Equine influenza
| Influenza (Flu) |
|---|
 |
| Types |
| Vaccines |
| Treatment |
| Pandemics |
| Outbreaks |
| See also |
Equine influenza (horse flu) is the disease caused by strains of influenza A that are enzootic in horse species. Equine influenza occurs globally, previously caused by two main strains of virus: equine-1 (H7N7) and equine-2 (H3N8).[1] The OIE now considers H7N7 strains likely to be extinct since these stains have not been isolated for over 20 years.[2] Predominant international circulating H3N8 strains are Florida sublineage of the American lineage; clade 1 predominates in the Americas and clade 2 in Europe. (Elton and Cullinane, 2013; Paillot, 2014; Slater et al., 2013).The disease has a nearly 100% infection rate in an unvaccinated horse population with no prior exposure to the virus.[3]
While equine influenza is historically not known to affect humans, impacts of past outbreaks have been devastating due to the economic reliance on horses for communication (postal service), military (cavalry), and general transportation. In modern times, though, the ramifications of equine influenza are most clear in the horse-racing industry.
Clinical Signs
Equine influenza is characterized by a very high rate of transmission among horses, and has a relatively short incubation time of one to three days.[4] Clinical signs of equine influenza include fever (up to 106°F [41.1°C]), nasal discharge, have a dry, hacking cough, depression, loss of appetite and weakness.[4] Secondary infections may include pneumonia.[5] Horses that are mildly affected will recover within 2-3 weeks, however, it may take up to 6 months for recovery for severely affected horses.[4] Horses that become immune may not show sings but will still shed the virus. [6]
An 1872 report on equine influenza describes the disease as:
"An epizootic specific fever of a very debilitating type, with inflammation of the respiratory mucous membrane, and less frequently of other organs, having an average duration of ten to fifteen days, and not conferring immunity from a second attack in subsequent epizootics."— James Law, Report of the Commissioner of Agriculture for the year 1872[7]
Causes
Equine influenza is caused by several strains of the influenza A virus endemic to horses. Viruses that cause equine influenza were first isolated in 1956. The equine-1 virus affects heart muscle, while the equine-2 virus is much more severe and systemic.[8] The virus is spread by infected, coughing horses in addition to contaminated buckets, brushes, tack and other stable equipment. The influenza virus causing symptoms by replicating within respiratory epithelial cells, resulting in destruction of tracheal and bronchial epithelium and cilia.[4]
Treatment
When a horse contracts the equine influenza virus, rest and supportive care is advised so that complications do not occur. Veterinarians recommend at least one week of rest for every day that the fever persists with a minimum of three days rest. This allows the damaged mucocilliary apparatus to regenerate. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are administered if the fever reaches greater than 104°F (40°C). If complications occur, such as the onset of pneumonia, or if the fever last more than 3-4 days, antibiotics are often administered.[4]
Prevention
Prevention of equine influenza outbreaks is maintained through vaccines and hygiene procedures.[4] Isolation of horses for two weeks is common practice when they are being moved to a new environment.
Vaccines
Vaccines (ATCvet codes: QI05AA01 (WHO) inactivated, QI05AD02 (WHO) live, plus various combinations) are a major defense against the disease. Vaccination schedules generally require a primary course of vaccines, followed by booster shots. It is recommended that horses be vaccinated against equine influenza annually, and competition horses that travel frequently be given a booster every six months as they are at higher risk of contracting the virus.[9] Foals are initially vaccinated at six months of age with a booster 3-6 weeks later and again between 10-12 months.[4] Standard schedules may not maintain absolutely foolproof levels of protection, and more frequent administration is advised in high-risk situations.[10]
Equine influenza virus (EIV) undergoes continuous antigenic drift, and vaccine protection from immunogenic stimulation is maximised when vaccines strains have greater homogeneity to circulating strains. Subclinically affected vaccinated horses can shed live virus and represent a threat to unvaccinated or inappropriately vaccinated horses. Neutralising immunity leading to an absence of infection is rare. (Paillot, 2014). An OIE expert surveillance panel annually assesses circulating strains and makes relevant vaccine recommendations.
The UK requires horses participating in show events be vaccinated against equine flu, and a vaccination card must be produced; the International Federation for Equestrian Sports requires vaccination every six months.[11] [12]
History
A comprehensive report describing the disease - compiled in response to the 1872 outbreak of the disease in North America - provided a thorough examination of the history of the disease.[7]
Early records
The report notes putative cases dating as far back as Hippocrates and Livius. Absyrtus, a Greek veterinarian from 330 CE, described a disease in the horse population having the general characters of influenza, which the report mentions as the earliest clear record of equine influenza in the lower animals.
The report notes the next recorded equine influenza case in 1299, the same year that a catarrhal epidemic affected Europe. Spanish records noted cases in which "The horse carried his head drooping, would eat nothing, ran from the eyes, and there was hurried beating of the flanks. The malady was epidemic, and in that year one thousand horses died."
Prevalence of influenza is found in historic records in the centuries of the Middle Ages, but direct implication of horses is not always clear. Neither are recorded instances of record deaths among horses and other animals clear on the exact cause of death.[7]
1872 North American outbreak
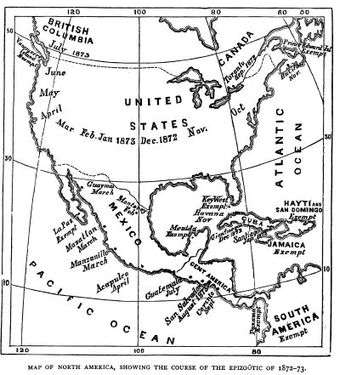
An epizootic outbreak of equine influenza during 1872 in North America became known as "The Great Epizootic of 1872". The outbreak is known as the "most destructive recorded episode of equine influenza in history".[14] In 1870, three-fourths of Americans lived in rural areas (towns under 2500 population, and farms). Horse and mule power was used for moving wagons and carriages, and pulling plows and farm equipment. The census of 1870 counted 7.1 million horses and 1.1 million mules, as well as 39 million humans.[15] With most urban horses and mules incapacitated for a week or two, humans used wheelbarrows and pulled the wagons. About 1% of the animals died, and the rest fully recovered.[16]
The first cases of the disease were reported from Ontario, Canada. By October 1, 1872, the first case occurred in Toronto. All the street car horses and major livery stables were affected within only three days. By the middle of October, the disease had reached Montreal, Detroit, and New England. On October 25, 1872, The New York Times reported on the extent of the outbreak, claiming that nearly all public stables in the city had been affected, and that the majority of the horses owned in the private sector had essentially been rendered useless to their owners.[17] Only days later, the Times went on to report that 95% of all horses in Rochester, New York, had been affected, while the disease was also making its way quickly through the state of Maine and had already affected all fire horses in the city of Providence, Rhode Island.[18][19]
On October 30, 1872, The New York Times reported that a complete suspension of travel had been noted in the state. The same report also took note of massive freight backups being caused by the lack of transportation ability that was arising as a result of the outbreak.[20] Cities such as Buffalo and New York were left without effective ways to move merchandise through the streets, and even the Erie Canal was left with boats full of goods idling in its waters because they were pulled by horses.[21] By November, many states were reporting cases. The street railway industry ground to a halt in late 1872.[22]
Boston was hard hit by a major fire downtown on November 9 as firemen pulled the necessary firefighting equipment by hand. The city commission investigating the fire found that fire crews' response times were delayed by only a matter of minutes. The city then began to buy steam-powered equipment.[23]
In New York, 7,000 of the city's approximately 11,000 horses fell ill, and mortality rates ranged between 1.0% and 10%.[24] Many horses were unable to stand in their stalls. Those that could stand coughed violently and were too weak to pull any loads or support riders. The vast majority of affected horses – save for those 10% that died as a result – were back to full health by the following spring.[25]
2004 United States outbreak
The equine influenza virus H3N8 caused an influenza outbreak in dogs in the United States.[26]
2007 Australian outbreak
Australia had remained free of equine influenza until an outbreak in August 2007 when 10, 651 horses were infected over a period of three months. The cost to eradicate the disease was estimated at $1 billion and eventually the virus was successfully contained and Australia has returned to its equine influenza-free status.[26] However, the outbreak had significant effects on the country's horse-racing industry.
See also
References
- ↑ "Equine Influenza". www.aaep.org. Retrieved 2016-12-04.
- ↑ Paillot, Romain (2014). "A Systematic Review of Recent Advances in Equine Influenza Vaccination". Vaccines. 2 (2): 797–831.
- ↑ "About of Equine influenza | Definition of Equine influenza - Viral Infections Blog Articles". viralinfections.info. Retrieved 2016-12-04.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Equine Influenza: Respiratory Diseases of Horses: Merck Veterinary Manual". www.merckvetmanual.com. Retrieved 2016-12-04.
- ↑ "Flu Virus in Horses | petMD". Retrieved 2016-12-04.
- ↑ "Equine Influenza". www.aaep.org. Retrieved 2016-12-04.
- 1 2 3 Report of the Commissioner of Agriculture for the year 1872]
- ↑ Primerdesign Ltd. "Equine/Canine Influenza" (PDF). Retrieved December 4, 2016.
- ↑ "Equine Influenza". www.aaep.org. Retrieved 2016-12-04.
- ↑ equiflunet_vaccines
- ↑ UAE Equestrian & Racing Federation
- ↑ FEI guidelines
- ↑ from Judson (1873) p 105
- ↑ Running Like Wildfire - A Study of the most destructive recorded episode of equine influenza in history.
- ↑ see "Changes in the Horse Industry"
- ↑ James P. McClure, "The epizootic of 1872: Horses and disease in a nation in motion." New York History (1998) 79#1 pp: 4-22.
- ↑ "The Horse Plague: Fifteen Thousand Horses in this City Unfit for Use." The New York Times [New York] 25 Oct. 1872:
- ↑ “The Horse Distemper: Further Increase of the Epidemic in this City” The New York Times 26 Oct. 1872:
- ↑ Adoniram B. Judson, "History and Course of the Epizoötic among Horses upon the North American Continent in 1872-73." Public health papers and reports 1 (1873): 88-109 online
- ↑ "The Horse Plague: Fifteen Thousand Horses in this City Unfit for Use." The New York Times 25 Oct. 1872
- ↑ "The Terrible Horse Disease." The New York Times 30 Oct. 1872:
- ↑ Brian J. Cudahy, Cash, Tokens, and Transfers: A History of Urban Mass Transit in North America (1990) pp 14-15
- ↑ Ballard C. Campbell, ed. American Disasters: 201 Calamities That Shook the Nation (2008) pp 131-32
- ↑ McClure, "The epizootic of 1872: Horses and disease in a nation in motion."
- ↑ Judson, "History and Course of the Epizoötic among Horses upon the North American Continent in 1872-73."
- 1 2 http://www.oie.int/doc/ged/D14001.PDF
Further reading
- Campbell, Ballard C. ed. American Disasters: 201 Calamities That Shook the Nation (2008) pp 131–32
- Judson, Adoniram B. "History and Course of the Epizoötic among Horses upon the North American Continent in 1872-73." Public health papers and reports 1 (1873): 88-109 online
- Law, James/ "Equine Influenza Epidemic" from Commissioner of Agriculture: 1872 Annual Report (Washington, 1872) online
- McClure, James P. "The epizootic of 1872: Horses and disease in a nation in motion." New York History (1998) 79#1 pp: 4-22.
External links
- health24.com
- Equi Flu Net
- EI Vaccination Debate - Australia equinetrader.co.nz
- COntrolling Equine Influenza - Japan equinetrader.co.nz
- Great Epizootic of 1872 equinetrader.co.nz
- Caring for a horse with equine influenza Horsetalk.co.nz (NZ)
- Equine flu resources: Q&A, latest news, contacts Horsetalk.co.nz (NZ)
- Veterinary Record
- Equine Quarterly Disease Surveillance Reports
- Horse Flu
- Great Epizootic of 1872 ravaged the horse population - Pantagraph (Bloomington, Illinois newspaper)