Declarations of war during World War II
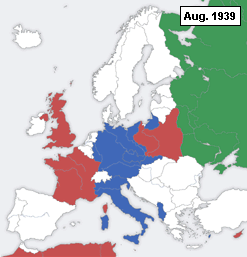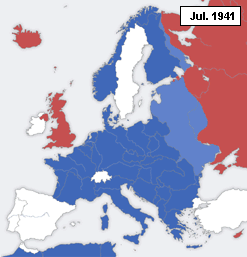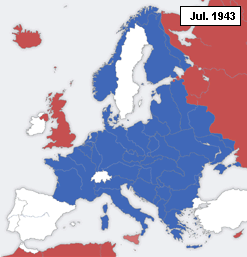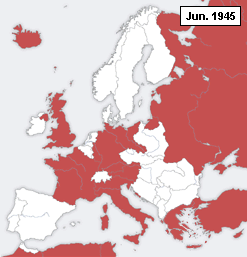
This is a timeline of formal declarations of War during World War II.
A declaration of war is a formal act by which one nation goes to war against another. The declaration is usually an act of delivering a performative speech (not to be confused with a mere speech) or the presentation of a signed document by an authorized party of a national government in order to create a state of war between two or more sovereign states. The official international protocol for declaring war was defined in The Hague Peace Conference of 1907 (or Hague II).[1] For the diplomatic maneuvering behind these events which led to hostilities between nations during World War II, see the article entitled Diplomatic history of World War II.
List of war declarations
Below is a table showing the Outbreaks of Wars between Nations which occurred during World War II. Indicated are the dates (during the immediate build-up to, or during the course of, World War II), from which a de facto state of war existed between nations. The table shows both the "Initiator Nation(s)" and the nation at which the aggression was aimed, or "Targeted Nation(s)". Events listed include those in which there were simple diplomatic breaking of relations that did not involve any physical attack, as well as those involving overt declarations or acts of aggression.[2]
Outbreaks of Wars between Nations during World War II Table Legend: Concerning "Declaration of War: Type." A = Attack without prior, formal declaration of war; U = State of war arrived at through use of ultimatum;
W = Formal declaration of war made.
| Date | Initiator Nation(s) | Targeted Nation(s) | Declaration of War: Type | Notes/Comments | Document/Event |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1939-09-01 | A[3][4] | German attack began at 4:44 am[3][5] | Invasion | ||
| 1939-09-03 | U[3][4] | At 11 O'clock (am) British PM, Neville Chamberlain publicly delivered his Ultimatum Speech.[4][6][7] | Document
Declaration | ||
| 1939-09-03 | W[3][4] |
Australia New Zealand | |||
| 1939-09-04 | Nepal | W |
Declaration | ||
| 1939-09-06 | W[3][4] | Declaration | |||
| 1939-09-10 | | W[3][4] | Declaration
Declaration | ||
| 1939-09-17 | A[3][4] | Invasion | |||
| 1939-11-30 | A[3][4] | First war between these nations. | Invasion | ||
| 1940-04-09 | A[3] | Invasion of Denmark Invasion of Norway | |||
| 1940-05-10 | A/W[3][4] | Date of the German offensive in the West, W from Belgium and the Netherlands.[8] | |||
| 1940-05-10 | A[4] | Luxembourg | |||
| 1940-05-10 | A | Invasion | |||
| 1940-06-10 | W[3][4] | France and the UK | |||
| 1940-06-10 | W[3] | Declaration | |||
| 1940-06-11 | W[3] |
South Africa Australia New Zealand | |||
| 1940-06-11 | [3] | Declaration | |||
| 1940-06-25 | | A | France cuts off diplomatic relations with the United Kingdom on 8 July 1940. | Attack | |
| 1940-09-09 | A | Egypt maintained neutrality until 1945. | Invasion | ||
| 1940-09-22 | A | Invasion | |||
| 1940-09-23 | | A | Invasion | ||
| 1940-10-?? | | A | Franco-Thai War | ||
| 1940-10-28 | U[4] | Italy invades Greece | Invasion | ||
| 1941-02-05 | | A | Invasion | ||
| 1941-04-06 | W[3][4] | Invasion | |||
| 1941-04-06 | A[3][4] | Invasion | |||
| 1941-04-06 | A[4] | Invasion | |||
| 1941-04-12 | Faroe Islands | A[4] | Invasion | ||
| 1941-04-14 | A | Egypt maintained neutrality until 1945. | Invasion | ||
| 1941-05-02 | | A | Invasion | ||
| 1941-06-08 | | A | Invasion | ||
| 1941-06-22 | A[3][4] | A timed-declaration of war was given by Germany at the time of the attack[9] | Invasion | ||
| 1941-06-25 | W | Finland recognized a state of war with the Soviet Union; second war between these nations. | Continuation War | ||
| 1941-06-27 | W[4] | Invasion | |||
| 1941-08-25 | A | Invasion | |||
| 1941-12-06 | U[4] | Declaration | |||
| 1941-12-07 | U[4] | Declaration | |||
| 1941-12-07 | A[3] | W (Japanese point of view); A The "Western" (Attack on Pearl Harbor); |
Declaration | ||
| 1941-12-07 | | | W[4] |
Canada Australia New Zealand | |
| 1941-12-07 | | W[4] | Declaration | ||
| 1941-12-07 | | | W[4] | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-08 | | | W[4] |
Australian declaration Cost Rican declaration Dominican Republic's declaration Salvadorian declaration Haitian declaration Honduran declaration Dutch declaration New Zealand's declaration Nicaraguan declaration Philippine declaration | |
| 1941-12-08 | W[4] | South African declaration | |||
| 1941-12-08 | W[4] | China and Japan had been at war since 1937 | Second Sino-Japanese war
Declaration | ||
| 1941-12-08 | | | W |
Mongolian declaration | |
| 1941-12-09 | W[4] |
Australian declaration New Zealand's declaration | |||
| 1941-12-11 | W[3][4] | ||||
| 1941-12-11 | W[3] | Germany | |||
| 1941-12-11 | | W[3] | Japan rejected declaration of War. Prime Minister Hideki Tōjō's answer was following: "We don't accept the Polish declaration of war. The Poles, fighting for their freedom, declared war under the British pressure". | ||
| 1941-12-12 | W[4] |
Romanian declaration Bulgarian declaration | |||
| 1941-12-12 | | A | Portugal maintained neutrality thought World War II. | ||
| 1941-12-13 | W[4] |
British declaration New Zealand's declaration South African declaration | |||
| 1941-12-13 | W[4] | Declaration | |||
| 1941-12-14 | W[4] | Declaration | |||
| 1941-12-16 | | | W | Declaration | |
| 1941-12-17 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1941-12-19 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1941-12-20 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1942-01-01 | United Nations | Axis Powers | W | Declared during Arcadia Conference | Declaration |
| 1942-01-06 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1942-01-16 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1942-01-25 | W |
British declaration New Zealand's declaration South African declaration | |||
| 1942-01-19 | | A | Portugal maintained neutrality thought World War II. | Invasion | |
| 1942-05-05 | | A | Invasion | ||
| 1942-05-05 | | A | Invasion | ||
| 1942-05-22 | W[4] | Declaration | |||
| 1942-08-22 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1942-11-08 | | A | Invasion | ||
| 1942-11-10 | | A | Invasion | ||
| 1942-12-14 | W | On 3 October 1935, Italy invaded Ethiopia without a formal declaration of war. In response to the Italian invasion, Ethiopia declared war on Italy. Most of Ethiopia was occupied by Italy in 1936, however parts of Ethiopia remained under the control of the Ethiopian Patriots Movement, which begun its guerrilla war against the occupying Italian forces the day Addis Ababa fell in May 1936. In May 1941, Addis Ababa was liberated by the Gideon Force, restoring sovereignty to Ethiopia. | Second Italo-Ethiopian War
Declaration | ||
| 1943-04-02 | Axis Powers | W | Declaration | ||
| 1943-09-09 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1943-10-13 | W[3] | Italy had changed side after the fall of Mussolini. The Declaration of War was given by Pietro Badoglio to the German ambassador in Madrid.[3] | Declaration | ||
| 1943-11-26 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1944-01-17 | | A | Invasion | ||
| 1944-01-27 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1944-06-06 | | | A | Invasion | |
| 1944-06-25 | | | A | Invasion | |
| 1944-08-25 | W | Romania switched sides | Declaration | ||
| 1944-09-05 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1944-09-08 | W | Bulgaria switched sides | Declaration | ||
| 1944-09-15 | A | Lapland War | |||
| 1944-12-31 | W[11] | Hungary switched sides | Declaration | ||
| 1945-02-02 | W | Ecuadorian declaration | |||
| 1945-02-07 | W |
Argentinean declaration Paraguayan declaration | |||
| 1945-02-12 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1945-02-15 | W |
Venezuelan declaration Uruguayan declaration | |||
| 1945-02-21 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1945-02-23 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1945-02-24 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1945-02-26 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1945-04-01 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1945-04-03 | W | Finland switched sides | Lapland War | ||
| 1945-04-11 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1945-07-06 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1945-07-14 | W | Declaration | |||
| 1945-08-08 | W[3] | Last outbreak of war during the entire Second World War. | Declaration | ||
-

Common parade of German Wehrmacht and Soviet Red Army on September 23, 1939 in Brest, Eastern Poland at the end of the Poland Campaign. In the center is Major General Heinz Guderian; and on the right is Brigadier General Semyon Krivoshein.
-

German paratroopers taking the Greek island of Crete, May 1941.
-

Photograph from a Japanese plane of Battleship Row at the beginning of the surprise Attack on Pearl Harbor. The explosion in the center is a torpedo strike on the USS Oklahoma. Two attacking Japanese planes can be seen: one over the USS Neosho and one over the Naval Yard.
Literature about the War
- Harman, Nicholas (1990). Dunkirk: the Necessary Myth. Jove. ISBN 978-0340517857.
- German White Book. All World Wars.
- Hitler, Adolph (2012). The Great Tragedy: Germany's Declaration of War against the United States of America. ISBN 978-1300127703.
- Torrie, Julia S. (2010). "For Their Own Good": Civilian Evacuations in Germany and France, 1939-1945. Berghahn Books. ISBN 978-1845457259.
References
- ↑ On the Opening of Hostilities; 1907; Yale Law School Library; retrieved March 2014.
- ↑ Note:In rare cases, war between two nations occurred twice, with an intermittent period of peace. The list here does not include peace treaties or periods of any armistices.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 "2194 Days of War"; (1977); Salmaggi, C. & Pallasvini, A.; ISBN 91-582-0426-1; per tables included. [Italian; American]
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 Timeline Data; World at War online; retrieved February 2014.
- ↑ On This Day
- ↑ Note: Included in the speech: "...This morning, the British Ambassador in Berlin handed the German Government a final note, stating that unless we heard from them by 11 O'clock that they were prepared at once to withdraw their troops from Poland a state of war would exist between us. I have to tell you now that no such undertaking has been received and that consequently this country is at war with Germany..."
- ↑ 1939: Britain and France declare war on Germany, BBC
- ↑ Swedish Encyklopedia; "Bonniers Lexikon" (Vol. 1); (c.1960s); table in article by Andra Världskriget: The Second World War; Pp. 461-462.
- ↑ "The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich"; Shirer, William L
- ↑ all countries at war with the United States, United Kingdom, or the Soviet Union
- ↑ Hungary declares war on Germany