List of public art in Hyde Park, London
This is a list of public art in Hyde Park, London.
A Royal Park since 1536, Hyde Park covers an area of over 350 acres.[1] Its present landscaping dates largely to the 18th century, when Queen Caroline introduced the Serpentine among other features, and to the 1820s, when Decimus Burton made improvements including the park’s triumphal entrance at Wellington Arch.[2] This was originally crowned with a colossal equestrian statue of the Duke of Wellington, removed later in the 19th century. In the immediate vicinity of the arch, at Hyde Park Corner, there is a high concentration of military memorials;[3] this has been called "one of the world's most important groups of war memorials".[4]
| Image | Title / subject | Location and coordinates |
Date | Artist / designer | Architect / other | Type | Designation | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 More images |
Wellington Monument |
Off Park Lane 51°30′16″N 0°09′10″W / 51.5045°N 0.1527°W |
1822 | Westmacott, RichardRichard Westmacott | N/A | Statue | Grade I | Unveiled 18 June 1822. Wellington is represented symbolically by the hero Achilles, although the head is said to be modelled on the Duke’s.[5] The statue, partly inspired by the classical sculptures of the Dioscuri on the Quirinal Hill in Rome, was cast from captured French cannon.[6] The first public nude statue in London since antiquity.[5] |
 |
Dell Megalith | The Dell, Hyde Park 51°30′16″N 0°09′33″W / 51.5044°N 0.1592°W |
1861 | Thomas, JohnJohn Thomas | N/A | Former drinking fountain | N/A | The remains of a drinking fountain originally formed of several large blocks of granite, possibly quarried at Moorswater, Cornwall. This became defunct in 1887 and only a single stone was still standing by 1900.[7] |
_in_the_rose_garden%2C_Hyde_Park_Corner%2C_London_(3794419310).jpg) More images |
Boy and Dolphin | Rose Garden, South Carriage Drive 51°30′13″N 0°09′17″W / 51.5036°N 0.1546°W |
1863 | Munro, AlexanderAlexander Munro | N/A | Fountain with sculpture | Grade II | Moved in 1962 from Hyde Park to the Broad Walk, Regent’s Park. Returned to Hyde Park in 1994, in a different location from its original setting.[8] |
 |
Conduit House Memorial | Serpentine Road 51°30′18″N 0°09′34″W / 51.505°N 0.1595°W |
1871 | ? | N/A | Urn on plinth | Grade II | Marks the site of a conduit house which supplied the precinct of Westminster with water until the spring was cut off by drainage works in 1861. The building was demolished in 1868.[9] |
 More images |
Byron, George Gordon Byron, 6th BaronGeorge Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron | Achilles Way traffic island, Park Lane 51°30′15″N 0°09′06″W / 51.5043°N 0.1518°W |
1880 | Richard Claude Belt (Q19899493) | N/A | Statue | Grade II | Unveiled 24 May 1880. Inspired by a line from Childe Harold's Pilgrimage (1812–18): "To sit on rocks and muse o’er flood and fell". Byron is depicted with his Newfoundland dog, Bo’sun. The marble pedestal, supplied by the Greek government, was added in 1882.[10] |
 More images |
Wellington, Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke ofArthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington | Hyde Park Corner 51°30′10″N 0°09′05″W / 51.5029°N 0.1514°W |
1888 | Boehm, Joseph EdgarJoseph Edgar Boehm | Ince, HowardHoward Ince | Equestrian statue | Grade II | Unveiled 21 December 1888. The pedestal is flanked by four soldiers representing the four nations of the United Kingdom. Alfred Gilbert, an assistant in Boehm’s studio, claimed to have modelled the horse.[11] |
 More images |
Diana | Rose Garden, South Carriage Drive 51°30′14″N 0°09′19″W / 51.5038°N 0.1553°W |
1899 | Gleichen, Lady FeodoraLady Feodora Gleichen | N/A | Fountain with sculpture | Grade II | Made for the garden of Sir Walter Palmer’s house Frognal, in Ascot, Berkshire; presented to Hyde Park by Lady Jean Palmer in 1906.[12] |
 More images |
Peace | Wellington Arch, Hyde Park Corner 51°30′09″N 0°09′03″W / 51.5025°N 0.1508°W |
1908–12 | Jones, AdrianAdrian Jones | Burton, DecimusDecimus Burton | Quadriga | Grade I | Unveiled 2 April 1912.[13] Burton originally intended for a quadriga to surmount his arch, but in 1845 an equestrian statue of Wellington was installed in its place. This was removed to Aldershot when the arch’s orientation was changed in 1883. Edward VII commissioned the present group, but did not live to see its completion.[14] |
 More images |
Memorial to the Cavalry of the Empire | Serpentine Road 51°30′17″N 0°09′19″W / 51.5047°N 0.1553°W |
1924 | Jones, AdrianAdrian Jones | Burnet, John JamesJohn James Burnet | Equestrian sculpture with stone screen | Grade II* | Unveiled 21 May 1924[15] at Stanhope Gate; moved in 1961 for the widening of Park Lane.[5] The armour was based on that of the fifteenth-century effigy of the Earl of Warwick at St Mary’s, Warwick, the horse’s furniture on that found in Dürer’s engraving of Saint George.[15] |
 More images |
Machine Gun Corps Memorial (David) | Hyde Park Corner 51°30′12″N 0°09′03″W / 51.5032°N 0.1508°W |
1925 | Wood, Francis DerwentFrancis Derwent Wood | N/A | Memorial with sculpture | Grade II* | Unveiled 10 May 1925 by the Duke of Connaught. Re-erected on current location in 1962. The second bronze model for the figure stood in Chelsea Embankment Gardens from 1963 until it was stolen in the 1970s; it has been replaced by a replica.[16] |
 |
Memorial to William Henry Hudson | West Carriage Drive 51°30′30″N 0°10′08″W / 51.5082°N 0.169°W |
1925 | Epstein, JacobJacob Epstein | Gill, EricEric Gill (lettering) | Stone screen with relief sculpture | Grade II | Unveiled 19 May 1925 by Stanley Baldwin.[17] Located near the Bird Sanctuary erected in Hudson’s memory, the memorial depicts the bird-spirit Rima, a character from his novel Green Mansions (1904). A controversial early work by Epstein which was dubbed "the Hyde Park Atrocity" by its detractors.[18] |
 More images |
Royal Artillery Memorial | Hyde Park Corner 51°30′09″N 0°09′07″W / 51.5025°N 0.1519°W |
1925 | Jagger, Charles SargeantCharles Sargeant Jagger | Pearson, LionelLionel Pearson | Memorial with sculpture | Grade I | Unveiled 18 October 1925 by the Duke of Connaught. The regiment demanded a "realistic" memorial and got one, crowned with a howitzer rendered in stone. The figure of a dead soldier shrouded in a greatcoat was still, however, found to be unsettling.[19] |
| |
Memorial to George Lansbury | Hyde Park Lido Pavilion 51°30′17″N 0°10′10″W / 51.5046°N 0.1694°W |
1953 | Harold Wilson Parker (Q20639672) | N/A | Plaque | N/A | Lansbury established the Hyde Park Lido in 1930.[1] The plaque in his honour was installed as part of the post-War reconstruction of the Lido Pavilion.[20] |
 |
Mosaics | Marble Arch pedestrian subway 51°30′46″N 0°09′35″W / 51.5129°N 0.1598°W |
1962 | Mitchell, WilliamWilliam Mitchell | N/A | Mosaics | N/A | Mitchell was chosen for this commission by the architect Sir Frederick Gibberd, with whom he had collaborated previously. The murals use a combination of traditional and experimental mosaic techniques. Another set of mosaics which was part of the same redevelopment scheme, at Hyde Park Corner, has been removed.[21] |
 |
Four Winds Fountain | Hyde Park, near Park Lane 51°30′29″N 0°09′25″W / 51.508°N 0.157°W |
1963 | Thomas Bayliss Huxley-Jones (Q20639660) | N/A | Fountain with sculptural group | N/A | Unveiled 25 June 1963; the site was formerly occupied by Munro’s Boy and Dolphin (see above). Originally titled Joy of Life, this was the last commission of the Constance Fund. The fountain basins were redesigned and the work’s name changed in 2000–1.[22] |
| |
Little Nell | Patte d’oie north of east end of Serpentine, Serpentine Road[23] 51°30′19″N 0°09′19″W / 51.5054°N 0.1554°W |
1975 (after an original of 1896) | after William Robert Colton | N/A | Fountain with sculpture | Grade II | A replica in artificial stone of a lost Art Nouveau original, described as depicting a "winged child with fish".[7] The name "Little Nell" has apparently only been attached to the work more recently;[24] it has also been referred to variously as the "Colton Memorial" and the "Mermaid Fountain".[25] |
 More images |
Norwegian War Memorial | Hyde Park, west of Ranger’s Lodge 51°30′23″N 0°10′05″W / 51.5064°N 0.1681°W |
1978 | ? | N/A | Commemorative stone mounted on three smaller stones | N/A | A large Precambrian boulder mounted on three smaller stones. Presented by the Norwegian Navy and Merchant Fleet in thanks for Britain’s support in World War II.[26] |
 More images |
Holocaust Memorial | Hyde Park, east of the Dell 51°30′15″N 0°09′32″W / 51.5043°N 0.1589°W |
1983 | Badger, MarkMark Badger | Richard Seifert; Derek Lovejoy and Partners | Commemorative stones | N/A | Unveiled 28 June 1983; the first public memorial in Britain to victims of the Holocaust.[27] The largest boulder bears an inscription from Lamentations (3:48) in Hebrew and English: FOR THESE I WEEP/ STREAMS OF TEARS FLOW/ FROM MY EYES/ BECAUSE OF THE DESTRUCTION/ OF MY PEOPLE. |
 |
Household Cavalry Memorial | South Carriage Drive 51°30′11″N 0°09′21″W / 51.5031°N 0.1559°W |
1985 | ? | N/A | Raised slate floor plaque in hedge enclosure | N/A | Commemorates the four soldiers of the Blues and Royals regiment who were killed in the IRA bombing of 20 July 1982 near this spot.[7] The horses killed by the bomb are commemorated by a water trough, which was moved from the Victoria Embankment to Hyde Park in 1985 to serve as a memorial.[28] |
 More images |
Queen Caroline Memorial Caroline of Ansbach |
Hyde Park, west of the Dell, overlooking the Serpentine 51°30′15″N 0°09′37″W / 51.5041°N 0.1602°W |
1990 | ? | N/A | Urn on plinth | N/A | Unveiled in 1990 by Queen Elizabeth II. Inscribed To the memory of/ QUEEN CAROLINE/ wife of George II/ for whom/ the Long Water/ and Serpentine/ were created/ between/ 1727–1731.[29] |
 More images |
Queen Elizabeth Gate | Hyde Park 51°30′15″N 0°09′08″W / 51.5041°N 0.1523°W |
1993 | Wynne, DavidDavid Wynne | Lund, GiuseppeGiuseppe Lund | Gates | N/A | Unveiled 6 July 1993 by Queen Elizabeth II.[30] Lund intended for the gates to be "feminine and fresh with the charm of an English garden", in contrast to their formal and "masculine" setting. There was much public criticism of the design.[31] |
 More images |
Tile murals | Hyde Park Corner pedestrian subway | 1995 | FreeForm Arts Trust | N/A | Tile murals | N/A | 900 m² of murals depicting the history of the area, painted by a team of six artists led by Alan Rossiter.[32] |
 More images |
Reformers’ Tree
The Reform League |
Hyde Park 51°30′33″N 0°09′41″W / 51.5091°N 0.1613°W |
2001 | Gray, HarryHarry Gray | Flint, RozRoz Flint | Mosaic | N/A | Unveiled in July 2000 by Tony Benn.[33] Depicts a tree near this site which burnt down during the Reform League Riots in 1866, the stump of which became a notice board for political demonstrations.[5] |
| More images |
Australian War Memorial | Hyde Park Corner 51°30′08″N 0°09′05″W / 51.5021°N 0.1515°W |
2003 | Laurence, JanetJanet Laurence | Tonkin Zulaikha Greer Architects | Stone screen | N/A | A curving granite wall inscribed with the names of 24,000 Australian towns and villages and of battles in both World Wars. Water runs down parts of the wall and slabs up against it bear the country’s coat of arms and military badges.[34] |
| More images |
Diana, Princess of Wales Memorial Fountain Diana, Princess of Wales |
Hyde Park, near West Carriage Drive and Rotten Row 51°30′17″N 0°10′17″W / 51.5046°N 0.1715°W |
2004 | Gustafson, KathrynKathryn Gustafson | N/A | Fountain | N/A | Unveiled 6 July 2004 by Queen Elizabeth II.[35] A low, granite oval, 210 metres in circumference, with water coursing along it.[5] The fountain was plagued by blockages and injuries and had to be closed off twice for repairs in its first two years.[35] |
 More images |
Animals in War Memorial | Park Lane 51°30′40″N 0°09′26″W / 51.5111°N 0.1572°W |
2004 | Backhouse, DavidDavid Backhouse | N/A | Stone screens with sculptures | N/A | Unveiled 24 November 2004 by Princess Anne. Two heavily laden mules are shown trudging towards an opening between two swelling Portland stone screens; beyond lies a grass mound with a cavorting horse and dog.[36] |
 More images |
New Zealand War Memorial | Hyde Park Corner 51°30′11″N 0°09′01″W / 51.5031°N 0.1504°W |
2006 | Dibble, PaulPaul Dibble | Hardwick-Smith, JohnJohn Hardwick-Smith | Stelae | N/A | Unveiled 11 November 2006 by Queen Elizabeth II. Consists of 16 bronze X beams (or "standards"), six of which are arranged in the shape of the Southern Cross constellation.[37] |
 More images |
7 July Memorial | Hyde Park, near Park Lane 51°30′21″N 0°09′10″W / 51.5059°N 0.1528°W |
2009 | N/A | Carmody Groarke Architects et al. | Stelae | N/A | Unveiled 7 July 2009 by the Prince of Wales and Duchess of Cornwall, on the fourth anniversary of the terrorist bombings. The 52 victims are commemorated by stainless steel stelae.[38] |
| More images |
Isis | Hyde Park, near West Carriage Drive, overlooking the Serpentine 51°30′19″N 0°10′18″W / 51.5052°N 0.1716°W |
2009 | Gudgeon, SimonSimon Gudgeon | N/A | Sculpture | N/A | Unveiled 7 September 2009. 1,000 plaques around the base were sold to donors for personalised inscriptions at £1,000 each,[39] as a way of funding the park’s Isis Education Centre for introducing young people to the study of nature. Donated to the park by the Halcyon Gallery.[40] |
| More images |
Freeman Family Drinking Fountain | North Carriage Drive, near Marble Arch 51°30′43″N 0°09′45″W / 51.512°N 0.1625°W |
2009 | Harber, DavidDavid Harber | N/A | Drinking fountain | N/A | Unveiled 23 September 2009.[41] A stainless steel sphere decorated with petals of oxidised bronze.[42] Donated to the park by Michael Freeman, a property developer and trustee of the Royal Parks Foundation, and his wife.[43] |
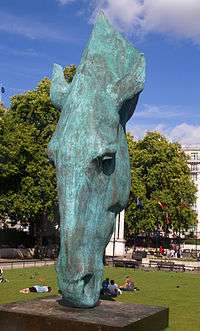 More images |
Still Water | Marble Arch 51°30′46″N 0°09′35″W / 51.5129°N 0.1596°W |
2010 | Fiddian-Green, NicNic Fiddian-Green | N/A | Sculpture | N/A | Unveiled 14 September 2010. The largest freestanding bronze sculpture in London at 33 ft high. Replaces a previous version temporarily installed on this site; commissioned by Sir Anthony Bamford and his wife, it is now on their estate in Daylesford, Gloucestershire.[44] |
References
- 1 2 "History and Architecture". The Royal Parks. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ↑ "Landscape History". The Royal Parks. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ↑ Kershman 2013, p. 271
- ↑ Historic England. "The Cavalry Memorial (1278118)". National Heritage List for England.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Monuments in Hyde Park". The Royal Parks. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ↑ Historic England. "The Achilles Statue (off Park Lane to North of Hyde Park Corner Screen) (1231393)". National Heritage List for England.
- 1 2 3 Land Use Consultants 2014, p. 48
- ↑ Historic England. "The Boy and Dolphin Fountain, Rose Garden, Hyde Park (1251181)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 20 November 2013.
- ↑ Historic England. "Westminster Precinct Conduit House Memorial at North Head of the Dell (1356753)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 20 November 2013.
- ↑ Ward-Jackson 2011, pp. 181–82
- ↑ Ward-Jackson 2011, pp. 88–91
- ↑ Garrihy, Andrea (2004). "Gleichen, Lady Feodora Georgina Maud (1861–1922)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 6 January 2013. (subscription required (help)).
- ↑ Ward-Jackson 2011, p. 92
- ↑ "A history of the Quadriga, Wellington Arch". Rupert Harris Conservation. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- 1 2 "Adrian Jones (1845–1938), sculptor and artist". Your Archives. The National Archives. Retrieved 6 January 2010.
- ↑ Ward-Jackson 2011, pp. 94–96
- ↑ Williamson, Philip; Baldwin, Edward, eds. (2004). Baldwin Papers: A conservative statesman 1908–1947. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 172. ISBN 9780521580809. Retrieved 10 November 2011.
- ↑ "Epstein, Sir Jacob (1880–1959) Knight sculptor". Your Archives. The National Archives. Retrieved 20 February 2012.
- ↑ Ward-Jackson 2011, pp. 96–100
- ↑ Land Use Consultants 2014, p. 49
- ↑ Pereira, Dawn (2012). "William Mitchell and the London County Council: the evolution of a classless form of public art". Sculpture Journal. 21 (1): 57–70. doi:10.3828/sj.2012.5. Retrieved 6 November 2014. (subscription required (help)).
- ↑ Ward-Jackson 2011, pp. 85–87
- ↑ Land Use Consultants 2014, p. 12
- ↑ Speel, Bob. "William Robert Colton (1867–1921)". Retrieved 13 July 2014.
- ↑ "Memorial Fountain (1896), Hyde Park, London, by William Robert Colton RA". The Victorian Web. Retrieved 23 July 2014.
- ↑ "Norwegian War Memorial". The Royal Parks. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ↑ "Garden in London's Hyde Park is Britain's Holocaust Memorial". Jewish Telegraphic Agency. 28 June 1983. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- ↑ "Fountain: Hyde Park bomb—the horses". London Remembers. Retrieved 20 July 2014.
- ↑ "Queen Caroline memorial". London Remembers. Retrieved 1 February 2015.
- ↑ Ward-Jackson 2011, p. 87
- ↑ "[Buildings and Monuments in the Royal Parks]" (PDF). Jones Morris Graphic Design. p. 44. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ↑ Pearson, Lynn; Dennis, Richard (2005). "Tile Gazetteer—
Westminster" . Tiles & Architectural Ceramics Society. Retrieved 17 August 2014. - ↑ "Annual Report and Accounts 2000–2001" (PDF). The Royal Parks. p. 9. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ↑ Ward-Jackson 2011, pp. 100–01
- 1 2 "Timeline: Diana memorial fountain". BBC News. 2 November 2005. Retrieved 3 September 2012.
- ↑ Ward-Jackson 2011, pp. 185–86
- ↑ Ward-Jackson 2011, pp. 101–04
- ↑ "7 July Memorial". The Royal Parks. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ↑ Ibrahim, Magda (8 September 2009). "Isis sculpture unveiled in London's Hyde Park". Horticulture Week. Retrieved 15 April 2013.
- ↑ "Isis". The Royal Parks Foundation. Retrieved 28 October 2012.
- ↑ Low, Valentine (24 September 2009). "£30,000 Hyde Park fountain aims to sink bottled water craze". Polaris Institute. Archived from the original on 2 December 2011. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ↑ "Freeman Family Drinking Fountain". Royal Parks Foundation. Retrieved 15 April 2013.
- ↑ "Michael Freeman". The Royal Parks Foundation. Retrieved 15 April 2013.
- ↑ "Tallest Free-Standing Bronze in London to Be Installed on Tuesday". ArtDaily. Retrieved 7 April 2013.
Bibliography
- Kershman, Andrew (2013), London’s Monuments, London: Metro Publications
- Land Use Consultants (2014), Hyde Park Management Plan (PDF), The Royal Parks, retrieved 6 July 2014
- Ward-Jackson, Philip (2011), Public Sculpture of Historic Westminster: Volume 1, Public Sculpture of Britain, Liverpool: Liverpool University Press
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/24/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.