Gum depigmentation
| Gum depigmentation | |
|---|---|
| Intervention |
Gum depigmentation, also known as gum bleaching, is a procedure used in cosmetic dentistry to lighten or remove black spots or patches on the gums caused by melanin. Discolouration may also be caused by long-term use of certain medications. The procedure itself can involve surgical, or laser ablation techniques.[1]
Laser gum depigmentation
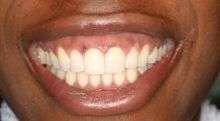
Gums before
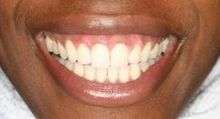
Gums after
Melanocytes are cells which reside in the basal layer of the gingival epithelium. These cells produce melanin, which are pigments that cause discoloration or dark spots in gums. A dental laser can target and ablate the melanocytes, thus reducing the production of melanin in the gingival tissue. Following laser depigmentation, the gingiva heals by secondary intention. This results in a lighter and more uniform color of the gums.
See also
References
- ↑ Lin, YH; Tu, YK; Lu, CT; Chung, WC; Huang, CF; Huang, MS; Lu, HK (2014). "Systematic review of treatment modalities for gingival depigmentation: a random-effects poisson regression analysis.". Journal of esthetic and restorative dentistry : official publication of the American Academy of Esthetic Dentistry ... [et al.] 26 (3): 162–78. PMID 24418367.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 12/4/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.