Intze principle
The Intze Principle (German: Intze-Prinzip) is a name given to two engineering principles, both named after the hydraulic engineer, Otto Intze, (1843–1904). In the one case, the Intze Principle relates to a type of water tower; in the other, a type of dam.
Intze Principle for water towers

A water tower built in accordance with the Intze Principle has a brick shaft on which the water tank sits. The base of the tank is fixed with a ring anchor (Ringanker) made of iron or steel, so that only vertical, not horizontal, forces are transmitted to the tower. Due to the lack of horizontal forces the tower shaft does not need to be quite as solidly built.[1] This type of design was used in Germany between 1885 and 1905.
- Water tanks designed on the Intze Principle
-
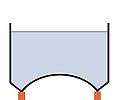
Intze 1 tank
-
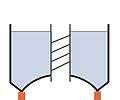
Intze 1 tank with inside cylinder
-
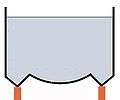
Intze 2 tank
Intze Principle for dams
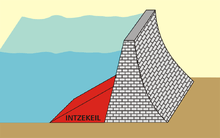
The method of dam construction invented by Otto Intze was used in Germany at the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th centuries. A dam built on the Intze Principle has the following features:
- it is a gravity dam with an almost triangular cross-section
- the wall is made of rubble stone with a high proportion of mortar
- it has a curved ground plan
- it has facing brickwork (Vorsatzmauerwerk or Verblendung) on the upper part of the upstream side
- it has an earth embankment against the lower part of the upstream side, the so-called Intze Wedge (Intze-Keil)[2]
- it has a cement-sealed upstream face, coated with a layer of bitumen or tar
- it has internal vertical drainage using clay pipes behind the upstream face
See also
References
- ↑ "zagermann.de - Wassertürme: Bauformen". zagermann.de. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
- ↑ "Ruhrverband: Technische Angaben". ruhrverband.de. Retrieved 9 March 2015.
External links
- Otto Intze and water tower construction
- Otto Intze and dam construction
- Intze tanks at wassertuerme.gmxhome.de