Große Fuge

The Große Fuge (or Grosse Fuge, also known in English as Great Fugue or Grand Fugue), Op. 133, is a single-movement composition for string quartet by Ludwig van Beethoven. A massive double fugue, it was universally condemned by contemporary critics. A reviewer writing for Allgemeine musikalische Zeitung in 1826 described the fugue as "incomprehensible, like Chinese" and "a confusion of Babel".[1] However critical opinion of the work has risen steadily since the beginning of the 20th century. The work is now considered among Beethoven's greatest achievements. Igor Stravinsky said of it, "[it is] an absolutely contemporary piece of music that will be contemporary forever."[2]
The Große Fuge originally served as the final movement of his Quartet No. 13 in B♭ major (Op. 130), written in 1825. But Beethoven's publisher, who was concerned about the dismal commercial prospects of the piece, urged Beethoven to replace the fugue with a new finale. Beethoven complied, and the Grosse Fuge was published separately in 1827 as Op. 133. It was composed when Beethoven was almost completely deaf, and is considered to be part of his set of late quartets. It was first performed in 1826, as the finale of the B♭ quartet, by the Schuppanzigh Quartet.
Analysts describe the Große Fuge as "inaccessible",[3] "eccentric",[4] "filled with paradoxes",[5] and "Armaggedon".[6] "[It] stands out as the most problematic single work in Beethoven's output and … doubtless in the entire literature of music," writes Joseph Kerman of the fugue.[7]
Also, writes violinist and composer David Matthews, "it is fiendishly difficult to play."[8]
History of composition
 |
Live performance of the work
by the Merel Quartet at Tonhalle Zürich, 3 July 2013: Mary Ellen Woodside and Julia Schröder, violin; Ylvali Zilliacus, viola; Rafael Rosenfeld, cello |
| Problems playing this file? See media help. | |
Beethoven originally composed the Große Fuge as the final movement of his String Quartet No. 13 (Op. 130). His choice of a fugal form for the last movement was well grounded in tradition: Haydn, Mozart, and Beethoven himself had used fugues as final movements of quartets. But in recent years, Beethoven had become increasingly concerned with the challenge of integrating this Baroque form, that was academic and highly formalized, with the expressive impulses of Romanticism. "In my student days I made dozens of [fugues]... but [imagination] also wishes to exert its privileges... and a new and really poetic element must be introduced into the traditional form," Beethoven wrote.[9] The resulting movement was a mammoth work, longer than all the other movements of the quartet together.[10] Beethoven wrote at the top of the score, "Grande fugue tantôt libre, tantôt recherchée" (a grand fugue, somewhat free, somewhat researched), an indication of his ambition to reconcile the academic and the romantic. The fugue is dedicated to the Archduke Rudolf of Austria, his student and patron.

At the first performance of the quartet, other movements were received enthusiastically, but the fugue was not a success. A review of the performance in the Allgemeine musikalische Zeitung, one of Vienna's leading music periodicals, called the fugue "incomprehensible, like Chinese" and "a confusion of Babel".[11] Composer and violinist Louis Spohr called the fugue, and the other late quartets, "an indecipherable, uncorrected horror."[12]
Despite the contemporary criticism, Beethoven himself never doubted the value of the fugue. Karl Holz, confidante of Beethoven's, and second violinist of the Schuppanzigh quartet that performed the work, brought Beethoven the news that the audience demanded encores of two middle movements. Beethoven, enraged, was reported to have growled, "And why didn't they encore the Fugue? That alone should have been repeated! Cattle! Asses!"[13]
However, the fugue was so roundly condemned by critics and audience alike that Beethoven's publisher, Matthias Artaria (1793–1835), decided to try to convince Beethoven to publish it separately. Holz was given the task of convincing Beethoven to separate the fugue from the rest of the quartet. Holz wrote:
Artaria...charged me with the terrible and difficult task of convincing Beethoven to compose a new finale, which would be more accessible to the listeners as well as the instrumentalists, to substitute for the fugue which was so difficult to understand. I maintained to Beethoven that this fugue, which departed from the ordinary and surpassed even the last quartets in originality, should be published as a separate work and that it merited a designation as a separate opus. I communicated to him that Artaria was disposed to pay him a supplementary honorarium for the new finale. Beethoven told me he would reflect on it, but already on the next day I received a letter giving his agreement.[14]
Why the notoriously stubborn Beethoven agreed so readily to replace the fugue is an enigma in the history of this quintessentially enigmatic piece. Historians have speculated that he did it for the money (he was notoriously bad at managing money), or to satisfy his critics, or because he simply believed the fugue stood best on its own.[15] The fugue is connected to the other movements of opus 130 by various hints of motifs, and by a tonal link to the preceding Cavatina movement (the Cavatina ends on a G, and the fugue begins with the same G[16]). The replacement last movement, on the other hand (which also begins on a G) is light in character and completely uncontroversial. Beethoven composed the replacement finale in late 1826. In May 1827, about two months after Beethoven's death, Matthias Artaria published the first edition of Op. 130 with the new finale, and the Große Fuge as Op. 133, as well as a four-hand piano arrangement, Op. 134.[17]
Analysis
Dozens of analyses have attempted to delve the structure of the Große Fuge, with conflicting results. The work has been described as an expansion of the formal Baroque grand fugue,[18] as a multi-movement work rolled into a single piece,[19] as a symphonic poem in sonata form.[20] Stephen Husarik has suggested that the relationships between the keys of the different sections of the fugue mirror what he describes as the wedge-like structure of the eight-note motif that is the main fugal subject, the "contour [that] is a driving force behind the Große Fuge."[21] All these approaches add insight into the understanding of the fugue, but, writes Husarik, "no critical analysis of Große Fuge has satisfactorily explained its compelling directionality, thus leaving even modern listeners unfulfilled."[22]
The building blocks
The central motif of the fugue is an eight-note subject that climbs chromatically upward:
 |
First fugal subject
|
| Problems playing this file? See media help. | |
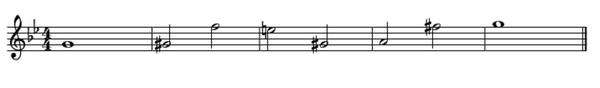

A similar motif appears in Act ii, measures 44-47, of the "Dance of the Blessed Spirits" from Gluck's opera Orfeo ed Euridice (1774), and also in Haydn's String Quartet in G, Op. 33 No. 5. ii, measures 27-29.[23] Another similar subject, with syncopated or gapped rhythm (called unterbrechung in German), appears in a treatise on counterpoint by Johann Georg Albrechtsberger,[24] who taught Beethoven composition. Joseph Kerman suggests that Beethoven modeled the motif after Bach's fugue in B minor from The Well-Tempered Clavier;[25] William Caplan has analyzed Beethoven's sketchbooks to come up with a plausible explanation of the origin of the motif.[26] Whatever the origin of the motif, Beethoven was fascinated by it. He used it, or fragments of it, in a number of places in the late quartets, most notably in the first movement of opus 132:
In the course of the Große Fuge, Beethoven plays this motif in every possible variation: fortissimo and pianissimo, in different rhythms, upside down and backwards. The usual practice in a traditional fugue is to make a simple, unadorned statement of the subject at the outset; but Beethoven from the very beginning presents the subject in a host of variations.
In stark contrast to this simple chromatic motif is the second subject of the fugue:
This motif leaps dramatically in huge intervals – tenths and twelfths.
The third motif is a lilting melody that serves as the theme of the Andante section of the fugue:
A fourth element – not so much a motif as an effect – is the trill.
Beethoven uses trills extensively, simultaneously creating a sense of disintegration of the motifs, and leading to a climax.
These four elements are, essentially, all the building blocks of the entire 16-minute work.
Overtura
Beethoven opens the fugue with a 24-bar overture,[27] which opens with a dramatic fortissimo unison G, and statement of the main fugal subject in the key of G major[28]
This statement of the subject disintegrates into a trill, and silence. Beethoven then repeats the subject, but in a completely different rhythm, in diminution (meaning at double the tempo), twice, climbing up the scale; and then, again silence, and again the subject, this time unadorned, in a dramatic drop to pianissimo in the key of F major.
This leads to a statement of the third fugal subject, with the first subject in the bass:
Thus, Beethoven, in this brief introduction, presents not only the material that will make up the entire piece, but also the spirit: violent shifts of mood, melodies disintegrating into chaos, dramatic silences, instability, and struggle. Here is the Overtura in its entirety:
First fugue
Following the overture is a strictly formal double fugue in the key of B♭ major, that follows all the rules of a Baroque fugue: An exposition and three variations, showcasing different contrapuntal devices. But this is anything but a tame Baroque fugue: it is violent and dissonant, pitting awkward leaps of the second subject in iambic rhythm against the main subject in syncopation, at a constant dynamic that never falls below Forte. The resulting angular rhythmic confusion and displaced dissonances last almost five minutes.
First, Beethoven restates the main subject, broken up by rests between each note:
Then begins a double fugue - two subjects, played one against the other: the second subject in the first violin, and the first subject, syncopated, in the viola. Then the second violin and cello take up the same thing.
The first variation, following the rules of fugue, opens in the subdominant key of E♭. Beethoven adds to the chaos with a triplet figure in the first violin, played against the quaternary rhythm of the second subject in the second violin and the syncopated main subject in the viola.
The second variation, back in the key of B♭, is a stretto section, meaning that the voices enter one after the other, To this Beethoven adds a countersubject in dactylic rhythm.

In the third variation, Beethoven presents a variation of the second subject in the triplet rhythm of the countersubject of the first variation, with the main subject syncopated in eighth notes, in diminution (meaning the subject is played at twice the speed).
This last variation grows increasingly chaotic, with triplets breaking out in the inner voices, until it ultimately collapses – each instrument finishing on a different part of the measure and ending inconclusively on a final fermata, leading to the next section in the key of G♭.
Meno mosso e moderato
This section is a complete change of character from the formal fugue that preceded it and the one that follows it. It is a fugato, a section that combines contrapuntal writing with homophony. "After the strenuousness of the B♭ Fugue [first section], the effect is of an almost blinding innocence," writes Joseph Kerman.[29] Analysts who see the fugue as a multi-movement work rolled into one view this as the traditional Andante movement.[30] It opens with a statement of the third subject, against a pedal tone in the viola, and continues with the third subject in the second violin, against the main subject cantus firmus in the viola.
The counterpoint becomes more complex, with the cello and first violin playing the main subject in canon while the second violin and viola pass the third subject between them.

Despite the growing complexity of the fugal writing, Beethoven instructs the players sempre piano – always quiet. Leonard Ratner writes of this section, "[This] comes as a wonderful change of color, offered with the silkiest of textures, and with exquisite moments of glowing diatonism.[31]"
The polyphony gradually dissipates into homophony, and from there into unison, finally tapering into a dying, measured sixteenth-note tremolo, when the next section bursts in in the key of B♭.
Interlude and second fugue
Beethoven shifts gears: from G♭ to B♭, from 2
4 to 6
8, from pianissimo to fortissimo. The fortissimo descends immediately to piano, for a short interlude before the second fugue. This interlude is based on the main subject in diminution, meaning in double time. On top of this, Beethoven adds a lilting, slightly comic melody; analysts who see the fugue as a multi-movement work consider this section the equivalent of a scherzo.[32]
In this interlude, Beethoven introduces the use of trill (hinted at at the end of the Meno mosso section). The music grows in intensity and shifts into A♭ major, for a new learned fugue.
In this fugue, Beethoven puts together three versions of the main subject. There is the subject in its simple form, but in augmentation (meaning half the speed):
There is the same subject, abbreviated, in retrograde (that is, played backwards):
And there is a variation of the first half of the subject in diminution (that is, double time):
Together, they sound like this:

Here Beethoven starts to use trills intensely. This adds to the extremely dense texture and rhythmic complexity. Kerman writes of this fugal section, "The piece seems to be in danger of cracking under the tension of its own rhythmic fury."[33]
In the second episode of this fugue, Beethoven adds in the triplet figure from the first variation of the first fugue:
The trills become more intense. In the third episode, in the dominant key of E♭ major, Beethoven uses a leaping motif that recalls the second subject of the first fugue:
The fourth episode returns to the key of A♭. The cello plays the main subject in a way that harks back to the Overtura. More elements of the first fugue return: the syncopation used for the main subject, the tenth leaps from the second subject, the diminuted main subject in the viola.
All leading back to...
Thematic convergence and coda
... a restatement of the Meno mosso e moderato section. This time, though, instead of a silky pianissimo, the fugato is played forte, heavily accented (Beethoven writes f on every sixteenth-note group), march-like. Analysts who see the fugue as a variation of sonata-allegro form consider this to be part of the recapitulation section, though the material does not return in home key. In this section, Beethoven uses another, complex contrapuntal device: the second violin plays the theme, the first violin plays the main subject in a high register, and the viola plays the main subject in inversion – that is, upside down.[34] According to Stephen Husarik, this section emphasizes the relationships between the different motifs of the fugue, and suggests that Beethoven was using the Baroque contrapuntal technique called reverse variation.[35]

A series of trills leads back to the home key of B♭, and a restatement of the scherzo section.
There follows a section that analysts have described as "uneasy hesitation"[36] or "puzzling" and "diffused".[37] Fragments of the various subjects appear and disappear, and the music seems to lose energy. A silence, and then a fragmentary burst of the opening of the first fugue. Another silence. A snippet of the "Meno mosso". Another silence. And then a Fortissimo restatement of the very opening of the piece, leading to the coda.[38]
From here the music moves forward, at first haltingly, but then with more and more energy, to the final passage, where the first subject is played in triplets below the soaring violin line playing a variant of the second subject.
Understanding the Große Fuge
Analyses of the Große Fuge help to understand the structure and contrapuntal devices of this mammoth piece. But, writes David Levy, "Regardless of how one hears the piece structurally, the composition remains filled with paradoxes that leave the listener ultimately dissatisfied with an exegesis derived solely from a structural perspective."[39] Since its composition, musicians, critics and listeners have tried to explain the tremendous impact this piece has.[40]
It "is one of the great artistic testaments to the human capacity for meaning in the face of the threat of chaos. Abiding faith in the relevance of visionary struggle in our lives powerfully informs the structure and character of the music," writes Mark Steinberg, violinist of the Brentano Quartet. "More than anything else in music... it justifies the ways of God to men," writes Leonard Ratner.[41]
But, beyond a recognition of the hugeness and almost mystical impact of the music, critics fail to agree on its character.[42] Robert Kahn says "it presents a titanic struggle overcome.".[43] Daniel Chua, on the contrary, writes, "The work speaks of failure, the very opposite of the triumphant synthesis associated with Beethovenian recapitulations."[44] Stephen Husarik, in his essay "Musical direction and the wedge in Beethoven's high comedy, Grosse Fuge op. 133", contends that in the fugue, Beethoven is actually writing a parody of Baroque formalism. "The B♭ Fuga of op.133 stumbles forward in what is probably the most relentless and humorous assertion of modal rhythms since 12th century Notre Dame organum."[45] Robert Kahn disagrees: "...the comparison to comic music is surprising. There is nothing comic about the Grosse Fuge..."[46]
In many discussions of the piece, the issue of struggle is central. Sara Bitloch, violinist of the Elias quartet, says this sense of struggle informs her group's interpretation of the fugue. "Every part has to feel like it's a huge struggle ... You need to finish the Grosse Fuge absolutely exhausted."[47] She calls the piece "apocalyptic." Arnold Steinhardt of the Guarneri quartet, calls it "Armageddon ... the chaos out of which life itself evolved."[48]
One way to express the impact of the fugue is through poetry. In her poem "Little Fugue", Sylvia Plath associates the fugue with death, in a melange of hazy associations with the Yew tree (a symbol of death in Celtic Britain), the Holocaust, and the death of her own father:[49]
He could hear Beethoven:
Black yew, white cloud,
The horrific complications.
Finger-traps--a tumult of keys.
Empty and silly as plates,
So the blind smile.
I envy big noises,
The yew hedge of the Grosse Fuge.
Deafness is something else.
Such a dark funnel, my father!
I see your voice
Black and leafy, as in my childhood.
- Sylvia Plath, from the poem "Little Fugue" (1965)
The poet Mark Doty wrote of his feelings on listening to the Große Fuge:[50]
What does it mean, chaos
gathered into a sudden bronze sweetness,
an October flourish, and then that moment
denied, turned acid, disassembling,
questioned, rephrased?
- Mark Doty, from the poem "Grosse Fuge" (1995)
Reception and musical influence
 |
Alfred Schnittke String Quartet number 3
performed by the Canto String Quartet (Eduardo Canto Arce and Guillem Cabre Salagre, violin; Marton Vineter, viola; Teodora Nedyalkova, cello) at Lutherse Kerk, Groningen, Netherlands, December 16, 2013. The quartet quotes the main subject. |
| Problems playing this file? See media help. | |
After the first performance in 1826, the fugue was not known to have been performed in public again until 1853 in Paris by the Maurin Quartet.[51] One hundred years after its publication, it still had not entered the standard quartet repertoire. "The attitude of mind in which most people listen to chamber music must undergo a radical change" to understand this piece, wrote Joseph de Marliave more than a century after its publication.[52] "this fugue is one of the two works by Beethoven—the other being the fugue from the piano sonata, Op. 106—which should be excluded from performance." As late as 1947, Daniel Gregory Mason called the fugue "repellent".[53]
By the 1920s some quartets were including the fugue in programs.[54] Since then, the fugue has grown greatly in the eyes of musicians and performers. "The Great Fugue... now seems to me the most perfect miracle in music," said Igor Stravinsky.[55] "... It is also the most absolutely contemporary piece of music I know, and contemporary forever... Hardly birthmarked by its age, the Great Fugue is, in rhythm alone, more subtle than any music of my own century... I love it beyond everything." Pianist Glenn Gould said, "for me, the 'Grosse Fuge' is not only the greatest work Beethoven ever wrote but just about the most astonishing piece in musical literature."[56]
Some analysts and musicians see the fugue as a first assault on the diatonic tonal system that prevailed in Classical music. Robert Kahn sees the main subject of the fugue as a precursor of the tone row,[57] the basis of the atonal system developed by Arnold Schoenberg. "Your cradle was Beethoven’s Grosse Fuge," artist Oskar Kokoschka wrote to Schoenberg in a letter.[58] Composer Alfred Schnittke quotes the subject in his third string quartet. There have also been numerous orchestral arrangements of the fugue, including by conductor Wilhelm Furtwängler, and by Felix Weingartner.
Performance
Performers approaching the Große Fuge face a host of technical and musical challenges. Among the technical difficulties of the piece are difficult passagework, complex cross-rhythms that require exact synchronization, and problems of intonation, where the harmonies pass from dissonance to resolution.[59]
Once mastering the technical difficulties, there are many interpretive issues to resolve.[60] The first of these is: in what context to play the fugue? As the finale of Opus 130, as it was originally written, or as a separate piece?[61] Playing the fugue as the final movement of Opus 130, rather than the light, Haydnesque replacement movement, completely changes the character of the quartet, note analysts Robert Winter and Robert Martin[62] Played with the new finale, the preceding movement, the "Cavatina", a heartfelt and intense aria, is the emotional center of the piece. Played with the fugue as the finale, the Cavatina is a prelude to the massive and compelling fugue. On the other hand, the fugue stands alone well. "Current taste is decisively in favor of the fugal finale," conclude Winter and Martin.[63] A number of quartets have recorded Opus 130 with the fugue and the replacement finale on separate disks.
A second issue facing performers is whether to choose a "learned" interpretation – one that clarifies the complex contrapuntal structure of the piece – or one that focuses primarily on the dramatic impulses of the music.[64] "Beethoven had taken a form that is basically an intellectual form, where the emotions take second place, compared to the structure, and he has completely turned that around, writing one of the most emotionally charged pieces ever," says Sara Bitloch of the Elias Quartet.[65] "As a performer that's a particularly difficult balance to find ... Our first approach was to find a kind of hierarchy in the themes... but we found that when we do that we're really missing the point of the piece."
After deciding on the overall approach to the music, there are numerous local decisions to be made about how to play particular passages.[66] Perhaps the most notable of these issues concerns the peculiar notation that Beethoven uses in the syncopated presentation of the main subject – first in the overtura, but later, throughout the piece. Rather than writing this as a series of quarter notes, he writes two tied eighth notes.[67]
What did Beethoven mean by this? Many musicologists have tried to explain this: David Levy has written an entire article on the notation,[68] and Stephen Husarik looked to the history of Baroque ornamentation for an explanation.[69] Performers have interpreted it in various ways. The Alban Berg Quartet plays the notes almost as a single note, but with an emphasis on the first eighth note to create a subtle differentiation. Eugene Drucker of the Emerson quartet plays this as two distinct eighth notes. Mark Steinberg of the Brentano quartet sometimes joins the eighth notes, and sometimes separates them, marking the difference by playing the first eighth without vibrato, then adding vibrato for the second eighth note.
| "Interpreting the eighth note notation" | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Arrangement for piano four-hands

In early 1826, the publisher of the Op. 130 String Quartet, Mathias Artaria, told Beethoven there were "many requests" for a piano four-hand arrangement of the Große Fuge.[73] This was well before any discussion of separating the fugue from the main body of the quartet. Artaria asked Beethoven to prepare the arrangement, but Beethoven wasn't interested, so Artaria instead asked Anton Halm to prepare it. Beethoven was not satisfied with Halm's work and subsequently made his own note-for-note arrangement of the quartet. Beethoven's arrangement was completed subsequent to the C♯ minor String Quartet, Op. 131 and was published by Artaria as Op. 134.[74]
Rediscovery of manuscript
In July 2005 an authentic 1826 Beethoven manuscript titled "Grande Tugue [sic] á quatre mains" was found[75][76] by a librarian at the Palmer Theological Seminary in Wynnewood, Pennsylvania. The manuscript was authenticated by Dr. Jeffrey Kallberg at the University of Pennsylvania and by Dr. Stephen Roe, head of Sotheby's Manuscript Department. This was the four-hand piano arrangement of the Große Fuge, Op. 134. The manuscript had been missing for 115 years. It was auctioned by Sotheby's Auction House on 1 December 2005; it was bought for GBP 1.12 million (USD 1.95 million) by a then-unknown purchaser, who has since revealed himself to be Bruce Kovner, a publicity-shy multi-billionaire who donated the manuscript—along with 139 other original and rare pieces of music—to the Juilliard School of Music in February 2006. It has since become available in their online manuscript collection.[77] The manuscript's known provenance is that it was listed in an 1890 catalogue and sold at an auction in Berlin to a Cincinnati, Ohio industrialist, whose daughter gave it and other manuscripts including a Mozart Fantasia to a church in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in 1952. It is not known how the Beethoven manuscript came to be in the possession of the library.
Notes
- ↑ Solomon (2003), p. page=35
- ↑ Stravinsky and Craft (1963), p. 24.
- ↑ B.H. Haggin, quoted in Chamber Music Northwest
- ↑ Kinderman (1997), p. 306
- ↑ Levy (2007), p. 130
- ↑ Steinhardt, in Miller (2006), p. 40
- ↑ Kerman (1979), p. 279
- ↑ Matthews, David (September 2006). "Form-Compelling". London Review of Books. 28:18: 28. For a discussion of the technical and musical difficulties of the fugue, see Große Fuge#Performance below.
- ↑ Alexander Wheelock Thayer: Ludwig van Beethovens Leben. quoted in Husarik (2012), p. 54.
- ↑ The fugue is 741 measures long; the total number of measures in the other movements is 643.
- ↑ Solomon (2003), p. 35
- ↑ Service (2008)
- ↑ Solomon (1977) p. 447
- ↑ Thayer' Ludwig van Beethovens Leben. quoted in Solomon (1977), p. 449
- ↑ For the differing opinions on this, see Solomon (1977), p. 449, Marliave (1928), p. 257, Winter and Martin (1994), p. 239.
- ↑ Bitloch (2012)
- ↑ Lockwood (2006), pp. 459–461
- ↑ Kirkendale (1963)
- ↑ Rosen (1972), Levy (2008)
- ↑ Radcliffe (1978)
- ↑ Husarik (2012)
- ↑ Husarik (2012)
- ↑ Husarik, p. 255
- ↑ Kirkendale, p. 18.
- ↑ Kerman (2008), p. 167.
- ↑ quoted in Husarik (2015)
- ↑ This analysis is based on the analysis by Vincent d'Indy, as transcribed by Joseph de Marliave (1923), pp. 293–295. The D'Indy analysis is considered the classic analysis.
- ↑ Musical examples are from the recording of the Fugue by the Merel quartet (Mary Ellen Woodside and Julia Schröder, Violins, Ylvali Zilliacus, Viola' Rafael Rosenfeld, Cello), live in performance at Tonhalle Zürich, 3/7/2013.
- ↑ Kerman (1979), p. 287
- ↑ See, for example, Kinderman (1995) or Kirkendale (1963)
- ↑ Ratner (1995), p. 288
- ↑ See Kinderman (1995) or Kirkendale (1963)
- ↑ Kerman (1979), p. 283
- ↑ Kirkendale, p. 21.
- ↑ Husarik (2016)
- ↑ D'Indy in Cobbett (1929), p. 104.
- ↑ Winter and Martin (1994), pp. 243–4
- ↑ Most analysts consider this unison the beginning of the coda, though Beethoven himself, in the autograph copy, writes "Coda" at bar 493 (key change to B♭).
- ↑ Levy (2007)
- ↑ For a summary of attempts at understanding the fugue, see Kirkendale, pp 14 - 18.
- ↑ Ratner (1995). Ratner attributes this quote to J.W.N. Sullivan's book Beethoven: His Spiritual Development (1927), however, the quote (a paraphrase from John Milton's Paradise Lost) does not appear in Sullivan.
- ↑ For a review of the divergent opinions on the fugue, see also Kirkendale, pp 14 - 18.
- ↑ Kahn (2010)
- ↑ Chua (1995), p. 240
- ↑ Husarik (2012), p. 58
- ↑ Kahn (2010)
- ↑ Bitloch (2012)
- ↑ Steinhardt, in Miller (2006), p. 40
- ↑ Sylvia Plath, Collected Poems (1981) Turtleback Books
- ↑ Mark Doty, "Grosse Fuge" in Atlantis (1995) Harper Perennial, ISBN 0-06-095106-0
- ↑ Winter and Martin (1994), p. 239
- ↑ de Marliave (1928), p. 220
- ↑ Kerman (1979), p. 294
- ↑ Winter and Martin (1994), p. 239
- ↑ Kirkendale, p.14.
- ↑ Page, p. 459
- ↑ Kahn (2010), p. 155
- ↑ Brand and Hailey p. 3
- ↑ For a description of some of the technical difficulties of the piece, see Rehearsal Notes at IMSLP, or David Blum, The Art of Quartet Playing(1987, Cornell Paperbacks, ISBN 0-8014-9456-7), pp 71, 73.
- ↑ For a discussion of some of the musical issues posed by the fugue, see Blum (1987), pp. 22, 59, 70, 71, 73, 158, 159, 164-165, 172, and 222.
- ↑ For further discussion of this see Solomon (1978) p. 448, Blum (1987), p 159, Griffiths (1983), p. 106.
- ↑ Winter and Martin (1994), p. 238. The word "Haydnesque" it theirs.
- ↑ Winter and Martin (1994), p. 238.
- ↑ Bitloch. Also see Arnold Steinhardt in Miller (2006), p. 40, Blum (1987), p. 164.
- ↑ Bitloch
- ↑ For discussion of specific interpretive issues in the fugue, see also Blum (1987, pp. 59, 70, 71, 73, 164-165, Rehearsal Notes (IMSLP), Winter and Martin (1994), pp. 239-244.
- ↑ Grosse Fuge, International edition, measures 26 - 30.
- ↑ Levy (2007)
- ↑ Husarik, Speck. p. 261. Husarik contends that the slur suggests a dissonant Baroque vocal figure known as "trilletto" which is removed and redistributed to another voice part at the end of Grosse Fuge in order to resolve long term dissonance.
- ↑ Alban Berg Quartet (Gunter Pichler, violin, Gerhard Schulz, violin, Thomas Kakuska, viola, Valentin Erben, cello), Recorded live at the Mozart-Saal, Konzerthaus, Wien, June 11, 1989
- ↑ Emerson Quartet (Eugene Drucker, violin, Philip Setzer, violin, Lawrence Dutton, viola, Paul Watkins, cello), from their album "LUDWIG VAN BEETHOVEN: The Late String Quartets" (Deutche Gramaphon, 02 May 2003)
- ↑ Brentano Quartet (Mark Steinberg, violin, Serena Canin, violin, Misha Amory, viola, Nina Lee, cello), recorded live in concert, Princeton University, April 2012
- ↑ Solomon (1977), p. 449. Considering the unpopularity of the piece, Solomon speculates that this was a ploy to convince Beethoven to separate the fugue from the rest of op. 130.
- ↑ Cooper (2008), p. 364
- ↑ Wakin (2005)
- ↑ CBC article (2005)
- ↑ "The Julliard Manuscript Collection".
References
Scores:
- Große Fuge, Op.133: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project
- First published edition of the fugue was by Matthias Artaria, 1825, available at IMSLP. The fugue was republished by Breitkopf and Hartel in 1866 in Ludwig van Beethoven's Werke Series 6 . Urtext editions are published by Henle and by Universal.
- Manuscript of the piano four-hand transcription by Beethoven is in the Juilliard Manuscript collection, viewable online at http://www.juilliardmanuscriptcollection.org/.
Books:
- Blum, David (1987). The Art of Quartet Playing. Cornell University Press. ISBN 0-8014-9456-7.
- Brand, Juliane; Hailey, Christopher (1997). Constructive Dissonance: Arnold Schoenberg and the Transformations of Twentieth-century Culture. University of California Press. ISBN 0520203143.
- Cooper, Barry (2008). Beethoven. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0195313314. Retrieved 3 July 2013.
- de Marliave, Joseph (1961) [1928]. Beethoven's Quartets. Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-20694-7.
- Kahn, Robert S (2010). Beethoven and the Grosse Fuge: Music, Meaning and Beethovens Most Difficult Work. Scarecrow Press Inc. ISBN 978-0-8108-7418-3.
- Kerman, Joseph (1979). The Beethoven quartets. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-00909-5. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
- Kinderman, William (1995). Beethoven. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-08796-5. Retrieved 25 December 2010.
- Lockwood, Lewis (2005). Beethoven: the music and the life. W. W. Norton. ISBN 978-0-393-32638-3. Retrieved 25 December 2010.
- Miller, Lucy (2006). Adams to Zemlinsky. Concert Artists Guild. ISBN 1-892862-09-3.
- Page, Tim (1990). Glenn Gould Reader. Vintage. ISBN 0679731350.
- Radcliffe, Philip (1978). Beethoven's string quartets. CUP Archive. ISBN 978-0-521-29326-6. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
- Ratner, Leonard G. (1995). The Beethoven String Quartets: Compositional Strategies and Rhetoric. Stanford Book Store. ISBN 1 887 98100 4.
- Rosen, Charles (1971). The Classical Style: Haydn, Mozart, Beethoven. Faber and Faber. ISBN 0 571 04916 8.
- Solomon, Maynard (1978). Beethoven. Granada Publishing. ISBN 0-586-05189-9.
- Solomon, Maynard (2003). Late Beethoven: music, thought, imagination. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-23746-9. Retrieved 25 December 2010.
- Speck, Christian (2016). The String Quartet: From the Private to the Public Sphere. Brepols. ISBN 978-2-503-56800-3.
- Stowell, Robert, editor (2003). The Cambridge Companion to the String Quartet. Cambridge Companions to Music. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-80194-X.
- Stravinsky, Igor; Craft, Robert (1963). Dialogues and a Diary. Doubleday.
- Winter, Robert; Martin, Robert, eds. (1994). The Beethoven Quartet Companion. University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-20420-4.
Journals and other sources:
- "String Quartet in B-Flat Major, Op. 130, with Grosse Fuge, Op. 133". Chamber Music Northwest. Retrieved 2014-05-21.
- Service, Tom (28 July 2008). "The Proms: What will they make of Beethoven?". The Guardian. Retrieved 2014-06-06.
- Levy, David B. ""Ma però beschleunigend": Notation and Meaning in Ops.133/134". Beethoven Forum. 20 (2): 129–149. Retrieved 2014-05-18.
- Husarik, Stephen. "Musical direction and the wedge in Beethoven's high comedy, Grosse Fuge op. 133". The Musical Times. Autumn 2012: 53–66.
- Matthews, David. "Form Compelling". London Review of Books. 28 (18): 27–29.
- Husarik, Stephen (2016). "Gluck's Theme and the Surrender of Ornamentation to the Countersubjects in Beethoven's Grosse Fuge, op. 133". In Speck, Christian. The String Quartet from the Private to the Public Sphere. pp. 251–261.
- Bitloch, Sara. "Elias String Quartet, Beethoven Op 130 & 133: an insight by Sara Bitloch". Retrieved 2014-05-19.
- Kirkendale, Warren. "The 'Great Fugue' Op.133: Beethoven's 'Art of Fugue'". Acta Musicologica. 35: 14–24. doi:10.2307/931606.
- d'Indy, Vincent (1929). "Beethoven". Cobbett's Cyclopedic Survey of Chamber Music.
- Daniel J. Wakin (2005-10-13). "A Historic Discovery, in Beethoven's Own Hand". The New York Times. Retrieved 2007-10-11.
- "Handwritten Beethoven score resurfaces". Canada: CBC. 2005-10-13. Retrieved 2007-10-11.
- "Rehearsal Notes". Canada: IMSLP. 2006. Retrieved 2016-10-22.
External links
- Alex Ross at "Great Fugue: Secrets of a Beethoven manuscript", originally published in The New Yorker, 6 February 2006
- Brødrene Gahl og jakten på Beethovenkoden, the film about die Große Fuge by the Oslo String Quartet
- Große Fuge, Op.133, Große Fuge for Piano Duet, Op.134: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project
- Große Fuge, animated graphical score with motivic material indicated on YouTube
- Beethoven's String Quartet Op. 130, with the Grosse Fuge as the final movement, performed by the Orion String Quartet