Engin de débarquement amphibie rapide
_pulls_into_the_well_deck_of_the_amphibious_assault_ship_USS_WASP_(LHD_1).jpg) | |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Builders: | Socarenam |
| Operators: |
|
| Preceded by: | CDIC |
| Completed: | 4 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type: | Roll-on/roll-off catamaran landing craft |
| Displacement: | 285 tons (light) |
| Length: | 30 m (98 ft 5 in) |
| Beam: | 12.8 m (42 ft 0 in) |
| Draft: |
|
| Propulsion: |
|
| Speed: |
|
| Range: | 1,000 nautical miles (1,900 km; 1,200 mi) at 15 knots (28 km/h; 17 mph) (laden) |
| Complement: | 8 |
| Notes: |
|
The Engin de débarquement amphibie rapide (EDA-R) is a class of Roll-on/Roll-off catamaran landing craft (L-CAT) ordered by the French Navy. They transport weapons systems, equipment, cargo and personnel of the assault elements from Mistral class amphibious assault ships to shore and across the beach.
Design and development
Concept design of the EDA-R began in 2000 at Constructions industrielles de la Méditerranée (CNIM) then was abandoned in 2003 and relaunched in 2008 with the full-scale Landing Catamaran (L-Cat). During the development stage, one prototype was built by Gamelin Shipyard and tested during an autonomous transfer from Saint-Malo to the Military port of Toulon. On 14 October 2008, the prototype of the L-Cat beached on the shores of Toulon.[1] On March 2010, it offloaded a 54-ton Leclerc main battle tank at Toulon.[2]
According to CNIM the craft delivers the performance of an aircushion landing craft but at the cost of a conventional landing craft.[3] Four units have been purchased and were presented to the Navy in January 2011.[4]
CNIM is proposing a variant of the L-CAT to fulfill the U.S. Army's requirement for a replacement for their aging LCM-8 "Mike boats."[5]
In October 2016, CNIM revealed a new variant called L-CAT shore-to-shore, designed for smaller navies that don't have larger amphibious ships to deploy landing craft from. It has a bigger hull to accommodate more personnel and provide improved seakeeping, with an expanded length of 32.6 metres (107 ft) and beam of 13.2 metres (43 ft), with seating increased from 40 to 54. The L-CAT shore-to-shore can carry enough fuel to travel 1,000 nautical miles (1,200 mi; 1,900 km) without payload, or 800 nmi (920 mi; 1,500 km) with a 100-ton payload, and be able to move at 22 knots (25 mph; 41 km/h) empty and 15 knots (17 mph; 28 km/h) with a full load. Because of its potential to operate independently, it is fitted with the LYNCEA naval mission management system, and can be mounted with various features such as two unmanned 20 mm guns or a towed array system providing submarine detection capabilities.[6]
Operators
- French Navy (4 units)[7]
- Egyptian Navy (February 2015: 2 units)[8]
Specifications (EDA-R)
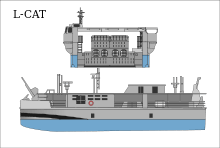
- Source: Naval-Technology Fact File[9]
- Builder: Socarenam
- Date Deployed: June 2011
- Propulsion:
- Four MTU Friedrichshafen 12V2000 M92 Diesel engines 1220 kW
- Four Wärtsilä Pump-jets
- Length: 30 metres (98 feet 43 inches)
- Beam: 12.8 metres (42 feet)
- Displacement: 285 metric tons
- Speed: 20 knots (37 km/h; 23 mph) with full load, 30 knots (56 km/h; 35 mph) maximum speed, 12 knots (22 km/h; 14 mph) platform lowered.
- Range: 400 nautical miles
- Crew: 8
- Load: 80 tons (110 tons overload in lighter mode)
- Military lift: cargo platform 126m² and 80 tons.
- Armament: two 12.7 mm and two 7.62 mm machine guns.
- Radar:
References
- ↑ Jean-Louis Venne (director) (14 October 2008). Landing Catamaran (L-Cat) démonstration à Toulon (Videotape) (in French). Retrieved 10 February 2010.
- ↑ Jean-Louis Venne (7 April 2010). "Le L-CAT débarque pour la première fois un char Leclerc". Mer et Marine. Retrieved 9 April 2010.
- ↑ Richard Scott (21 February 2007). "Novel L-Cat bridges the gap". Jane's Information Group. Retrieved 8 February 2010.
- ↑ Jean-Louis Venne (20 January 2011). "Le major général de la marine se fait présenter le L-Cat". Le portail des sous-marins. Retrieved 15 July 2011.
- ↑ CNIM is teaming with Fincantieri Marine Group to propose its L-CAT® landing craft to the US Military - Navyrecognition.com, 14 April 2015
- ↑ New L-CAT Amphibious Craft Being Offered - Defensenews.com, 20 October 2016
- ↑ Bruno Daffix (30 November 2012). "CNIM livre le quatrième EDAR à la Marine nationale" (in French). Mer et Marine. Retrieved 18 January 2013.
- ↑ "BPC russes : La batellerie comprend aussi des EDAR…" (in French). Mer et Marine. 2 February 2015.
- ↑ "CNIM - Landing Craft and Multipurpose Patrol Craft". naval-technology.org. Retrieved 8 February 2010.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Engin de débarquement amphibie rapide. |