Nepean Highway
| Nepean Highway Victoria | |
|---|---|
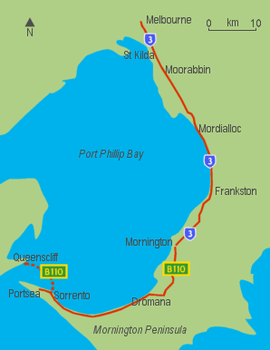 | |
| Route of the Nepean Highway between Melbourne and Portsea | |
| General information | |
| Type | Highway |
| Length | 95.1 km (59 mi)[1] |
| Route number(s) |
|
| Major junctions | |
| North end |
|
| |
| South end | |
| Location(s) | |
| Major settlements | Elsternwick, Moorabbin, Cheltenham, Mordialloc, Chelsea, Carrum, Seaford, Frankston, Mount Eliza, Mornington, Dromana, Rosebud, Sorrento |
| Highway system | |
|
Highways in Australia National Highway • Freeways in Australia Highways in Victoria | |
| |
Nepean Highway runs south from the corner of Glen Huntly Road and Brighton Road in Victoria, Australia to Portsea, along the eastern shore of Port Phillip. It is the primary road route to central Melbourne from Melbourne's southern suburbs.
History
Originally known as Arthurs Seat Road it was built in the 1850s to provide a road (originally a crude sandy track) from the farms (owned by Alexander Balcombe) south of Melbourne and link the city with its southern bay settlements and sea defences at Point Nepean. By the turn of the 20th century it had come to be known as Point Nepean Road and in 1948 was officially named Nepean Highway (indirectly after the British Politician and Colonial Administrator, Sir Evan Nepean, 1st Baronet PC).
Between the 1950s and about 1980, the road was progressively upgraded to a divided highway between the City and Mordialloc. From Mordialloc to Frankston, the highway is an undivided four lane road. The widening of the Mordialloc Bridge,[2] the last section of less than four lanes, was completed in early 2009.
The Nepean Highway has kept the Metro Route 3 signage throughout the suburbs but is designated B110 at the town of Mornington.
Route
Melbourne to Elsternwick
The length of road starts as Swanston Street at the Melbourne General Cemetery and passes through the Melbourne CBD and over the Princes Bridge to the Melbourne Arts Precinct before becoming St Kilda Road, a leafy four lane boulevard shared with trams. Metro Route 3 begins at the Victorian Arts Centre and passes the Shrine of Remembrance. It passes through St Kilda Junction then shortly after, at the intersection with Carlisle Street, the road changes name to Brighton Road, until its intersection with Glen Huntly Road, Elsternwick where it finally becomes Nepean Highway. The Route 67 Carnegie Tram runs down the middle of the highway until it turns into Glen Huntly Road.
Elsternwick to Mornington
At Glen Huntly Road, the speed limit increases to 80 km/h and the road widens to become an eight-lane divided highway. It is reduced to six lanes at Moorabbin, passing through Cheltenham and Mentone, and then to the 60 km/h or 70 km/h four-lane single carriageway after the roundabouts at Mordialloc. The highway then travels virtually along the foreshore of Port Phillip Bay, to Frankston, with several stretches of dual carriageway, and then up Olivers Hill, from which there are good views across Frankston and the bay.
Mornington Peninsula
In the late 1960s a bypass road was constructed in the town of Mount Eliza. Previously the highway travelled through the main shopping village.
Just after passing through Mount Martha, the highway joins with the Mornington Peninsula Freeway, before turning toward the town of Dromana. Here the highway changes name again, to become Point Nepean Road – which was the former name of the entire highway in the early years of settlement. From here, Arthurs Seat is easily accessible, which gives spectacular views across the bay, and on a clear day, the skyscrapers of Melbourne are visible. Anthonys Nose is a point, or escarpment located on the southern shore of Port Phillip Bay, between Dromana and McCrae. The highway passes between "The Nose" and the shores of the bay. It was named by Charles La Trobe in 1839. In the 1920s "The Nose" was modified in order to combat the daily tides that blocked the highway.
B110 leaves the highway at Sorrento to cross the bay to Queenscliff, via the ferry where it continues to Geelong, via Bellarine Highway, but the highway continues as a two lane road down to the seaside resort of Portsea. The end of the highway is the very nondescript painted turning circle, before the gates of the former Commonwealth quarantine and defence station of Point Nepean, a humble ending to Melbourne's main southern highway.
Possible future north-south connection
Transurban, in their Response to the Eddington Report, July 2008,[3] believe a north-south corridor from the Hume Freeway and Metropolitan Ring Road to the Nepean Highway south of Glen Huntly Road, Elsternwick, generally via the Hoddle Highway corridor, deserves attention.
This alignment would follow the original F2 Freeway corridor as proposed in the 1969 Melbourne Transportation Plan.
Gallery
 Nepean Highway section in Elsternwick.
Nepean Highway section in Elsternwick. Nepean Highway at Gardenvale.
Nepean Highway at Gardenvale.
See also
References
- ↑ Google (5 October 2013). "Nepean Highway" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- ↑ Archived 23 July 2008 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Response to the Eddington Report, July 2008
