Hexaphenylbenzene
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2,3,4,5,6-hexa(phenyl)benzene | |
| Identifiers | |
| 992-04-1 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 63611 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.356 |
| PubChem | 70432 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C42H30 | |
| Molar mass | 534.6876 |
| Melting point | 454 to 456 °C (849 to 853 °F; 727 to 729 K)[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
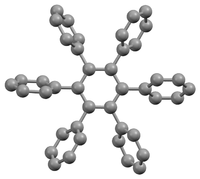
Hexaphenylbenzene is an aromatic compound composed of a benzene ring substituted with six phenyl rings.
It may be prepared through a Diels-Alder reaction by refluxing tetraphenylcyclopentadienone and diphenylacetylene in benzophenone or other high-temperature solvent.[1]
Structure
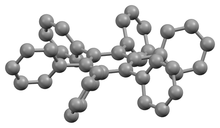
Due to steric congestion among the phenyl rings, the stable conformation of this molecule has the phenyl rings rotated out of the plane of the central benzene ring. In the crystalline form shown on the left, the molecule forms a propeller-like conformation in which the phenyl rings are rotated about 65°,[2] while in the gas phase, they are perpendicular with some slight oscillations.[3]
Hexaarylbenzenes
Compounds belonging to the wider class of hexaarylbenzenes are of some scientific interest [4]
References
- 1 2 Louis Fieser (1973). "Hexaphenylbenzene". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol., 5, p. 604
- 1 2 Bart, J. C. J. (1968). "The crystal structure of a modification of hexaphenylbenzene". Acta Crystallographica Section B. 24 (10): 1277. doi:10.1107/S0567740868004176.
- ↑ Gust, D. (1977). "Restricted Rotation in Hexaarylbenzenes". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 99 (21): 6980–6982. doi:10.1021/ja00463a034.
- ↑ Hexaarylbenzene: Evolution of Properties and Applications of Multitalented Scaffold Varun Vij, Vandana Bhalla, and Manoj Kumar Chemical Reviews Article ASAP 2016 doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00144

