Local hidden variable theory
The term "hidden variable theory" is used in the interpretation of quantum mechanics. It refers to all types of the theory that attempt to account for the probabilistic features of quantum mechanics by the mechanism of underlying inaccessible variables. A local hidden variable theory has the added requirement of being consistent with local realism, requiring that distant events be independent, ruling out instantaneous (i.e. faster-than-light) interactions between separate events.
The mathematical implications of a local hidden variable theory in regard to the phenomenon of quantum entanglement were explored by physicist John S Bell. Bell's 1964 paper (see Bell's theorem) showed that local hidden variables of certain type cannot reproduce the quantum measurement correlations that quantum mechanics predicts.
The theory of quantum entanglement predicts that separated particles can briefly share common properties and respond to certain types of measurement as if they were a single particle. In particular, a measurement on one particle in one place can alter the probability distribution for the outcomes of a measurement on the other particle at a different location. If a measurement setting in one location instantaneously modifies the probability distribution that applies at a distant location, then local hidden variables are ruled out. For an expanded description, see Bell's theorem.
A series of experiments, called Bell test experiments, have provided partial experimental confirmation of the entanglement phenomenon, but local hidden variable theory can still explain the probabilistic nature of quantum measurement due to loopholes in experimental Bell tests.
Local hidden variables and the Bell tests
Bell's theorem starts with the implication of the principle of local realism: That separated measurement processes are independent. Based on this premise, the probability of a coincidence between separated measurements of particles with correlated (e.g. identical or opposite) orientation properties can be written:
-
(1)
where is the probability of detection of particle with hidden variable by detector , set in direction , and similarly is the probability at detector , set in direction , for particle , sharing the same value of . The source is assumed to produce particles in the state with probability .
Using (1), various Bell inequalities can be derived, these inequalities provide limits on the possible behaviour of local hidden variable models.
When John Bell originally derived his inequality, it was in relation to pairs of entangled spin-1/2 particles, every one of those emitted being detected. Bell showed that when detectors are rotated with respect to each other, local realist models must yield a correlation curve that is bounded by a straight line between maxima (detectors aligned), whereas the quantum correlation curve is a cosine relationship.
The first Bell test experiments were not performed with spin 1/2 particles, and were performed with photons which have spin 1. A classical local hidden variable prediction for photons, based on Maxwell's equations, yields a cosine curve but of reduced amplitude such that the curve still lies within the straight-line limits specified in the original Bell inequality.
Note that while a great variety of realist models could be proposed, they cannot be arbitrary because they must still yield results consistent with classical experiments, as in the example with photons, where the model must still yield Malus' Law.
Bell's theorem assumes that measurement settings are completely independent, and not in principle determined by the universe at large. If this assumption were to be incorrect, as proposed in superdeterminism, conclusions drawn from Bell's theorem may be invalidated. The theorem also relies on very efficient and space-like separated measurements, not yet satisfied simultaneously experimentally. Such flaws are generally called loopholes.
Bell tests with no "non-detections"
Consider, for example, David Bohm's thought-experiment (Bohm, 1951), in which a molecule breaks into two atoms with opposite spins. Assume this spin can be represented by a real vector, pointing in any direction. It will be the "hidden variable" in our model. Taking it to be a unit vector, all possible values of the hidden variable are represented by all points on the surface of a unit sphere.
Suppose the spin is to be measured in the direction a. Then the natural assumption, given that all atoms are detected, is that all atoms the projection of whose spin in the direction a is positive will be detected as spin up (coded as +1) while all whose projection is negative will be detected as spin down (coded as −1). The surface of the sphere will be divided into two regions, one for +1, one for −1, separated by a great circle in the plane perpendicular to a. Assuming for convenience that a is horizontal, corresponding to the angle a with respect to some suitable reference direction, the dividing circle will be in a vertical plane. So far we have modelled side A of our experiment.
Now to model side B. Assume that b too is horizontal, corresponding to the angle b. There will be second great circle drawn on the same sphere, to one side of which we have +1, the other −1 for particle B. The circle will be again in a vertical plane.
The two circles divide the surface of the sphere into four regions. The type of "coincidence" (++, −−, +− or −+) observed for any given pair of particles is determined by the region within which their hidden variable falls. Assuming the source to be "rotationally invariant" (to produce all possible states λ with equal probability), the probability of a given type of coincidence will clearly be proportional to the corresponding area, and these areas will vary linearly with the angle between a and b. (To see this, think of an orange and its segments. The area of peel corresponding to a number n of segments is roughly proportional to n. More accurately, it is proportional to the angle subtended at the centre.)
The formula (1) above has not been used explicitly — it is hardly relevant when, as here, the situation is fully deterministic. The problem could be reformulated in terms of the functions in the formula, with ρ constant and the probability functions step functions. The principle behind (1) has in fact been used, but purely intuitively.

Thus the local hidden variable prediction for the probability of coincidence is proportional to the angle (b − a) between the detector settings. The quantum correlation is defined to be the expectation value of the sum of the individual outcomes, and this is
- (2) E = P++ + P−− − P+− − P−+
where P++ is the probability of a '+' outcome on both sides, P+− that of a + on side A, a '−' on side B, etc..
Since each individual term varies linearly with the difference (b − a), so does their sum.
The result is shown in fig. 1.
Optical Bell tests
In almost all real applications of Bell's inequalities, the particles used have been photons. It is not necessarily assumed that the photons are particle-like. They may be just short pulses of classical light (Clauser, 1978). It is not assumed that every single one is detected. Instead the hidden variable set at the source is taken to determine only the probability of a given outcome, the actual individual outcomes being partly determined by other hidden variables local to the analyser and detector. It is assumed that these other hidden variables are independent on the two sides of the experiment (Clauser, 1974; Bell, 1971).
In this stochastic model, in contrast to the above deterministic case, we do need equation (1) to find the local realist prediction for coincidences. It is necessary first to make some assumption regarding the functions and , the usual one being that these are both cosine-squares, in line with Malus' Law. Assuming the hidden variable to be polarisation direction (parallel on the two sides in real applications, not orthogonal), equation (1) becomes:
- (3) , where .
The predicted quantum correlation can be derived from this and is shown in fig. 2.
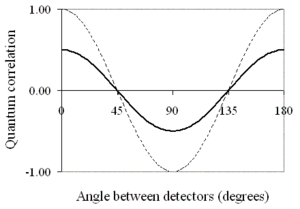
In optical tests, incidentally, it is not certain that the quantum correlation is well-defined. Under a classical model of light, a single photon can go partly into the + channel, partly into the − one, resulting in the possibility of simultaneous detections in both. Though experiments such as Grangier et al.'s (Grangier, 1986) have shown that this probability is very low, it is not logical to assume that it is actually zero. The definition of quantum correlation is adapted to the idea that outcomes will always be +1, −1 or 0. There is no obvious way of including any other possibility, which is one of the reasons why Clauser and Horne's 1974 Bell test, using single-channel polarisers, should be used instead of the CHSH Bell test. The CH74 inequality concerns just probabilities of detection, not quantum correlations.
Generalizations of the models
By varying the assumed probability and density functions in equation (1) we can arrive at a considerable variety of local realist predictions.
Time effects
Previously some new hypotheses were conjectured concerning the role of time in constructing hidden variables theory. One approach is suggested by K. Hess and W. Philipp (Hess, 2002) and discusses possible consequences of time dependences of hidden variables, previously not taken into account by Bell's theorem. This hypothesis has been criticized by R.D. Gill, G. Weihs, A. Zeilinger and M. Żukowski (Gill, 2002).
Another hypothesis suggests to review the notion of physical time (Kurakin, 2004). Hidden variables in this concept evolve in so called 'hidden time', not equivalent to physical time. Physical time relates to 'hidden time' by some 'sewing procedure'. This model stays physically non-local, though the locality is achieved in mathematical sense.
Optical models deviating from Malus' Law
If we make realistic (wave-based) assumptions regarding the behaviour of light on encountering polarisers and photodetectors, we find that we are not compelled to accept that the probability of detection will reflect Malus' Law exactly.
We might perhaps suppose the polarisers to be perfect, with output intensity of polariser A proportional to cos2(a − λ), but reject the quantum-mechanical assumption that the function relating this intensity to the probability of detection is a straight line through the origin. Real detectors, after all, have "dark counts" that are there even when the input intensity is zero, and become saturated when the intensity is very high. It is not possible for them to produce outputs in exact proportion to input intensity for all intensities.
By varying our assumptions, it seems possible that the realist prediction could approach the quantum-mechanical one within the limits of experimental error (Marshall, 1983), though clearly a compromise must be reached. We have to match both the behaviour of the individual light beam on passage through a polariser and the observed coincidence curves. The former would be expected to follow Malus' Law fairly closely, though experimental evidence here is not so easy to obtain. We are interested in the behaviour of very weak light and the law may be slightly different from that of stronger light.
References
- Bell, 1971: J. S. Bell, in Foundations of Quantum Mechanics, Proceedings of the International School of Physics “Enrico Fermi”, Course XLIX, B. d’Espagnat (Ed.) (Academic, New York, 1971), p. 171 and Appendix B. Pages 171-81 are reproduced as Ch. 4, pp 29–39, of J. S. Bell, Speakable and Unspeakable in Quantum Mechanics (Cambridge University Press 1987)
- Bohm, 1951: D. Bohm, Quantum Theory, Prentice-Hall 1951
- Clauser, 1974: J. F. Clauser and M. A. Horne, Experimental consequences of objective local theories, Physical Review D, 10, 526-35 (1974)
- Clauser, 1978: J. F. Clauser and A. Shimony, Bell’s theorem: experimental tests and implications, Reports on Progress in Physics 41, 1881 (1978)
- Gill, 2002: R.D. Gill, G. Weihs, A. Zeilinger and M. Żukowski, No time loophole in Bell's theorem; the Hess-Philipp model is non-local, quant-ph/0208187 (2002)
- Grangier, 1986: P. Grangier, G. Roger and A. Aspect, Experimental evidence for a photon anticorrelation effect on a beam splitter: a new light on single-photon interferences, Europhysics Letters 1, 173–179 (1986)
- Hess, 2002: K. Hess and W. Philipp, Europhys. Lett., 57:775 (2002)
- Kurakin, 2004: Pavel V. Kurakin, Hidden variables and hidden time in quantum theory, a preprint #33 by Keldysh Inst. of Appl. Math., Russian Academy of Sciences (2004)
- Marshall, 1983: T. W. Marshall, E. Santos and F. Selleri, Local Realism has not been Refuted by Atomic-Cascade Experiments, Physics Letters A, 98, 5–9 (1983)
- Shadbolt, 2012: P. J. Shadbolt, M. R. Verde, A. Peruzzo, A. Politi, A. Laing, M. Lobino, J. C. F. Matthews, M. G. Thompson, and J. L. O'Brien, Generating, manipulating and measuring entanglement and mixture with a reconfigurable photonic circuit, a preprint. Figure 5 highlights experimental data points inexplicable by local hidden variable theory.