Rankine half body
In the field of fluid dynamics, a Rankine half body is a feature of fluid flow discovered by Scottish physicist and engineer William Rankine that is formed when a fluid source is added to a fluid undergoing laminar flow. Superposition of uniform flow and source flow yields rankine half body flow. A practical example of this type of flow is a bridge pier or a strut placed in a uniform stream. The resulting streamline () and velocity potential () is obtained by simply adding the streamline and velocity potential for individual flows.
Solution
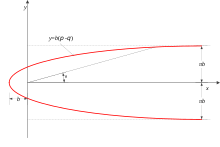
The flow equations of the Rankine half body are solved using the principle of superposition, combining the solutions of the linear flow of the stream and the circular flow of the source.
Given the linear flow field and the source , we have
The stagnation point for this flow can be determined by equating the velocity to zero in either directions. Because of symmetry of flow in y-direction, stagnation point must lie on x-axis.
Equating both and to zero, we obtain .
At and we have stagnation points.
- (equation of flow over Rankine half body)
Significance
This type of flow provides important information about flow in front part of streamlined body. It is probable that at the boundary, flow is not properly represented for real flow. The pressure and velocity of flow near to boundary layer is calculated by applying the Bernoulli's principle and is approximated with potential flow. The above equations may be used to calculate the stress on the body placed into the flow stream.
References
- http://www.iust.ac.ir/files/mech/mazidi_9920c/fluid_ii/lecture8.pdf (pg no 22.23)
- http://www-mdp.eng.cam.ac.uk/web/library/enginfo/aerothermal_dvd_only/aero/fprops/poten/node35.html
- http://nptel.ac.in/courses/101103004/15
- http://poisson.me.dal.ca/site2/courses/mech3300/Superposition.pdf
- http://faculty.poly.edu/~rlevicky/Handout14_6333.pdf
- http://web.mit.edu/2.016/www/handouts/2005Reading4.pdf
- http://www1.maths.leeds.ac.uk/~kersale/2620/Notes/chapter_4.pdf
