Potassium chromate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium chromate | |
| Other names
Chromic acid, (K2CrO4), dipotassium salt | |
| Identifiers | |
| 7789-00-6 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:75249 |
| ChemSpider | 22999 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.218 |
| EC Number | 232-140-5 |
| PubChem | 24597 |
| RTECS number | GB2940000 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CrK2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 194.19 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.7320 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 968 °C (1,774 °F; 1,241 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,000 °C (1,830 °F; 1,270 K) |
| 62.9 g/100 mL (20 °C) 75.1 g/100 mL (80 °C) 79.2 g/100 mL (100 °C) | |
| Solubility | insoluble in alcohol |
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.74 |
| Structure | |
| rhombic | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Chemical Safety Data |
| EU classification (DSD) |
Carc. Cat. 2 Muta. Cat. 2 Toxic (T) Irritant (Xi) Dangerous for the environment (N) |
| R-phrases | R49, R46, R36/37/38, R43, R50/53 |
| S-phrases | S53, S45, S60, S61 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions |
Potassium dichromate Potassium molybdate Potassium tungstate |
| Other cations |
Sodium chromate Calcium chromate Barium chromate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Potassium chromate is the inorganic compound with the formula (K2CrO4). This yellow solid is the potassium salt of the chromate anion. It is a common laboratory chemical, whereas sodium chromate is important industrially. It is a class two carcinogen.[1]
Structure
Two crystalline forms are known, both being very similar to the corresponding potassium sulfate. Orthorhombic β-K2CrO4 is the common form, but it converts to an α-form above 66 °C.[2] These structures are complex, although the sulfate adopts the typical tetrahedral geometry.[3]
 Structure of β-K2CrO4.
Structure of β-K2CrO4.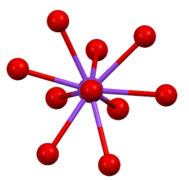 Coordination sphere of one of two types of K+ site.
Coordination sphere of one of two types of K+ site.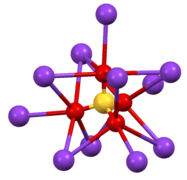 The environment about the tetrahedral CrO42- center in β-K2CrO4.
The environment about the tetrahedral CrO42- center in β-K2CrO4.
Production and reactions
It is prepared by treating potassium dichromate with potassium hydroxide.
In solution, the behavior of potassium and sodium dichromates are very similar. When treated with lead(II) nitrate, it gives an orange-yellow precipitate, lead(II) chromate.
Applications
Unlike the less expensive sodium salt, potassium salt is mainly used for laboratory work in situations where an anhydrous salt is required.[2] It is as an oxidizing agent in organic synthesis. It is used as in qualitative inorganic analysis, e.g. as a colorimetric test for silver ion. It is also used as an indicator in precipitation titrations with silver nitrate and sodium chloride (they can be used as standard as well as titrant for each other) as potassium chromate turns red in the presence of excess of silver ions.
Occurrence
Tarapacaite is the natural, mineral form of potassium chromate. It occurs very rarely and until now is known from only few localities on Atacama desert.
Safety
Potassium chromate is a carcinogen and strong oxidant.
References
- ↑ Potassium chromate information URL last accessed 15 March 2007
- 1 2 Gerd Anger, Jost Halstenberg, Klaus Hochgeschwender, Christoph Scherhag, Ulrich Korallus, Herbert Knopf, Peter Schmidt, Manfred Ohlinger, "Chromium Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. doi:10.1002/14356007.a07_067
- ↑ Gaultier, M.; Pannetier, G. "Structure cristalline de la forme 'basse temperature' du sulfate de potassium K2SO4-beta" (Crystal structure of the "low temperature" β-form of potassium sulfate) Bulletin de la Societe Chimique de France 1968, vol. 1, pp. 105-12.
