Japanese passport
| Japanese passport | |
|---|---|
|
The front cover of a contemporary 10 years Japanese ePassport. | |
 Identity Information Page of a contemporary 5 years Japanese ePassport. | |
| Issued by |
|
| Type of document | Passport |
| Purpose | Identification |
| Eligibility requirements | Japanese citizenship |
| Expiration | 10 years or 5 years after acquisition for adults, 5 for ages under 19 |
Japanese passports are issued to Japanese citizens to travel outside Japan.
Types of passports
- Ordinary passport: Issued to normal Japanese citizens.
- Ordinary passports are issued in two different lengths of validity: five and ten years. Japanese citizens up to 19 years of age can only be issued a five-year passport, while those who are 20 years of age or older can choose either a five-year (blue) or ten-year (red) passport for different registration fees.
- Official passport: Issued to members of the National Diet and public servants.
- Diplomatic passport: Issued to members of the Imperial Family, diplomats and their family members, and high-level government officials.
- By convention, the Emperor and Empress of Japan do not hold a passport.
All Japanese passports issued after March 20, 2006 are biometric passports.
Physical appearance


Japanese passports have the Imperial Seal of Japan inscribed in the center of the front cover, with the Japanese characters reading Nipponkoku Ryoken (日本国旅券) inscribed above in seal script and its English translation JAPAN PASSPORT in Latin letters below the Seal. Ordinary passports valid for five years are in dark blue, and those valid for ten years are in crimson in color. Additionally, official passports are in dark green, and diplomatic passports in dark brown.
Identity information page
- Photograph of passport holder
- Type
- Issuing country
- Passport number
- Surname
- Given name
- Nationality
- Date of birth
- Sex
- Registered Domicile
- Date of issue
- Date of expiry
- Issuing authority
- Signature of bearer
Also, beneath these is the machine readable zone.
Passport note
The passports contain a note from the issuing country that is addressed to the authorities of all other countries, identifying the bearer as a citizen of that country and requesting that he or she be allowed to pass and be treated according to international norms. The note inside of Japanese passports states:
In Japanese:
- 日本国民である本旅券の所持人を通路故障なく旅行させ、かつ、同人に必要な保護扶助を与えられるよう、関係の諸官に要請する。
In English:
- The Minister for Foreign Affairs of Japan requests all those whom it may concern to allow the bearer, a Japanese national, to pass freely and without hindrance and, in case of need, to afford him or her every possible aid and protection.
Language
Japanese passports are entirely printed in both Japanese and English, except for the note of caution that is found at the end of the passport (e.g. on page 51 of the ten-year biometric ordinary passport), which is only printed in Japanese. This note contains information about what the bearer should know when encountering various situations in a foreign country.
The surname, given name and other personalized mentions (like registered domicile) are only indicated in Latin uppercase letters. Japanese names are in principle transcribed according to the Hepburn romanization system, but exceptions are admitted in certain cases, notably when the name is the katakana transcription of a foreign name (Japanese spouse or Japanese child of a foreigner), in which case the original spelling of the name in the Latin alphabet may be used, only if you submit the official document with the original spelling issued by the government (passport etc.).
The signature may be written in any language and in any spelling the individual desires.
Visa requirements
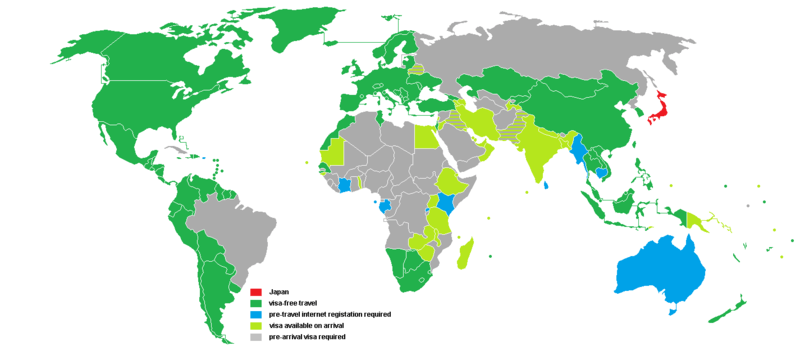
In 2016, Japanese citizens had visa-free or visa on arrival access to 173 countries and territories, ranking the Japanese passport 5th in the world according to the Visa Restrictions Index.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Passports of Japan. |