Muhammad in the Bible
| Part of a series on |
| Muhammad |
|---|
|
Views |
|
Perspectives |
|
Related |
|
| Part of a series on the |
| Bible |
|---|
 |
|
Interpretation |
|
Perspectives |
|
|
Arguments that prophecies of Muhammad in the Bible presaged his birth, teachings, and death have formed part of Muslim tradition from the early history of Muhammad’s Ummah (Arabic: أُمَّـة, Community). Subsequent Muslim writers have expanded on these viewpoints and have argued that they can specifically identify references to Muhammad in the text of the Bible, being found both in the Jewish Tanakh and in the Christian New Testament. Several verses in the Qur'an, as well as several Hadiths, state that Muhammad is described in the Bible. The apocryphal Gospel of Barnabas, which explicitly mentions Muhammad, has also been identified as an ancient prediction about the Prophet, but is widely seen by Christian scholars as a fabrication from the Early Modern Age.
Some Muslim writers argue that expectations of forthcoming prophets existed within the Jewish community from before the lifetime of Jesus through to that of Muhammad, and that Muhammad was the final fulfillment of these expectations. Muslims venerate Jesus and other religious figures, such as Moses and David, as having laid the groundwork for Muhammad’s later efforts.
In terms of Christian perspectives, some notable figures such as John of Damascus and John Calvin have interpreted Muhammad in the context of Bible prophecy as being either the False Prophet or the Antichrist. However, many other Christian figures have taken alternate approaches. The Roman Catholic Church's viewpoint, as stated in the 1910 Catholic Encyclopedia, holds that "contradictory opinions have been expressed by scholars in the last three centuries" about Muhammad’s "moral character and sincerity" since "Many of these opinions are biased either by an extreme hatred of Islam and its founder or by an exaggerated admiration, coupled with a hatred of Christianity."[1]
Islamic view
Qur’an
| “ | And We have not sent you, [O Muhammad], except as a mercy to all the creation. | ” |
| — Qur'an 21:107 | ||
Several Qur’anic verses state that the coming of Muhammad was preached by the previous Prophets, and foretold in the original Jewish and the original Christian Scriptures. For example:
- Qur’an 3:81 says that the prophets of God bore witness of the Apostle Muhammad and believed in him:
Qur'an 3:81 And [recall, O People of the Scripture], when Allah took the covenant of the prophets, [saying], "Whatever I give you of the Scripture and wisdom and then there comes to you an Apostle confirming what is with you, you [must] believe in him and support him." [Allah] said, "Have you acknowledged and taken upon that My commitment?" They said, "We have acknowledged it." He said, "Then bear witness, and I am with you among the witnesses."
- Qur’an 46:10 was interpreted by some Muslim scholars to be a reference to Deuteronomy 18:18. The witness from among the Children of Israel is thought to be Moses, and the one like him is believed to be Muhammad:[2]
Qur’an 46:10 Say: Have you considered if it is from Allah, and you disbelieve in it, and a witness from among the Children of Israel has borne witness of one like him, so he believed, while you are big with pride? Surely Allah doesn't guide the wrongdoing people.[3]
- Qur’an 7:157 says that the mention of Muhammad can still be found in the Jewish and the Christian Scriptures[4][5] in spite of the Tahrif which is referred to in other verses in the Qur’an:
Qur’an 7:157 Those who follow the Apostle, the illiterate prophet, whom they find written in what they have of the Torah and the Gospel, who enjoins upon them what is right and forbids them what is wrong and makes lawful for them the good things and prohibits for them the evil and relieves them of their burden and the shackles which were upon them. So they who have believed in him, honored him, supported him and followed the light which was sent down with him - it is those who will be the successful.[6][7]
- Qur’an 61:6 says that Jesus brought Good News of an Apostle to come after him whose name Jesus praises:
Qur'an 61:6 And [mention] when Jesus, the son of Mary, said, "O children of Israel, indeed I am the apostle of Allah to you confirming what came before me of the Torah and bringing Good Tidings of an Apostle to come after me, whose name shall be Ahmad." But when he came to them with clear evidences, they said, "This is obvious magic."
- Qur’an 2:127-129 tells that Abraham and Ishmael supplicated to God, when they were raising the foundations of the Ka'aba, to send an Apostle from the children of Ishmael:
Qur'an 2:127 And [mention] when Abraham was raising the foundations of the House [the Ka'aba] and [with him] Ishmael, [saying], "Our Lord, accept [this] from us. Indeed You are the Hearing, the Knowing. 128 Our Lord, and make us Muslims [in submission] to You and from our descendants a Muslim nation [in submission] to You. And show us our rites and accept our repentance. Indeed, You are the Accepting of repentance, the Merciful. 129 Our Lord, and send among them an Apostle from themselves who will recite to them Your verses and teach them the Book and wisdom and purify them. Indeed, You are the Exalted in Might, the Wise."
Ahadith
It is narrated that a small group of Muhammad's companions said to him: "O Apostle of Allah, tell us about yourself." He answered them that he is the Servant of God, the Seal of the prophets, the Prayer of his forefather Abraham, and the Good News of Jesus."[8][9]
The books of Hadiths narrate the stories of many Jews and Christians who embraced Islam. Those converts like Ka'ab al-Ahbar, Abdullah ibn Salam, Salman the Persian, Waraka ibn Nawfal, Bahira the monk, Aṣḥama ibn Abjar, Safiyya bint Huyayy and others, reported that Muhammad was foretold in both the Jewish and the Christian Scriptures as the promised Prophet to come. Isaiah 42, where the Chosen Servant of God "the Light of the Gentiles" is being discussed, was probably the most common chapter referred to by those converts as a prophecy fulfilled by Muhammad.
Biblical verses alleged to be prophecies of Muhammad
Genesis, 49:10
The scepter shall not depart from Judah, Nor a lawgiver from between his feet, Until Shiloh comes; And to Him shall be the obedience of the people.— Genesis 49:10
This prophecy is often read in the light of Qur'an 3:81 as a prophecy of Muhammad.[10][11] Some writers, like David Benjamin, believe that the Hebrew word Shiloh is actually a distortion of the Hebrew word "Shaluh" which means "Apostle/Messenger/One to be sent" or of the Hebrew word "Shiluah" which means "Apostle of God".[12]
The Latin Vulgate also translates the word to "He ... that is to be sent",[13]
Deuteronomy, 18:18
18 I will raise up for them a prophet (Prophet) from among their brethren like you, and will put My words in his mouth; and he shall speak to them all that I command him. 19 And whoever will not hearken to My words which he shall speak in My name, I Myself will require it of him. 20 But the prophet who presumes to speak a word in My name which I have not commanded him to speak, or who speaks in the name of other gods, that same prophet shall die.— Deuteronomy 18:18-20
Samau'al al-Maghribi, a Jewish mathematician who converted to Islam, pointed to Deuteronomy 18:18 in his book Convincing the Jews as a prophecy fulfilled by Muhammad.[14] Samau'al argued in his book that since the children of Esau are described in Deuteronomy 2:4-6 [and in Numbers 20:14 as well] as the brethren of the children of Israel, the children of Ishmael can also be described the same way.[15]
The comparison between Moses and Muhammad is quite common in the Qur'an and the Islamic tradition. Ka'ab al-Ahbar said: "Verily God Most High divided His vision and His conversation between Muhammad and Moses. He spoke to Moses twice, and Muhammad saw Him twice."[16][17][note 1]
It is also reported in the books of hadiths that Muhammad declared before his companions that he and Ali are like Moses and Aaron.[23][24][25][26]
Some Muslim writers, like Muhammad Ali, interpreted Qur'an 46:10 as a reference to Deuteronomy 18:18. The witness from among the Children of Israel is thought to be Moses, and the one like him is believed to be Muhammad:[2]
The Qur’an (73:15) was also interpreted by some Muslim writers, like Fethullah Gülen, as a reference to Deuteronomy 18:18.[27][28] Similarly, Qur'an 53:3-4, where it has been stated that "Nor does he (Muhammad) speak of his own desire. It is but an Inspiration that is inspired [unto him]", was further interpreted by Muslim writers, as a reference to Deuteronomy 18:18[29]
John 1:20-21 was also cited by Muslims as a proof from the canonical gospels that Deuteronomy 18:18 is not a prophecy of the Christ[30]
Deuteronomy, 33:2
"He said,"The Lord came from Sinai and dawned from Seir upon us; he shone forth from Mount Paran; he came from the ten thousand of holy ones, with flaming fire at his right hand."
— Deuteronomy 33:2
Samau'al al-Maghribi referred to this verse also in his book as a prophecy of Muhammad. He said that Mount Sinai refers to Moses, Mount Seir "the Mount of Esau" refers to Jesus, and Mount Paran "the Mount of Ishmael" refers to Muhammad.[31]
some contemporary Muslim scholars have also pointed to the similarity between Deuteronomy 33:2 and Qur'an 95:1-3 where "the Fig and the Olive" refers to Jesus, "Mount Sinai" refers to Moses, and "Mecca" refers to Muhammad.[32]
The "ten thousand of holy ones" are thought to be the ten thousand. companions of Muhammad.[33]
Psalm, 45

The Psalm (45:1-17) is a prophecy and a song of praise for the king. Several Muslim writers raised the argument that it is describing no one other than Muhammad for the following reasons:[34][35]
- The beauty of the king: "You are the most excellent of men". [Psalm 45:2]
- The sword of the king and his glorious victories over his enemies: "Gird your sword on your side, you mighty one; clothe yourself with splendor and majesty. In your majesty ride forth victoriously in the cause of truth, humility and justice; let your right hand achieve awesome deeds. Let your sharp arrows pierce the hearts of the king's enemies; let the nations fall beneath your feet". [Psalm 45:3-5]
- Kings’ daughters [Ayesha, Hafsa and Safiyya] are among the honorable women of the king: "Daughters of kings are among your honored women" [Psalm 45:9]:
- King David addressing Safiyya bint Huyayy "his daughter" who married Muhammad: "Listen, daughter, and pay careful attention: Forget your people and your father's house. Let the king be enthralled by your beauty; honor him, for he is your lord." [Psalm 45:10-11]
- gifts sent by kings [Al-Muqawqis] to him: "The city of Tyre will come with a gift, people of wealth will seek your favor." [Psalm 45:12]
- His name is "the highly-praised one": "I will perpetuate your memory through all generations; therefore the nations will praise you for ever and ever." [Psalm 45:17]
Psalm, 110:1
A Psalm of David. The LORD said to my lord: "Sit at My right, Until I make thine enemies thy footstool."— Psalm 110:1
Several Muslim writers, like Afzal-ur-Rahman and David Benjamin Keldani, raised the argument that Psalm 110:1 is also a prophecy of Muhammad and his ascension to the Throne of God during the journey of al-Isra and al-Miraj.[36][37]
Song of Solomon, 5
His mouth is sweetness itself; he is altogether lovely. This is my beloved, this is my friend, daughters of Jerusalem.— Song of Songs, 5:16
The Hebrew word 'מַחֲמַדִּים' (consonant letters: m-ħ-m-d-y-m, read as meħmadim or maħammaddīm) appears once in the Hebrew Bible, in the Song of Songs (5:16), where it is translated into English as "altogether desirable" or "altogether lovely." The plural word meħmadim means 'delights' or 'pleasuring' in Hebrew. Some Muslim scholars treat this verse as a prophecy of the coming of Muhammad,[38]:139[39] though the basic, literal meaning of muħammad (Arabic: مُـحَـمَّـد, consonant letters: m-ħ-m-d) in Arabic is "One who is praised." Muslims including Zakir Naik claim that "In the Hebrew language im (Hebrew: ים) is added for respect"[40] (though there are few examples other than Elohim).
Isaiah, 29:12
And the book is delivered to him that is not learned, saying, Read this, I pray thee: and he saith, I am not learned.— Isaiah 29:12
Zakir Naik interprets this verse as a prophecy of Muhammad, as tradition says that when the Archangel Gabriel commanded Muhammad to read something, he replied "I am not learned."[40]
Isaiah, 40
The voice of one crying in the wilderness:"Prepare the way of the Lord; Make straight in the desert a highway for our God.
— Isaiah 40:3
Christians accept that this text as referring to John the Baptist, the cousin of Jesus, as he lived in the wilderness and prophesied about the coming of Jesus. The interpretation of Isaiah 40:3-5 as a prophecy of Muhammad is common among Muslims.[41][42] Ali Ünal cites Qur'an 1:6-7 which reads: "[1:6] Guide us to the straight path: [1:7] the path of those You have blessed; not of those who have incurred Your wrath, nor of those who have gone astray."[42]
Isaiah, 42

"Behold! My Servant, whom I uphold; My Elect One, in whom My soul delights! I have put My Spirit upon Him; He will bring forth justice to the Gentiles. 2 He shall not cry out, nor raise His voice, nor cause His voice to be heard in the street. 3 A bruised reed shall He not break, and smoking flax shall He not quench. In truth He shall bring forth justice. 4 He shall not fail nor be discouraged, till He has established justice in the earth; and the islands shall wait for His law."— Isaiah 42:1-4
Isaiah 42 is among the earliest and the most common prophecies referred to by Muslims. Since the time of Muhammad, Muslims believed that it was fulfilled by no one other than him.[43][44] The first verse begins with: "Behold my Servant, whom I uphold; mine Elect...". The Hebrew word which was translated to "whom I uphold" is "אתמך"(Atmc). This word never appears anywhere in the entire Bible except here. Muslim authors, pointing to the similarity between the writing of "אתמך"(Atmc) and the writing of "אחמד" which is the name Ahmad, suggested that an intended distortion might have been done by the scribes of Scripture in the first verse of this chapter in order to hide the name of the Chosen Servant of God which is "אחמד" (Ahmad). Muhammad is believed by Muslims to be the Chosen Servant of God and his Light, while Christians believe that Jesus was God, begotten of God, not the servant of God. Thus, some Muslim writers argue Christians have no right to call Isaiah 42 a prophecy of Jesus. Qur'an 3:159, Qur'an 9:128 and Qur'an 68:4 shed a light on the gentle character of Muhammad, and from the time they knew him, Muslims looked at Muhammad as the mercy sent by God to all the creation.[45] Among the ones who believed that Muhammad fulfilled Isaiah 42 was Ayeshah bint Abī Bakr "the wife of Muhammad",[43] 'Abd Allah ibn 'Amr ibn al-'As,[44] Ka'ab al-Ahbar, and Abdullah ibn Salam.
Sing unto the Lord a new song, and His praise from the ends of the earth, you who go down to the sea, and all that is therein, the islands, and the inhabitants thereof! 11 Let the wilderness and its cities lift up their voice, the villages that Kedar inhabits. Let the inhabitants of Sela sing, let them shout from the top of the mountains. 12 Let them give glory to the Lord, and declare His praise in the islands. 13 The Lord shall go forth like a mighty man; He shall stir up jealousy like a man of war: He shall cry, yea, roar; He shall prevail against His enemies.— Isaiah 42:10-13
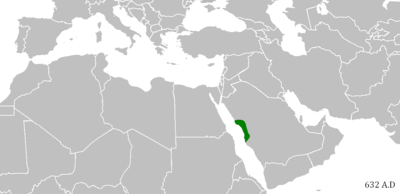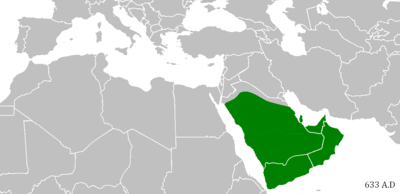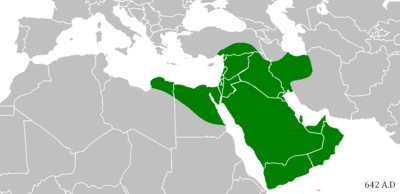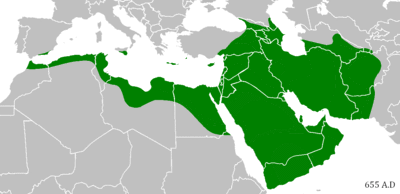
Isaiah 42:13 is believed to be a prophecy of the Muslim conquests.[46] "the new song" is often interpreted as a reference to the Arabic Qur'an or to the Adhan "the Islamic call to prayer".[47] The Islands could be a reference to Indonesia and Malaysia.[48]
The mention of Mount Sela‘ "the mountain of Medina" and the mention of Kedar "the forefather of Muhammad", in verse 11, is also considered by Muslims to be a proof.[46]
Isaiah, 54
"Sing, O barren, You who have not borne! Break forth into singing, and cry aloud,You who have not labored with child! For more are the children of the desolate than the children of the married woman," says the Lord.
— Isaiah 54:1
Muslim writers argue that the "barren one" refers to Mecca, since no prophet came from it before Muhammad. Rahmatullah Kairanawi argues in his book that "have not labored with child" means "haven't received a prophet".[50] They argue that the "desolate woman" refers to Hagar, and the "married woman" refers to Sarah.[51]
"Enlarge the place of your tent, stretch your tent curtains wide, do not hold back;lengthen your cords, strengthen your stakes.
For you will spread out to the right and to the left
— Isaiah 54:2-3
This passage is believed to be a prophecy of the Muslim conquests.[49]
Daniel, 7
Daniel 7 was discussed by various Muslim authors who identified the fourth beast in the vision as the Roman Empire.[52] The 10 horns which came from the Roman Empire were identified as the 10 Roman emperors who ran what is widely known in history as the 10 Major Persecutions:
- Nero.
- Domitian.
- Trajan.
- Marcus Aurelius.
- Septimius Severus.
- Maximinus.
- Decius.
- Valerian.
- Aurelian.
- Diocletian.[53]
The 11th horn was identified as the Roman emperor Constantine I and the Nicene Creed which was produced by him in order to change the law and time.[54] Consequently, the Nicene Christianity persecuted the followers of Jesus whom they called Arians for three centuries and a half [Daniel 7:25 says that the persecution will continue for a time, times and half a time] before the rise of the Kingdom of Islam.[55] "The One like the Son of man" in this vision is interpreted by Muslims as a prophecy of Muhammad and his ascension to the Throne of God.[56] The three horns which were subdued by the 11th horn are identified as the three Roman emperors Licinius, Maxentius and Maximian who were subdued by Constantine I.[57]
Some circulated opinions leaded Muslims to think that Mahoma is deformed by Paulus Alvarus from the word Maozim in the Latin Vulgate version of the Bible, the Book of Daniel (XI, 38) "Deum autem Maozim in loco suo venerabitur". Maozim has been related to the worship of a false god, then to the Antichrist.[58][59] This point has been discussed in Ahlam Sbaihat's investigation about prototypes and stereotypes related to the Prophet's name since the Greek era. In this paper, she discusses the possibility of missing words in the Latin manuscript of Alvarus of Cordoba that may lead to a misconception of the text: "why would the muezzins to safeguard such Maozim"? In addition, in the Old Greek Septuagint, then in Arabic and Hebrew translations the word Maozim is translated as "the God of forces".[60]
Habakkuk, 3:3
God will come from the south, and the holy one from mount Pharan: His glory covered the heavens, and the earth is full of his praise.— Habakkuk 3:3[61]
This prophecy is also commonly cited by Muslims as a prophecy of Muhammad. Since there is no connection between Jesus and Mount Paran "the Mount of Ishmael", Muslims argue that the "holy one" in this verse is Muhammad.[62] They often interpret the Coming of God from the south of Palestine as a reference to the cradle of Islam in the western coast of Arabia.[62]
Dead Sea Scrolls
These scrolls predict the coming of two messiahs. These two messiahs are referred to as a priestly messiah from the lineage of Aaron and a kingly messiah from the lineage of David.[63] The priestly messiah of Aaron is identified as Jesus son of Mary in the light of Qur'an 19:28 which says that Mary "the mother of Jesus" came from the lineage of Aaron. The kingly messiah is identified as Muhammad in the light of the gospel of Barnabas, Mark 12:35-37, Luke 20:41-44 and Matthew 22:42-46 which all assert that the coming messiah "the kingly messiah" is not going to be from the lineage of David. Margaret S. King argues, in Chapter 12 of her book "Unveiling The Messiah in the Dead Sea Scrolls", that the Jews were informed by the son of Mary that the kingly messiah whom they were expecting would come from the lineage of Ishmael.[64]
In canonical gospels
Parable of the Tenants
33 "Listen to another parable. There was a householder who planted a vineyard, made a fence round it, dug a wine-tank in it, and built a strong lodge; then let the place to vine-dressers, and went abroad.34 When vintage-time approached, he sent his servants to the vine-dressers to receive his share of the grapes;35 but the vine-dressers seized the servants, and one they cruelly beat, one they killed, one they pelted with stones.36 Again he sent another party of servants more numerous than the first; and these they treated in the same manner.37 Later still he sent to them his son, saying, "'They will respect my son.'38 "But the vine-dressers, when they saw the son, said to one another, "'Here is the heir: come, let us kill him and get his inheritance.'39 "So they seized him, dragged him out of the vineyard, and killed him.40 When then the owner of the vineyard comes, what will he do to those vine-dressers?" 41 "He will put the wretches to a wretched death," was the reply, "and will entrust the vineyard to other vine-dressers who will render the produce to him at the vintage season."42 "Have you never read in the Scriptures," said Jesus, "'The Stone which the builders rejected has been made the Cornerstone: this Cornerstone came from the Lord, and is wonderful (θαυμαστὴ) in our eyes'?
43 "That, I tell you, is the reason why the Kingdom of God will be taken away from you, and given to a nation that will exhibit the power of it. 44 He who falls on this stone will be severely hurt; but he on whom it falls will be utterly crushed." 45 After listening to His parables the High Priests and the Pharisees perceived that He was speaking about them; 46 but though they were eager to lay hands upon Him, they were afraid of the people, for by them He was regarded as a Prophet.
— Matthew 21:33-46 (Mark 12:1-12; Luke 20:9-18)[65]
Matthew (21:33-46) has been interpreted by Muslim authors like Kais as follows: The vineyard refers to the kingdom of God. The tenant farmers portray the people of Israel. The servants represent the prophets of God who were sent by him to them. However, the children of Israel used to reject many prophets and to kill many others, and when God sent to them his beloved servant Jesus, they intended to kill him too. For this reason, Jesus said to them that: "the kingdom of God will be taken away from them and given to a people who will produce its fruit [i.e. the nation of Muhammad]".[66]
Muslims read the Parable of the tenants in the light of the following Hadith:[67][68]
Narrated Abu Huraira:
Allah's Apostle said, "My similitude in comparison with the other prophets before me, is that of a man who has built a house nicely and beautifully, except for a place of one brick in a corner. The people go about it and wonder at its beauty, but say: 'Would that this brick be put in its place!' So I am that brick, and I am the Seal of the Prophets."[69]
The Qur'an addresses the Jews in many verses and blames them for killing the Prophets of God:
Qur'an 2:91 And when it is said to them, "Believe in what Allah has revealed," they say, "We believe [only] in what was revealed to us." And they disbelieve in what came after it, while it is the truth confirming that which is with them. Say, "Then why did you kill the prophets of Allah before, if you are [indeed] believers?"[70]
Qur'an 2:87 And We did certainly give Moses the Torah and followed up after him with apostles. And We gave Jesus, the son of Mary, clear proofs and supported him with the Holy Spirit. But is it [not] that every time an apostle came to you, [O Children of Israel], with what your souls did not desire, you were arrogant? And a party [of apostles] you denied and another party you killed.[71]
Christians argue that the stone the builders rejected was Jesus himself. However, some Muslim writers argue that Jesus was rejected by the tenants, not by the builders.[67][72]
Muslim writers like Sami Ameri argued that the Greek word for wonderful (θαυμαστὴ) in Matthew 21:42 and Mark 12:11 has a similar meaning to the Arabic word for Ahmad in Qur'an 61:6.[73] Sami cites "the New Testament Greek Lexicon - King James Version" which translates (θαυμαστὴ) to "worthy of pious admiration";[74] a meaning which is quite similar to the meaning of the Arabic words for Ahmad and Muhammad.[73]
Paraclete
John, 14:16-17: "And I will ask the Father, and he will give you another Helper, to be with you forever, even the Spirit of truth, whom the world cannot receive, because it neither sees him nor knows him. You know him, for he dwells with you and will be in you."
John, 15:26: "When the Advocate (Paraclete) is come whom I will send to you from the Father's presence--the Spirit of Truth who comes forth from the Father's presence--He will be a witness concerning me."[75]
John, 16:7: "Nevertheless, I tell you the truth; it is expedient for you that I go away: for if I go not away, the Comforter will not come unto you; but if I depart, I will send him unto you."[76]
John, 16:12-14: "I have yet many things to say unto you, but ye cannot bear them now. Howbeit when he, the Spirit of truth is come, he will guide you unto all truth: for he shall not speak of himself; but whatsoever he shall hear, that shall he speak: and he will shew you things to come. He shall glorify me."[77]
According to many Muslim scholars like Zakir Naik ``"Ahmed" or "Muhammad" meaning "the one who praises" or "the praised one" is almost the translation of the Greek word Periclytos. In the Gospel of John 14:16, 15:26, and 16:7. The word 'Comforter' is used in the English translation for the Greek word Paracletos which means advocate or a kind friend rather than a comforter. Paracletos is the warped reading for Periclytos.
Some Christians say that the Comforter mentioned in these prophecies refers to the Holy Sprit. Another interpretation is that the prophecy says that only if Jesus departs will the Comforter come. The Bible states that the Holy Spirit was already present on earth before and during the time of Jesus, in the womb of Elizabeth, and again when Jesus was being baptised, etc. Hence this prophecy could be seen as a reference to Muhammad.``[40]
One of the names and titles of Muhammad in Islam is Aš-Šafī` (in Arabic: الشفيع) which means "the intercessor" or "the advocate".[78] This led several Muslim writers to believe that the Advocate (the Paraclete) promised in the gospel of John is himself Muhammad.[79]
In John 16:12-13, the Advocate is described in a similar way to the description of the Prophet like Moses in Deuteronomy 18:18.[80] The Advocate is called the spirit of Truth, for he will not speak as himself originating what he says, but all that he hears he will speak, and he will show you things to come.[80][81] Rahmatullah Kairanawi cites Qur'an 53:3-4 in his argument to prove that Muhammad fulfilled this description of the Advocate in John 16:12-13.[82]
The earliest Muslim scholar to identify the Paraclete with Muhammad is likely Ibn Ishaq (died 767). Others who interpreted the Paraclete as a reference to Muhammad include Ibn Taymiyyah, Ibn Kathir, Al-Qurtubi, Rahmatullah Kairanawi (1818–1891), and contemporary Muslim scholars such as Martin Lings.[83]
A variation on this argument is the suggestion that the word Paraclete (παρακλητος paraklētos) in the text of the Greek New Testament was a corruption or alteration of the original Greek word Periclyte (περικλυτος periklytos), meaning "widely famed". This meaning is very similar to the literal translations of the names Ahmad or Muhammad in Arabic ("one who is highly praised"). George Sale refers to this view in his 1734 translation of the Qur'an, pointing out that Muslim scholars connect this to the Qur'anic passage in the Sura As-Saff in which it is stated that Jesus spoke of an Apostle to come after him, "whose name shall be Ahmad".
Gospel of Barnabas
Muslims including Muhammad Abu Zahra claim that changes were made to the present-day canon of the Christian Bible, by excluding material that represented the authentic message of Jesus, claiming that the authentic tradition is represented in the Gospel of Barnabas, which contains predictions of Muhammad.[84] A later Muslim writer, Ata ur-Rahîm, claimed that "The Gospel Barnabas was accepted as a Canonical Gospel in the churches of Alexandria up until 325".[84] The Gospel of Barnabas is generally seen to be a fabrication made during the Renaissance.[85][86][87]
People "with Muhammad" in the Bible
Qur'an 48:29 tells what the example of “Those who are with Muhammad” in the Torah, and what their parable is in the Gospel:
Qur'an 48:29 Muhammad is the Apostle of Allah; and "those with him" are forceful against the disbelievers, merciful among themselves. You see them bowing and prostrating [in prayer], seeking grace from Allah and [His] pleasure. The signs of Faith are apparent on their faces because of prostration. That is their example in the Torah. And their Parable in the Gospel is like a seed that puts forth its shoot, then strengthens it, so it becomes stout and stands firmly on its stem, delighting the sowers - so that Allah may enrage by them the disbelievers. Allah has promised those who believe and do righteous deeds among them forgiveness and a great reward.


According to this verse, the example of “those who are with Muhammad” in the Torah are those who are seen bowing, kneeling [in prayer], falling upon their faces [seeking grace from God and his pleasure] and the signs of their faith are apparent on their faces because of prostration. This example can be traced in the many verses from the Torah, and other Biblical chapters as well, which were commonly referred to by Muslims to show that all the prophets of God including Abraham, Moses, Aaron, David, and even Jesus himself prayed like Muslims pray; by kneeling, bowing down, falling upon their faces before the World's Maker, and praising him:
Genesis 17:3-4 And Abram fell on his face: and God talked with him, saying, As for me, behold, my covenant is with thee, and thou shalt be a father of many nations.
Numbers 20:6 And Moses and Aaron went from the presence of the assembly unto the door of the tabernacle of the congregation, and they fell upon their faces: and the glory of the Lord appeared unto them.
Numbers 16:20-22 And the Lord spake unto Moses and unto Aaron, saying, Separate yourselves from among this congregation, that I may consume them in a moment. And they fell upon their faces, and said, O God, the God of the spirits of all flesh, shall one man sin, and wilt thou be wroth with all the congregation?
Psalm 95:6 Come, let us bow down in worship, let us kneel before the Lord our Maker;
1 Kings 18:42 So Ahab went up to eat and drink. And Elijah went up to the top of Carmel; then he bowed down on the ground, and put his face between his knees,
2 Chronicles 7:3 And when all the children of Israel saw how the fire came down, and the glory of the Lord upon the house, they bowed themselves with their faces to the ground upon the pavement, and worshiped, and praised the Lord, saying, For he is good; for his mercy endureth for ever.
Nehemiah 8:6 Ezra praised the Lord, the great God; and all the people lifted their hands and responded, "Amen! Amen!" Then they bowed down and worshiped the Lord with their faces to the ground.
Matthew 26:39 And he [Jesus] went a little farther, and fell on his face, and prayed, saying, O my Father, if it be possible, let this cup pass from me: nevertheless not as I will, but as thou wilt.
Luke 6:12 And it came to pass in those days, that he [Jesus] went out into a mountain to pray, and continued all night in prayer to God.
- According to this verse also, the Parable of “those who are with Muhammad” in the Gospel is: "like a seed that puts forth its shoot, then strengthens it, so it becomes stout and stands firmly on its stem, delighting the sowers":
- The Parable of the Growing Seed
Mark 4:26-29
26 He also said, "This is what the kingdom of God is like. A man scatters seed on the ground. 27 Night and day, whether he sleeps or gets up, the seed sprouts and grows, though he does not know how. 28 All by itself the soil produces grain—first the stalk, then the head, then the full kernel in the head. 29 As soon as the grain is ripe, he puts the sickle to it, because the harvest has come."
- The Parable of the Mustard Seed
Mark, 4:30-32
30 Again he said, "What shall we say the kingdom of God is like, or what parable shall we use to describe it? 31 It is like a mustard seed, which is the smallest of all seeds on earth. 32 Yet when planted, it grows and becomes the largest of all garden plants, with such big branches that the birds can perch in its shade."
‘Umar and the Battle of Yarmouk
9 Rejoice greatly, Daughter Zion! Shout, Daughter Jerusalem! See, your king comes to you, righteous and victorious, lowly and riding on a donkey, on a colt, the foal of a donkey.— Zechariah 9:9
Al-Waqidi (c. 130 – 207 AH; c. 748 – 822 CE) mentioned in his book Futuh al-Sham ("Conquests of Levant") that Sophronius and the Churchmen in Jerusalem believed that Umar ibn Al-Khattab fulfilled a prophecy they have in their Scripture.[89]
Muslim writers argue that Umar was the victorious king mentioned in Zechariah 9:9.[89][90] They argue that Umar is well recognized in history for his pious and just nature, and according to several sources, he entered Jerusalem riding on a donkey.[91]
It was for the first time [following the entrance of Muslims to Jerusalem] that the Jews, after almost 500 years of oppressive Roman-Christian rule, were once again allowed to live and worship freely inside Jerusalem.[92]
14 Then the LORD will appear over them, and His arrow will go forth like lightning; and the Lord GOD will blow the trumpet, and will march forth in the windstorms of the south.— Zechariah 9:14
This passage is thought to be a prophecy of the Battle of Yarmouk. "The windstorms of the south" is a key point in this claim.
Non-Islamic view
Early Christian writers claimed that Muhammad was predicted in the Bible, as a forthcoming Antichrist, false prophet, or false Messiah. According to Albert Hourani, initial interactions between Christian and Muslim peoples were characterized by hostility on the part of the Europeans because they interpreted Muhammad in a Biblical context as being the Antichrist.[93] The earliest known exponent of this view was John of Damascus in the 7th century.[94] In c. 850 CE about 50 Christians were killed in Muslim-ruled Córdoba, Andalusia after a Christian priest named Perfectus said that Muhammad was one of the "false Christs" prophesied in Matthew 24:16.42. The monk Eulogius of Córdoba (c. 800-859 AD) justified the views of Perfectus and the other Martyrs of Córdoba, saying that they witnessed "against the angel of Satan and forerunner of Antichrist...Muhammed, the heresiarch."[95] John Calvin argued that "The name Antichrist does not designate a single individual, but a single kingdom which extends throughout many generations", saying that both Muhammad and the Catholic popes were "antichrists".[95]
The prophecy of the "Four kingdoms of Daniel" in Chapter 7 of the Book of Daniel has also been interpreted by Christians as a prediction of Muhammad. Eulogius argued that Muhammad was the Fourth Beast in the prophesy.[96] Another medieval monk, Alvarus, argued that Muhammad was the "eleventh king" that emerged from the Fourth Beast. According to historian John Tolan,
In Daniel's description of this beast, Alvarus sees the career of the Antichrist Muhammad and his disciples. This eleventh king who arises after the others, "diverse from the first," who subdues three kings, is it not Muhammad, who vanquished the Greeks, the Romans, and the Goths? "And he shall speak great words against the most High": did he not deny the divinity of Christ, thus, according to Saint John, showing himself to be an Antichrist? He "shall wear out the saints of the most High": is this not a prediction of the persecutions inflicted by the Muslims, in particular of the martyrdoms of Córdoba? He will "think to change times and laws": did he not introduce the Muslim calendar and the Koran? "[97]
Since the seventh century, the Prophet of Islam's name has been the focus of several stereotypes. Greek and Latin sources presented exaggerated and sometimes wrong stereotypes in literature, and the orthographic forms, which varied among them, were shared by two Western cultures: Spain and France. These variants and forms of the Prophet of Islam's name formulated stereotypes that molded the opinion and feelings of the West toward the leader of the new religion. Their references played a principal role in introducing Muhammad and his religion to the West as a false prophet who wrote the Koran, a Saracen prince or deity, the Biblical beast, a schismatic from Christianity, a satanic creature, and the Antichrist.[98]
See also
Notes
Explanatory footnotes
Citation footnotes
- ↑ "CATHOLIC ENCYCLOPEDIA: Mohammed and Mohammedanism (Islam)". Newadvent.org. Retrieved 2015-11-25.
- 1 2 English Translation of the Holy Quran: With Explanatory Notes, by Muhammad Ali and Zahid Aziz, Revised 2010 edition, ISBN 978-1-906109-07-3, p 627
- ↑ Ali, M.M.; Aziz, Z. (2010). English Translation of the Holy Quran: With Explanatory Notes. Ahmadiyya Anjuman Lahore. ISBN 9781906109073. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ David A. Cheetham, Ulrich Winkler, Interreligious Hermeneutics in Pluralistic Europe: Between Texts and People, Rodopi, 2011, p.372
- ↑ R. G. Ghattas, Carol B. Ghattas, A Christian Guide to the Qur'an: Building Bridges in Muslim Evangelism, Kregel Academic, 2009, p.103
- ↑ "Tanzil : Quran Navigator". tanzil.net. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ "Surat Al-'A`raf - The Noble Qur'an - القرآن الكريم". quran.com. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ Musnad Ahmad, Hadith number: 17150-17151
- ↑ Al-Mustadrak 'ala al-Sahîhayn, Hadith number: 4174
- ↑ Kais Al-Kalby, 2005, 207
- ↑ Keldani, Muhammad in World Scriptures, 2006, p 42
- ↑ Keldani, Muhammad in World Scriptures, 2006, p 45
- ↑ "Douay-Rheims translation". Latinvulgate.com. Retrieved 2013-04-16.
- ↑ al-Maghribi, Al-Samawal; Taweile, Abdulwahab. بذل المجهود في إفحام اليهود [Confuting the Jews] (in Arabic) (1st 1989 ed.). Syria: Dar Al Qalam. p 75
- ↑ al-Maghribi, Al-Samawal; Taweile, Abdulwahab. بذل المجهود في إفحام اليهود [Confuting the Jews] (in Arabic) (1st 1989 ed.). Syria: Dar Al Qalam. p 77
- ↑ Jami` at-Tirmidhi » Chapters on Tafsir, English reference: Vol. 1, Book 44, Hadith 3278, Arabic reference: Book 47, Hadith 3589
- ↑ Al-Mustadrak 'ala al-Sahîhayn, Hadith number: 4099
- ↑ As-Seerah Al-Halabiyyah, Ali ibn Burhanuddin Al-Halabi, volume 1, p 138-139
- ↑ Dr. Abdel-Halim Mahmoud, الإسراء و المعراج (al-Isra and al-Mi'raj), in Arabic, 11th edition 2004, ISBN 977-02-6711-2
- ↑ Abd Allah ibn Abbas reported that Muhammad saw God twice: http://sunnah.com/muslim/1/343
- ↑ It was also reported that Imam Hasan Al-Basri would take an oath upon insisting that the Prophet saw his Lord. http://mauritianmuslim.co.uk/The%20Isra%20and%20Mi%27raaj%20completed.pdf
- ↑ Imam Ahmad ibn Hanbal was asked if the Prophet saw his Lord. He said, ‘he saw him, he saw him’ until he became breathless. (p. 537 Ibid.) http://mauritianmuslim.co.uk/The%20Isra%20and%20Mi%27raaj%20completed.pdf
- ↑ Sahih al-Bukhari » Book of Companions of the Prophet
- ↑ Sahih Muslim » The Book of the Merits of the Companions
- ↑ Sunan Ibn Majah » The Book of the Sunnah
- ↑ Jami` at-Tirmidhi » Chapters on Virtues
- ↑ The Messenger of God Muhammad, Fethullah Gülen, 2008, ISBN 978-1-59784-137-5, p 11
- ↑ English Translation of the Holy Quran: With Explanatory Notes, by Muhammad Ali and Zahid Aziz, Revised 2010 edition, ISBN 978-1-906109-07-3, p 732
- ↑ "Muhammad in the Gospel of John". answering-christianity.com. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ "Prophet Muhammad The last Messenger in the Bible", Kais Al-Kalby, ISBN 0-9638520-2-7, p 397
- ↑ al-Maghribi, Al-Samawal; Taweile, Abdulwahab. بذل المجهود في إفحام اليهود [Confuting the Jews] (in Arabic) (1st 1989 ed.). Syria: Dar Al Qalam. p 67
- ↑ Kais Al-Kalby, 2005, p 223
- ↑ Kais Al-Kalby, 2005, p 221
- ↑ Rahmatullah Kairanawi, Izhar ul-Haq (Truth Revealed), Council of Senior Scholars (Saudi Arabia) 1989, p 1143
- ↑ Munqidh As-Saqqar, p24
- ↑ Muhammad, encyclopaedia of seerah, 1st volume, Afzal-ur-Rahman, 1985, p 143
- ↑ David Benjamin Keldani, 2006, p 80-85
- ↑ Richard S. Hess; Gordon J. Wenham (1998). Make the Old Testament Live: From Curriculum to Classroom. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. ISBN 978-0-8028-4427-9. Retrieved 4 April 2013.
- ↑ "The Absolute Truth About Muhammad in the Bible With Arabic Titles". Truth Will Prevail Productions. Retrieved 2016-10-07.
- 1 2 3 "Islamic Research Foundation". Irf.net. Retrieved 2015-11-25.
- ↑ Margaret S. King, in the second part of Chapter 13 of her book "Unveiling The Messiah in the Dead Sea Scrolls".
- 1 2 Ali Ünal, 2013, chapter about the straight highway of the Lord in Arabia.
- 1 2 Al-Mustadrak 'ala al-Sahîhayn, Hadith number 4224
- 1 2 "Hadith - Book of Dealing with people cheerfully - Al-Adab Al-Mufrad - Sunnah.com - Sayings and Teachings of Prophet Muhammad (صلى الله عليه و سلم)". sunnah.com. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ Qur'an 21:107
- 1 2 Kais Al-Kalby, 2005, 267
- ↑ Jamal Badawi, 2005, p 39
- ↑ In Search of God, Mohamed Gad, 2009, ISBN 978-0-595-33644-9 (pbk), ISBN 978-0-595-78446-2 (ebk), USA, p 28
- 1 2 Rahmatullah Kairanawi, Izhar ul-Haq (Truth Revealed), Council of Senior Scholars (Saudi Arabia) 1989, p 1161
- ↑ Rahmatullah Kairanawi, Izhar ul-Haq (Truth Revealed), Council of Senior Scholars (Saudi Arabia) 1989, p 1160
- ↑ Rahmatullah Kairanawi, Izhar ul-Haq (Truth Revealed), Council of Senior Scholars (Saudi Arabia) 1989, p 1159
- ↑ David Benjamin, Malaysian edition 2006 ed, p 54
- ↑ Nasrullah Abu Talib, 4th 2009 ed, p 85
- ↑ David Benjamin, Malaysian edition 2006 ed, p 52-74
- ↑ Nasrullah Abu Talib, 4th 2009 ed, p 90
- ↑ David Benjamin, Malaysian edition 2006 ed, p 63
- ↑ Nasrullah Abu Talib, 4th 2009 ed, p 86
- ↑ De Lisle, Ambrose Lisle M. Phillipps. 1855. Mahometanism in its Relation to Prophecy; or, An Inquiry into the Prophecies Concerning Antichrist. Oxford: Oxford University, pp. 198-191.
- ↑ Scio de San Miguel, Felipe. 1857. La Biblia Vulgata Latina. Traducida al español y anotada. Paris: Rosa y Bouret, p. 599.
- ↑ Sbaihat, Ahlam (2015), "Stereotypes associated with real prototypes of the prophet of Islam's name till the 19th century". Jordan Journal of Modern Languages and Literature Vol. 7, No. 1, 2015, p. 27. http://journals.yu.edu.jo/jjmll/Issues/vol7no12015/Nom2.pdf
- ↑ "Habakkuk 3 DRB". biblehub.com. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- 1 2 Munqidh As-Saqqar, 1st 2007 ed, p 87
- ↑ Misha'al Abdullah, 1995, p 279
- ↑ Margaret S. King, Chapter 12 of her book "Unveiling The Messiah in the Dead Sea Scrolls".
- ↑ "Matthew 21 WEY". biblehub.com. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ Kais, 2005, p 387
- 1 2 Rahmatullah Kairanawi, Izhar ul-Haq (Truth Revealed), Council of Senior Scholars (Saudi Arabia) 1989, p 1181
- ↑ Ali Ünal, 2013, chapter about the Parable of the tenants.
- ↑ Sahih al-Bukhari, Book of Virtues and Merits of the Prophet and his Companions, Chapter: The Seal of all the Prophets, Hadith number: 44
- ↑ "Surat Al-Baqarah [2:91] - The Noble Qur'an - القرآن الكريم". quran.com. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ "Surat Al-Baqarah [2:87] - The Noble Qur'an - القرآن الكريم". quran.com. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ Misha'al Abdullah, 1995, p 194
- 1 2 Sami Ameri, 2006, p 235
- ↑ "Thaumastos - New Testament Greek Lexicon - King James Version". biblestudytools.com. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ "John 15 WEY". biblehub.com. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ "JOHN CHAPTER 16 KJV". Kingjamesbibleonline.org. 2015-11-18. Retrieved 2015-11-25.
- ↑ "John 16:12-14". Bible Gateway. Retrieved 2015-11-25.
- ↑ Dur al-Manthur, Al-Suyuti, volume 4, p 341
- ↑ Rahmatullah Kairanawi, Izhar ul-Haq (Truth Revealed), Council of Senior Scholars (Saudi Arabia) 1989, p 1191
- 1 2 Margaret S. King, the second part of Chapter 13
- ↑ "John 16 WEY". biblehub.com. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ Rahmatullah Kairanawi, Izhar ul-Haq (Truth Revealed), Council of Senior Scholars (Saudi Arabia) 1989, p 1197
- ↑ Al-Masāq: studia arabo-islamica mediterranea: Volumes 9 à 10 ;Volume 9 University of Leeds. Dept. of Modern Arabic Studies, Taylor & Francis - 1997
- 1 2 Leirvik, Oddbjørn (2002). "History as a Literary Weapon: The Gospel of Barnabas in Muslim-Christian Polemics". Studia Theologica - Nordic Journal of Theology. 56: 4. doi:10.1080/003933802760115417.
- ↑ Cirillo, Luigi; Fremaux, Michel (1977). Évangile de Barnabé. Beauchesne. p. 88.
- ↑ Ragg, L & L (1907). The Gospel of Barnabas. Oxford. pp. xi. ISBN 1-881316-15-7.
- ↑ Joosten, Jan (April 2010). "The date and provenance of the Gospel of Barnabas". Journal of Theological Studies. 61 (1): 200–215. doi:10.1093/jts/flq010.
- ↑ Kais, 2005, p 227
- 1 2 Nasrullah, 2009, p 271
- ↑ Kais, 2005, p 365
- ↑ Kais, 2005, p 367
- ↑ Moshe Gil, A History of Palestine, 634–1099, ISBN 0-521-59984-9, 1997, p 70-71
- ↑ Hourani, Albert (1967). "Islam and the philosophers of history". Middle Eastern Studies. 3 (3): 206. doi:10.1080/00263206708700074.
- ↑ Esposito, John L., The Oxford History of Islam: Oxford University Press, 1999, p.322.
- 1 2 McGinn, Bernard, Antichrist: Two Thousand Years of the Human Fascination with Evil, Columbia University Press. 2000, p.86; 212.
- ↑ Quinn, Frederick, The Sum of All Heresies: The Image of Islam in Western Thought, Oxford University Press, 2008, p.30
- ↑ John Tolan, Saracens: Islam in the Medieval European Imagination, Columbia University Press. New York: 2002, p.81.
- ↑ See Sbaihat, Ahlam (2015), "Stereotypes associated with real prototypes of the prophet of Islam's name till the 19th century"
Bibliography
- S. King, Margaret. Unveiling The Messiah in the Dead Sea Scrolls (2012 ed.). USA: Library of Congress. ISBN 978-1-4653-9219-0.
- al-Kalby, Kais. Prophet Muhammad The last Messenger in the Bible (PDF) (8th 2005 ed.). USA: Tahrike Tarsile Qur’an. ISBN 0-9638520-2-7.
- Abu Talib, Nasrullah. تباشير الإنجيل والتوراة بالإسلام ورسوله محمد [The Good News of the Coming of Muhammad in the Gospel and the Torah] (PDF) (in Arabic) (4th 2009 ed.). Egypt: Dar al-Wafaa.
- Badawi, Jamal. Muhammad in the Bible (3rd 2005 ed.). Egypt: al-Falah Foundation. ISBN 977-5813-05-0.
- Keldani, David Benjamin. Muhammad in World Scriptures (Volume II): The Bible (Malaysian edition 2006 ed.). Malaysia: Islamic Book Trust. ISBN 983-9154-65-6.
- al-Maghribi, Al-Samawal; Taweile, Abdulwahab. بذل المجهود في إفحام اليهود [Confuting the Jews] (PDF) (in Arabic) (1st 1989 ed.). Syria: Dar Al-Qalam.
- Turmeda, Anselm; Wafeeq, Omar. تحفة الأريب في الرد على أهل الصليب [The Gift to the Intelligent for Refuting the Arguments of the Christians] (PDF) (in Arabic) (1st 1988 ed.). Lebanon: Dar Albashaer.
- As-Saqqar, Munqidh. هل بشر الكتاب المقدس بمحمد؟ [Did the Bible herald the Coming of Muhammad?] (PDF) (in Arabic) (1st 2007 ed.). Dar Al-Islam. ISBN 9960-49-525-6.
- As-Saqqar, Munqidh. The Promised Prophet of the Bible.
- Deedat, Ahmed. Muhammad: The Natural Successor To Christ.
- Abu Laylah, Muhammad (2005). The Qur'an and the Gospels: A Comparative Study (PDF) (3rd ed.). Egypt: Al-Falah foundation. OCLC 229013115.
- Abdullah, Misha'al. What Did Jesus Really Say? (PDF) (1995 ed.).
- Ünal, Ali; Gültekin, Harun. The Prophet Promised In World Scriptures (2013 ed.). USA: Tughra Books. ISBN 978-1-59784-271-6.
- Ameri, Sami. محمد رسول الله في الكتب المقدسة [Muhammad, the Apostle of God, in the Holy Scriptures of Judaism, Christianity, Zoroastrianism, Hinduism and Buddhism] (PDF) (in Arabic) (1st 2006 ed.). Tanweer Publishing center. ISBN 977-289-127-1.
- Kairanawi, Rahmatullah. إظهار الحق [Izhar ul-Haq (Truth Revealed)] (PDF) (in Arabic) (1989 ed.). Council of Senior Scholars (Saudi Arabia).
- Mohammed, Jibril. Above the Law 360 (2013 ed.). USA: AuthorHouse. ISBN 978-1-4817-0042-9.
External links
- Is Muhammad Found in the Bible?
- Prophet Muhammad in the Old and New Testament
- Jesus is Muslim
- Mission-Islam
- Prophet Muhammad in the Bible
- Prophet Muhammad in the Bible: Torah and Psalms

