FLII
| FLII | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | FLII, FLI, FLIL, Fli1, actin remodeling protein | ||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 1342286 HomoloGene: 11092 GeneCards: FLII | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||||||
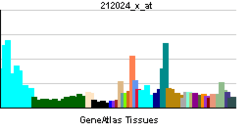 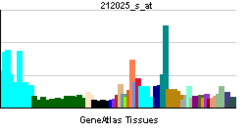 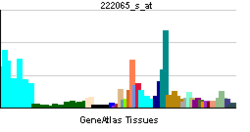 | |||||||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 17: 18.24 – 18.26 Mb | Chr 11: 60.71 – 60.73 Mb | |||||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [1] | [2] | |||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
Protein flightless-1 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FLII gene.[3][4]
This gene encodes a protein with a gelsolin-like actin binding domain and an N-terminal leucine-rich repeat-protein protein interaction domain.[5] The protein is similar to a Drosophila protein involved in early embryogenesis and the structural organization of indirect flight muscle. The gene is located within the Smith-Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17.[4]
Interactions
FLII has been shown to interact with LRRFIP1[6][7] and TRAF interacting protein.[8]
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Chen KS, Gunaratne PH, Hoheisel JD, Young IG, Miklos GL, Greenberg F, Shaffer LG, Campbell HD, Lupski JR (Feb 1995). "The human homologue of the Drosophila melanogaster flightless-I gene (flil) maps within the Smith-Magenis microdeletion critical region in 17p11.2". Am J Hum Genet. 56 (1): 175–82. PMC 1801336
 . PMID 7825574.
. PMID 7825574. - 1 2 "Entrez Gene: FLII flightless I homolog (Drosophila)".
- ↑ Ghoshdastider U, Popp D, Burtnick LD, Robinson RC (2013). "The expanding superfamily of gelsolin homology domain proteins". Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 70 (11): 775–95. doi:10.1002/cm.21149. PMID 24155256.
- ↑ Liu, Y T; Yin H L (Apr 1998). "Identification of the binding partners for flightless I, A novel protein bridging the leucine-rich repeat and the gelsolin superfamilies". J. Biol. Chem. UNITED STATES. 273 (14): 7920–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.14.7920. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9525888.
- ↑ Fong, K S; de Couet H G (Jun 1999). "Novel proteins interacting with the leucine-rich repeat domain of human flightless-I identified by the yeast two-hybrid system". Genomics. UNITED STATES. 58 (2): 146–57. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5817. ISSN 0888-7543. PMID 10366446.
- ↑ Wilson, S A; Brown E C; Kingsman A J; Kingsman S M (Aug 1998). "TRIP: a novel double stranded RNA binding protein which interacts with the leucine rich repeat of flightless I". Nucleic Acids Res. ENGLAND. 26 (15): 3460–7. doi:10.1093/nar/26.15.3460. ISSN 0305-1048. PMC 147727
 . PMID 9671805.
. PMID 9671805.
Further reading
- Campbell HD, Schimansky T, Claudianos C, et al. (1994). "The Drosophila melanogaster flightless-I gene involved in gastrulation and muscle degeneration encodes gelsolin-like and leucine-rich repeat domains and is conserved in Caenorhabditis elegans and humans.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90 (23): 11386–90. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.23.11386. PMC 47987
 . PMID 8248259.
. PMID 8248259. - Campbell HD, Fountain S, Young IG, et al. (1997). "Genomic structure, evolution, and expression of human FLII, a gelsolin and leucine-rich-repeat family member: overlap with LLGL.". Genomics. 42 (1): 46–54. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4709. PMID 9177775.
- Liu YT, Yin HL (1998). "Identification of the binding partners for flightless I, A novel protein bridging the leucine-rich repeat and the gelsolin superfamilies.". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (14): 7920–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.14.7920. PMID 9525888.
- Wilson SA, Brown EC, Kingsman AJ, Kingsman SM (1998). "TRIP: a novel double stranded RNA binding protein which interacts with the leucine rich repeat of flightless I.". Nucleic Acids Res. 26 (15): 3460–7. doi:10.1093/nar/26.15.3460. PMC 147727
 . PMID 9671805.
. PMID 9671805. - Fong KS, de Couet HG (1999). "Novel proteins interacting with the leucine-rich repeat domain of human flightless-I identified by the yeast two-hybrid system.". Genomics. 58 (2): 146–57. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5817. PMID 10366446.
- Davy DA, Campbell HD, Fountain S, et al. (2001). "The flightless I protein colocalizes with actin- and microtubule-based structures in motile Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts: evidence for the involvement of PI 3-kinase and Ras-related small GTPases.". J. Cell. Sci. 114 (Pt 3): 549–62. PMID 11171324.
- Campbell HD, Fountain S, McLennan IS, et al. (2002). "Fliih, a gelsolin-related cytoskeletal regulator essential for early mammalian embryonic development.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (10): 3518–26. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.10.3518-3526.2002. PMC 133791
 . PMID 11971982.
. PMID 11971982. - Bi W, Yan J, Stankiewicz P, et al. (2002). "Genes in a refined Smith-Magenis syndrome critical deletion interval on chromosome 17p11.2 and the syntenic region of the mouse.". Genome Res. 12 (5): 713–28. doi:10.1101/gr.73702. PMC 186594
 . PMID 11997338.
. PMID 11997338. - Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932. - Gevaert K, Goethals M, Martens L, et al. (2004). "Exploring proteomes and analyzing protein processing by mass spectrometric identification of sorted N-terminal peptides.". Nat. Biotechnol. 21 (5): 566–9. doi:10.1038/nbt810. PMID 12665801.
- Lee YH, Campbell HD, Stallcup MR (2004). "Developmentally essential protein flightless I is a nuclear receptor coactivator with actin binding activity.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 24 (5): 2103–17. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.5.2103-2117.2004. PMC 350567
 . PMID 14966289.
. PMID 14966289. - Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446
 . PMID 15302935.
. PMID 15302935. - Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928
 . PMID 15489334.
. PMID 15489334. - Wang T, Chuang TH, Ronni T, et al. (2006). "Flightless I homolog negatively modulates the TLR pathway.". J. Immunol. 176 (3): 1355–62. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.176.3.1355. PMID 16424162.
- Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Gerber SA, et al. (2006). "A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization.". Nat. Biotechnol. 24 (10): 1285–92. doi:10.1038/nbt1240. PMID 16964243.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, et al. (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks.". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.