The 24th Infantry Division, along with its South Korean allies, was hence nearly alone for several weeks while the Americans and South Koreans held out inside the Pusan Perimeter and awaited reinforcements and counterattacks against the North Koreans.
Among the American units that reinforced the Pusan Perimeter as soon as they could arrive were the U.S. 1st Cavalry Division, the 7th Infantry Division, and the 25th Infantry Divisions, along with other units of the U.S. Eighth Army that provided logistical, medical, and intelligence support.[2] Advance units of the 24th Infantry Division were badly defeated in the Battle of Osan on July 5 in the first encounter between American and North Korean troops.[3] For the first month after the defeat at Osan, the 24th Infantry were repeatedly pushed back and forced southeastward by larger numbers of North Korean troops equipped with rugged Soviet-made T-34 tanks.[4][5]
The troops of the 24th Infantry were systematically pushed southeast in the Battle of Chochiwon, the Battle of Chonan, and the Battle of Pyongtaek, as well as in smaller engaagements.[4] The 24th Infantry made a desperate stand against the North Koreans in the Battle of Taejon, where it was badly battered, but it delayed the North Korean advance until July 20.[6] By that time, the Eighth Army's force of combat troops were roughly equal in numbers to North Korean forces attacking the Pusan Perimeter, with new U.N. forces arriving from America, Australia, New Zealand, etc., nearly every day.[7]
North Korean advance
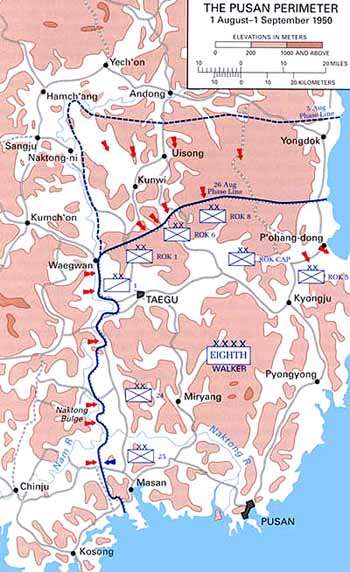
With the city of Taejon captured, the KPA began surrounding the Pusan Perimeter on the north and the west in an attempt to crush it. The 4th and 6th KPA Infantry Divisions advanced south in a wide flanking maneuver. These two KPA divisions attempted to turn the American's and South Korean's left flank in order to capture Pusan from the southwest, but they became dispersed in the process. They were also exposed to repeated air attacks from the U.S. Air Force and the U.S. Navy. The North Koreans attacked the U.S. troops with superior numbers at first, and with the rugged T-34 tanks, but despite local defeats, the U.N. troops, with the help of aviation and naval units were able to extend the Pusan Perimeter all the way south to the East China Sea and to blunt all North Korean attacks toward Pusan.[8] American air supremacy using airfields in Japan and the aircraft carriers of the 7th Fleet in the Sea of Japan were probably the decisive ingredient in enabling the Pusan Perimeter to hold out.
American forces were pushed back repeatedly before finally halting the North Korean advance in a series of battles around the edges of the Pusan Perimeter. Forces of the 3rd Battalion, 29th Infantry, newly arrived in the country, were wiped out at Hadong in a coordinated ambush by KPA forces on July 27, opening a pass to the Pusan area.[9][10] Soon after, North Korean forces took Chinju to the west, pushing back the US 19th Infantry Regiment and leaving routes to the Pusan open for more North Korean attacks.[11] US formations were subsequently able to defeat and push back the North Koreans on the flank in the Battle of the Notch on August 2. Suffering mounting losses, the KPA force in the west withdrew for several days to re-equip and receive reinforcements. This granted both sides a reprieve to prepare for the attack on the Pusan Perimeter.[12][13]
Taegu
In the meantime, Eighth Army commander Lieutenant General Walton Walker had established Taegu as the Eighth Army's headquarters.[14] Right at the center of the Pusan Perimeter, Taegu stood at the entrance to the Naktong River valley, an area where North Korean forces could advance in large numbers in close support. The natural barriers provided by the Naktong River to the south and the mountainous terrain to the north converged around Taegu, which was also the major transportation hub and last major South Korean city aside from Pusan itself to remain in UN hands.[15] From south to north, the city was defended by the US 1st Cavalry Division, and the ROK 1st Division and ROK 6th Division of ROK II Corps. 1st Cavalry Division was spread out along a long line along the Naktong River to the south, with its 5th Cavalry and 8th Cavalry regiments holding a 24,000 metres (79,000 ft) line along the river south of Waegwan, facing west. The 7th Cavalry held position to the east in reserve, along with artillery forces, ready to reinforce anywhere a crossing could be attempted. The ROK 1st Division held a northwest-facing line in the mountains immediately north of the city while the ROKA 6th Division held position to the east, guarding the narrow valley holding the Kunwi road into the Pusan Perimeter area.[16]
Five KPA divisions amassed to oppose the UN at Taegu. From south to north, the 10th,[17] 3rd, 15th, 13th,[18] and 1st Divisions occupied a wide line encircling Taegu from Tuksong-dong and around Waegwan to Kunwi.[19] The KPA planned to use the natural corridor of the Naktong valley from Sangju to Taegu as its main axis of attack for the next push south, so the divisions all eventually moved through this valley, crossing the Naktong at different areas along the low ground.[20] Elements of the DPRK 105th Armored Division also supported the attack.[16][21]
Battle
On the night of 4 to 5 August, the KPA 13th Division began crossing the Naktong River at Naktong-ni, 40 miles (64 km) northwest of Taegu. The crossing was not discovered until 5 August when ROK artillery and mortar fire was called on the crossing. Over the course of three nights, KPA soldiers from the division's three regiments crossed the river on rafts or by wading, carrying their weapons and equipment over their heads. The entire division was across by 7 August, and assembling several miles from the ROK 1st Division's prepared defenses.[16]
At the same time, the KPA 1st Division crossed the river on barges between Hamch'ang and Sangju, in the ROK 6th Division's sector from 6 to 8 August. This attack was discovered quickly by American reconnaissance planes and the KPA 1st Division was immediately engaged by the ROK forces. The two divisions locked in battle around Kunwi until 17 August, with the KPA division facing stubborn resistance, heavy air attacks, and heavy casualties.[16]
Opening moves

ROK troops attacked the 13th Division immediately after it completing its crossing, forcing scattered North Korean troops into the mountains. The division reassembled to the east and launched a concerted night attack, broke the ROK defenses, and began an advance that carried it twenty miles southeast of Naktong-ni on the main road to Taegu. Within a week, the KPA 1st and 13th divisions were converging on the Tabu-dong area, about 15 miles (24 km) north of Taegu.[22]
The KPA 15th Division, the next of the KPA divisions in the line to the south, received 1,500 replacements at Kumch'on on 5 August, which brought its strength to about 6,500 troops. On the next day, its 45th Regiment marched northeast toward the Naktong River. This regiment passed through Sonsan on 7 August and crossed the river southeast of that town while under attack by American aircraft. Once across the river, this regiment headed into the mountains, initially encountering no opposition. Its other two regiments, the 48th and 50th, departed from Kumch'on later and began crossing the Naktong between Indong and [Waegwan before dawn of 8 August, constructing underwater bridges for their vehicles. The North Koreans supported this crossing by direct tank fire from the western side of the river. These tanks next carried out their own river crossing during the day. The KPA 15th Division seized Hills 201 and 346 on the east side of the river at the crossing site before advancing eastward into the mountains toward Tabu-dong, 7 miles (11 km) away.[22] On the next day, the ROK 1st Division regained the high ground at the crossing sites, driving the KPA forces further eastward into the mountains. From 12 through 16 August, the three regiments of the KPA 15th Division united on the east side of the Naktong River in the vicinity of Yuhak-san, 5 miles (8.0 km) east of the crossing site and 3 miles (4.8 km) northwest of Tabu-dong. The KPA 13th Division quickly locked in combat on Yuhak-san with the ROK 1st Division.[23][24]

South of Waegwan, two more KPA divisions stood ready to cross the Naktong in a coordinated attack with the divisions to the north.[23] The experienced KPA 3rd Division, concentrated in the vicinity of Songju, and the untested KPA 10th Division, concentrated in the Koryong area, and both mobilized for an attack.[25] These two divisions crossed in the American 1st Cavalry Division's sector. The KPA 3rd Division's 7th Regiment started crossing the Naktong at about 03:00 on 9 August near Noch'on, 2 miles (3.2 km) south of the Waegwan bridge.[23] After discovering this crossing, units of the American 5th Cavalry Regiment directed automatic-weapon fire against the North Korean units and also called in pre-registered artillery fire on the crossing site.[25] Although the enemy regiment suffered some casualties, the bulk of it reached the east bank and then moved inland into the hills. About 30 minutes later, the 8th and 9th Regiments began crossing the river to the south.[23] The 5th Cavalry Regiment and all its supporting mortars and artillery, now fully alerted, spotted and decimated the troops of the two regiments and turned them back to the west bank.[25] Only a small number of North Koreans reached the eastern side. From there, they were either captured by the U.N. troops or hid out until the next night – when they retreated across the river.[23]
Triangulation Hill
At dawn on 9 August, the division commander Major General Hobart R. Gay at the 1st Cavalry Division headquarters in Taegu learned of the enemy's river crossing in the area of his division south of Waegwan. Since the first reports were vague, General Gay decided to withhold counterattack until he learned more about the situation.[26] He quickly learned that around 750 KPA infantry troops had gathered on Hill 268, also known as "Triangulation Hill", which was 3 miles (4.8 km) southeast of Waegwan and 10 miles (16 km) northwest of Taegu.[27] General Gay ordered his division to counterattack the enemy gathering to force them across the river. He and General Walker thought that this attack could be a feint, and that the North Koreans could be planning a larger attack to their north. Furthermore, the hill was important because of its proximity to the lines of supply. The main Korean north-south highway and the main Seoul-Pusan railroad skirted the base of Triangulation Hill.[26]
At about 09:30, General Gay ordered the 1st Battalion of the 7th Cavalry, to counter the KPA army penetration. This battalion moved from its bivouac area just outside Taegu, accompanied by five tanks of A Company, 71st Heavy Tank Battalion. This motorized force proceeded to the foot of Hill 268. Meanwhile, the 61st Field Artillery Battalion shelled the hill heavily.[26]

At about 12:00 the artillery fired a preparation on Hill 268, and the 1st Battalion next attacked it with orders to continue on southwest to Hill 154. Hill 268 was covered with thick brush from about 4 feet (1.2 m) and trees eight to 10 feet (3.0 m) high. The day was very hot, and many of the American soldiers collapsed from heat exhaustion during the attack, which was not well-coordinated with the artillery fire. The North Koreans repulsed the attack.
On the next morning, 10 August, air raids and artillery rocked Hill 268, devastating the North Korean battalion. That afternoon, General Gay ordered the five American tanks to move along the Waegwan road until they could fire onto the hill from the northwest into its reverse slope. This tank-gun fire caught the KPA troops unprepared while they were hiding from the artillery fire. Trapped between the two barrages, they started to vacate their positions. An American infantry attack next reached the crest of the Triangulation Hill without much trouble, and this battle was over by about 16:00. American artillery and mortar fire was now shifted westward, and this cut off the retreat of the KPA troops. White phosphorus shells fired from the 61st Field Artillery Battalion caught North Korean troops in a village while they attempted to retreat, and they were then routed by American infantry, suffering over 200 killed. That evening the 1st Battalion, 7th Cavalry, returned to the serve as the division reserve, and elements of the 5th Cavalry finished securing Hill 268.[28]
The 7th Regiment of the KPA 3rd Division had been destroyed on the hill. The 1st Battalion, 7th Cavalry suffered 14 men killed and another 48 wounded in the two-day battle.[28] About 1,000 men of the 7th Regiment had crossed the Naktong to Hill 268, and about 700 of at them became casualties.[27] Artillery and mortars had inflicted most of the crippling casualties on the regiment. After crossing to the east side of the Naktong, the enemy regiment had received no food or ammunition supply.[28] An estimated 300 survivors retreated across the river the night of 10–11 August.[27] The KPA 3rd Division's attempted crossing of the Naktong south of Waegwan had ended in catastrophe. When the survivors of the 7th Regiment rejoined the division on or about 12 August, the once powerful 3rd Division was reduced to a disorganized unit of only about 2,500 troops. The KPA placed this division in reserve to be rebuilt by replacements.[27][29]
Yongp'o crossing
The North Korean plan for the attack against Taegu from the west and southwest demanded that the KPA 10th Division make a coordinated attack with the KPA 3rd Division. The 10th Division, so far untested in combat, had started from Sukch'on for the front by rail on July 25. At Chonan it left the trains and continued south on foot through Taejon, arriving at the Naktong opposite Waegwan around 8 August. The division was ordered to cross the Naktong River in the vicinity of Tuksong-dong, penetrate east, and cut the main supply route of the U.N. troops from Pusan to Taegu. The division assembled in the Koryong area on 11 August.[29]
Two regiments of the KPA 10th Division, the 29th to the south and the 25th to the north, were to make the assault crossing with the 27th Regiment in reserve. The 2nd Battalion, 29th Regiment, was the first unit of the division to cross the river.[30] Its troops waded across undetected during the night of August 11/12, west of Hyongp'ung.[27] It then occupied Hill 265, a northern spur of Hill 409, 2 miles (3.2 km) southwest of Hyongp'ung, and set up machine gun positions. The other two battalions followed it and occupied Hill 409. The North Koreans on Hill 409 soon ambushed a patrol from the 21st Infantry Regiment of the 24th Infantry Division, which was moving north and trying to establish contact with the 7th Cavalry Regiment during the Battle of the Naktong Bulge occurring simultaneously to the south.[30]
Further north, the 25th Regiment started crossing the Naktong around 03:00 on August 12, in the vicinity of Tuksong-dong, on the Koryong-Taegu road. The 2nd Battalion, 7th Cavalry Regiment, covered this crossing site, which was 14 miles (23 km) southwest of Taegu. By daylight, a North Korean force of 300 to 400 had penetrated to Wich'on-dong and 2nd Battalion's H Company engaged it in close combat. In a grenade and automatic weapons attack, the North Koreans overran the advance positions of the company, the mortar observation post, and the heavy machine gun positions. The North Koreans were apparently attempting to control high ground east of Yongp'o in order to provide protection for the main crossing that was to follow.[30] By 09:00, however, the 2nd Battalion, supported by the 77th Field Artillery Battalion and air strikes, drove the North Koreans troops back through Yongp'o and dispersed them.[27]
Second Yongp'o attack
In the three days from 10 to 12 August, the Naktong River had dropped 3 feet (0.91 m) in depth and it was only shoulder-deep at many places due to the lack of rain and the torrid weather. This made any attempt at crossing the river considerably easier.[21][30]
A more determined North Korean crossing of the Naktong in the vicinity of the blown bridge between Tuksong-dong and Yongp'o began early in the morning on 14 August.[27] By 06:20, about 500 North Korean soldiers had penetrated as far as Yongp'o. Fifteen minutes later, 2nd Battalion, 7th Cavalry soldiers engaged the North Koreans at Wich'on-dong, 1 mile (1.6 km) east of the crossing site. At 08:00, General Gay ordered 1st Battalion, 7th Cavalry to move to the Yongp'o area to support the 2nd Battalion.[31]
North Korean artillery and tank fire from the west side of the river supporting the infantry crossing. A large number of North Korean reinforcements were crossing in barges near the bridge, while under fire from American air strikes and artillery. This attack also stalled, with the deepest North Korean penetration reaching Samuni-dong, 1.5 miles (2.4 km) beyond the blown-up bridge. From there the combined fire of US light weapons, mortars, and artillery drove them back to the river.[24] By noon, large groups of North Koreans were trying to recross the river to the west side as American artillery continued hammering them, causing heavy casualties.[31]
By nightfall, the 7th Cavalry Regiment had eliminated the North Korean bridgehead at Yongp'o.[31] In the fight, the only major one to take place along the Naktong at a prefabricated crossing site, the 25th and 27th Regiments of the KPA 10th Division suffered crippling losses. The 7th Cavalry estimated that of 1,700 North Korean troops that had succeeded in crossing the river, 1,500 had been killed. Two days after the battle, H Company reported it had buried 267 enemy dead behind its lines. In front of its position, G Company counted 150 enemy dead. In contrast, G Company suffered only two men killed and three wounded during the battle.[32] In its first combat mission, the crossing of the Naktong, the 10th Division suffered 2,500 casualties.[27][32]
Hill 303

Almost simultaneously with the KPA 10th Division's crossing in the southern part of the 1st Cavalry Division sector at Tuksong-dong and Yongp'o, another was taking place northward above Waegwan near the boundary between the division's sector and the ROK 1st Division's sector. The northernmost unit of the 1st Cavalry Division was G Company of the 5th Cavalry Regiment. It held Hill 303, the furthest position on the Eighth Army's extreme right flank.[32]
For several days UN intelligence sources had reported heavy North Korean concentrations across the Naktong opposite the ROK 1st Division. Early in the morning on August 14, a North Korean regiment crossed the Naktong 6 miles (9.7 km) north of Waegwan into the ROK 1st Division sector through an underwater bridge. Shortly after midnight that night, ROK forces on the high ground just north of the U.S.-ROK Army boundary were attacked by this force. After daylight an air strike partially destroyed the underwater bridge. The North Korean attack spread south and by 12:00 North Korean small arms fire fell on G Company, 5th Cavalry Regiment, on Hill 303. Instead of moving east into the mountains as other landings had, this force turned south and headed for Waegwan.[33]

Early in the morning on August 15, G Company men on Hill 303 spotted 50 North Korean infantry supported by two T-34 tanks moving south along the river road at the base of the hill. They also spotted another column moving to their rear which quickly engaged F Company with small arms fire. In order to escape the enemy encirclement, F Company withdrew south, but G Company did not. By 08:30, the North Koreans had completely surrounded it and a supporting platoon of H Company mortarmen on Hill 303. A relief column, composed of B Company, 5th Cavalry, and a platoon of US tanks tried to reach G Company, but was unable to penetrate the North Korean force that was surrounding Hill 303.[33]
Later that day, B Company and the tanks tried again to retake the hill, now estimated to contain a 700-man battalion. The 61st Field Artillery Battalion and elements of the 82nd Field Artillery Battalion, fired on the hill during the day. During the night, G Company succeeded in escaping from Hill 303.[34] Before dawn on the 17th, troops from both the 1st and 2nd Battalions of the 5th Cavalry Regiment, supported by A Company of the 70th Tank Battalion, attacked Hill 303, but heavy North Korean mortar fire stopped them at the edge of Waegwan.[35] During the morning, heavy artillery preparations pounded the North Korean positions on the hill.[34]
At 14:00, an air strike came in, with planes bombarded the hill with napalm, conventional bombs, rockets, and machine guns. The strike and artillery preparation, were successful in pushing North Korean forces off the hill. After the strike, the infantry attacked up the hill at 15:30 unopposed and secured it by 16:30. The combined strength of E and F Companies on top of the hill was about sixty men. The artillery preparations and the air strike killed and wounded an estimated 500 enemy troops on Hill 303, with survivors had fleeing in complete rout after the air strike.[34]
In regaining Hill 303 on August 17, the 5th Cavalry Regiment discovered the bodies of 26 mortarmen of H Company, hands tied in back, with gunshot wounds to the back.[35][36] First knowledge of the event came in the afternoon when scouts brought in a man from Hill 303, Pvt. Roy Manring of the Heavy Mortar Platoon, who had been wounded by automatic weapons fire. Manring had crawled down the hill until he saw scouts of the attacking force.[34] In all about 45 men were shot by the North Koreans in the event, of which only five survived.[37] The total number of men executed around Hill 303 is unclear, as several more men were subsequently discovered in other locations around the hill with evidence of execution.[38] Angered, General of the Army Douglas MacArthur, commander of all UN forces in Korea, broadcast a warning to North Korean leaders they would be held accountable for the atrocity.[35][39] However intercepted documents show the North Korean command was also concerned with the conduct of its troops and issued orders to limit killing of Prisoners of War.[36]
Carpet bombing
In the mountains northeast of Waegwan and Hill 303, the ROK 1st Division continued to suffer North Korean attacks throughout mid-August. North Korean pressure against the ROK division never ceased for long. Under the command of Brigadier General Paik Sun Yup,[40] this division fought an extremely bloody defense of the mountain approaches to Taegu.[41] US planners believed the main North Korean attack would come from west, and so the US command massed its forces to the west of Taegu. The US command mistakenly believed up to 40,000 North Korean troops were near Taegu. This number was above the actual troop numbers for North Korea, which had only 70,000 men along the entire perimeter.[27] American artillery fire from the 1st Cavalry Division sector supported the South Koreans in this area. The division's 13th Regiment still held some positions along the river, while the 11th and 12th Regiments battled the North Koreans in the high mountain masses of Suam-san and Yuhak-san, west and northwest of Tabu-dong and 4 miles (6.4 km) to 6 miles (9.7 km) east of the Naktong River. The North Koreans continued to use the underwater bridge across the Naktong 6 miles (9.7 km) north of Waegwan as their major route for supply and reinforcements. UN forces continued to target this bridge, even scoring a direct hit with a 155mm howitzer, but it was not seriously damaged.[41]

Through the middle of August, North Korean forces relentlessly attacked the sectors occupied by the ROK 13th Regiment and the US 5th Cavalry. This assault, together with increasingly heavy pressure against the main force of the ROK 1st Division in the Tabu-dong area, began to endanger the UN control of Taegu. On August 16, 750 Korean police were stationed on the outskirts of the city to reinforce faltering military lines. Refugees had swollen Taegu's normal population of 300,000 to 700,000.[41] A crisis seemed to be developing among the people on August 18 when several North Korean artillery shells landed in Taegu.[21] The shells, falling near the railroad station, damaged the roundhouse, destroyed one yard engine, killed one Korean civilian, and wounded eight others. The Korean Provincial Government subsequently ordered the evacuation of Taegu, and President Syngman Rhee moved the national leaders to Pusan.[36] Following the ordered evacuation, swarms of panicked Korean refugees began to pour out on the roads leading from the city, threatening to stop all military traffic, but Eighth Army eventually halted the evacuations.[21][41]
On August 14, General MacArthur ordered Lieutenant General George E. Stratemeyer to conduct a carpet bombing of a 27-square-mile (70 km2) rectangular area on the west side of the Naktong River opposite the ROK 1st Division.[27] Intelligence estimates placed the greatest concentrations of enemy troops in this area, some estimates being as high as four enemy divisions and several armored regiments, totalling 40,000 men, who were reportedly using the area to stage their attack on Taegu. General Gay, commanding the 1st Cavalry Division, repeatedly requested that the bombing include the area northeast of Waegwan. This request was denied because of fear that bombing there might cause casualties among the 1st Cavalry and ROK 1st Division troops.[42] Stratemeyer did not think his aircraft could successfully carpet bomb an area larger than 3 miles (4.8 km) square but he complied with MacArthur's order anyway.[43]
At 11:58, on August 16, the first of the 98 B-29 Superfortresses of the 19th, 22nd, 92nd, 98th, and 307th Bomber Groups arrived over the target area from their Far East Air Force bases in Japan and Okinawa. The last planes cleared the target at 12:24. The bombers from 10,000 feet (3,000 m) dropped approximately 960 tons of 500- and 1,000-pound bombs.[42][44] The attack had required the entirety of the FEAF bombing component, and they had dropped 3,084 500 pounds (230 kg) bombs and 150 1,000 pounds (450 kg) bombs. This comprised the largest Air Force operation since the Battle of Normandy in World War II.[43]
General Walker reported to General MacArthur the next day that the damage done to the North Koreans by the bombing could not be evaluated because of smoke and dust, and ground forces could not reach it because of North Korean fire.[42] Information obtained later from North Korean prisoners revealed the enemy divisions the Far East Command thought to be still west of the Naktong had already crossed to the east side and were not in the bombed area.[45] No evidence was found that the bombing killed a single North Korean soldier.[43] However, the bombing seems to have destroyed a significant number of North Korean artillery batteries. The UN ground and air commanders opposed future massive carpet bombing attacks against enemy tactical troops unless there was precise information on an enemy concentration and the situation was critical.[45] Instead, they recommended fighter-bombers and dive bombers would better support ground forces.[43] They subsequently canceled a second bombing of an area east of the Naktong scheduled for August 19.[44][45]
Aftermath
The battles around Taegu saw repeated attempts by the KPA to attack the city. However, the North Korean troops repeatedly stopped or slowed by American and ROK troops and airstrikes. The five KPA divisions each suffered heavy casualties, and each of them finally collapsed under the strain of both mounting losses and lack of supplies. However, some of these division's troops were able to disperse into the mountains. Some of these troops later assembled for different battles.[45] These final elements of the KPA were finally defeated in the Battle of the Bowling Alley.[21]
Casualties among the American 1st Cavalry Division were relatively light. This division suffered a total of about 600 casualties, with around 200 killed in action, including those at Hill 303. American forces in established positions were able to decimate North Korean units crossing the Naktong in the open with their artillery fire and air attacks.[46] The exact numbers of soldiers captured and executed compared with those killed in combat are difficult to determine, because of conflicting accounts of how many prisoners were actually held on Hill 303.[47] The KPA suffered much higher casualties, and also a much higher percentage of them killed in action (KIA). This included 2,500 at Yongp'o,[32] 500 at Hill 303,[34] and 700 on Triangulation Hill.[27] This places the total KIA at over 3,700 troops, though the exact number of casualties is unknown in the carpet-bombing operation because the patrols of the U.N. troops were unable to reconnitor this area until much later.[45]
References
Citations
- ↑ Varhola 2000, p. 3
- 1 2 Alexander 2003, p. 52
- ↑ Catchpole 2001, p. 15
- 1 2 Varhola 2000, p. 4
- ↑ Alexander 2003, p. 90
- ↑ Alexander 2003, p. 105
- ↑ Fehrenbach 2001, p. 103
- ↑ Appleman 1998, p. 222
- ↑ Appleman 1998, p. 221
- ↑ Alexander 2003, p. 114
- ↑ Catchpole 2001, p. 24
- ↑ Catchpole 2001, p. 25
- ↑ Appleman 1998, p. 247
- ↑ Fehrenbach 2001, p. 135
- ↑ Appleman 1998, p. 335
- 1 2 3 4 Appleman 1998, p. 337
- ↑ Appleman 1998, p. 253
- ↑ Appleman 1998, p. 254
- ↑ Leckie 1996, p. 112
- ↑ Appleman 1998, p. 336
- 1 2 3 4 5 Catchpole 2001, p. 31
- 1 2 Appleman 1998, p. 338
- 1 2 3 4 5 Appleman 1998, p. 339
- 1 2 Leckie 1996, p. 113
- 1 2 3 Alexander 2003, p. 141
- 1 2 3 Appleman 1998, p. 340
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Alexander 2003, p. 142
- 1 2 3 Appleman 1998, p. 341
- 1 2 Appleman 1998, p. 342
- 1 2 3 4 Appleman 1998, p. 343
- 1 2 3 Appleman 1998, p. 344
- 1 2 3 4 Appleman 1998, p. 345
- 1 2 Appleman 1998, p. 346
- 1 2 3 4 5 Appleman 1998, p. 347
- 1 2 3 Alexander 2003, p. 144
- 1 2 3 Fehrenbach 2001, p. 136
- ↑ Ecker 2004, p. 16
- ↑ Ecker 2004, p. 17
- ↑ Leckie 1996, p. 114
- ↑ Paik 1992, p. 28
- 1 2 3 4 Appleman 1998, p. 351
- 1 2 3 Appleman 1998, p. 352
- 1 2 3 4 Alexander 2003, p. 143
- 1 2 Fehrenbach 2001, p. 137
- 1 2 3 4 5 Appleman 1998, p. 353
- ↑ Ecker 2004, p. 14
- ↑ Ecker 2004, p. 15
Sources
- Alexander, Bevin (2003), Korea: The First War We Lost, Hippocrene Books, ISBN 978-0-7818-1019-7
- Appleman, Roy E. (1998), South to the Naktong, North to the Yalu: United States Army in the Korean War, Department of the Army, ISBN 978-0-16-001918-0
- Catchpole, Brian (2001), The Korean War, Robinson Publishing, ISBN 978-1-84119-413-4
- Ecker, Richard E. (2004), Battles of the Korean War: A Chronology, with Unit-by-Unit United States Casualty Figures & Medal of Honor Citations, McFarland & Company, ISBN 978-0-7864-1980-7
- Fehrenbach, T.R. (2001), This Kind of War: The Classic Korean War History – Fiftieth Anniversary Edition, Potomac Books Inc., ISBN 978-1-57488-334-3
- Leckie, Robert (1996). Conflict: The History Of The Korean War, 1950–1953. Da Capo Press. ISBN 978-0-306-80716-9.
- Paik, Sun Yup (1992), From Pusan to Panmunjom, Riverside, NJ: Brassey Inc., ISBN 0-02-881002-3
- Varhola, Michael J. (2000), Fire and Ice: The Korean War, 1950–1953, Da Capo Press, ISBN 978-1-882810-44-4
