SimScale
 | |
 | |
| Developer(s) | SimScale GmbH |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 2013 |
| Development status | Active |
| Platform | Web browser |
| Type | Computer-aided engineering |
| Website |
simscale |
SimScale is a computer-aided engineering (CAE) software product based on cloud computing. SimScale was developed by SimScale GmbH and allows structural, fluids, particle and acoustic simulations.[1] [2] The backend of the platform uses open source codes:
- CFD: OpenFOAM and SU2
- FEM: Code Aster and CalculiX
- Particles: YADE
History
SimScale GmbH was founded in 2012 by five graduates of TU Munich, David Heiny, Vincenz Dölle, Alexander Fischer, Johannes Probst, and Anatol Dammer[3] with the goal of building a cloud-based 3D CAE platform that was easy-to-use and affordable. After a beta phase, the SimScale platform was launched in the second half of 2013.[4]
Further, on 2 December 2015, a community plan was announced making the platform accessible to everyone for free[5][6] and hence making simulation technologies more accessible to small and medium scale industries.[7] [8]
Features
The SimScale platform has several capabilities. Each capability with a suitable example for visualization is given below.
Finite element analysis module
The FEM module uses the open-source codes / solvers CalculiX and Code Aster. These codes allow linear and nonlinear analysis of structures. Linear static/dynamic analysis is possible using either codes / solvers but the nonlinear static/dynamic analysis is possible only through the usage of Code Aster.
| Type of analysis permitted | Examples | Type of analysis permitted | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear static analysis | 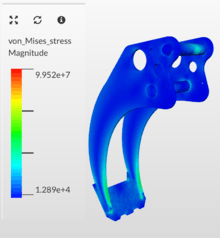 The image describes the contour plot of stresses obtained from linear static analysis of a gripper arm. The analysis was done using the SimScale FEM software |
Nonlinear static analysis | 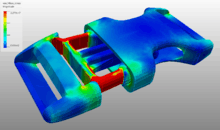 This image shows the contour plot of a nonlinear static analysis on a snap-fit. The analysis is done using the finite element software SimScale. Here the analysis is time-independent and hence static. But also involves nonlinearities like contact and plasticity |
| Linear dynamic analysis | 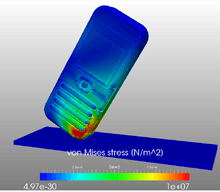 The image shows the contour plot of stresses from the linear dynamic analysis. A mobile case is dropped from 2m to plot the stresses due to impact. The FEM simulation was performed using the SimScale FEM software. |
Nonlinear dynamic analysis | 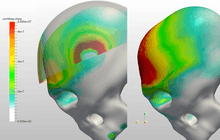 The image shows the contour plot of stresses during an impact event. The image shows the impact of an object with the skull in the presence of a helmet and without a helmet. The simulation was done using the FEM software SimScale. |
| Modal analysis (frequency) | 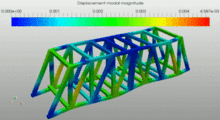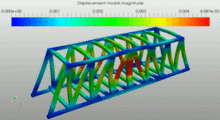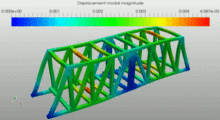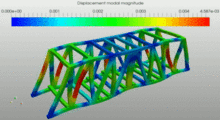 This image shows the contour plot of displacements. The image corresponds to a modal analysis done using SimScale FEM software. The gif image shows the different eigenmodes of the truss bridge |
Harmonic analysis | 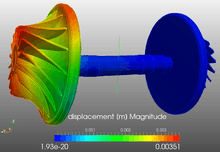 The image shows the contour plot of displacements. The Harmonic analysis was done at 520 Hz. The simulation was done using the FEM software SimScale. |
Computational fluid dynamics module
The CFD module of SimScale primarily uses OpenFOAM for fluid flow simulations. It is also possible to choose SU2, alternatively, for solutions to compressible flows.[9] Both steady state and transient analysis for the below simulations are possible.
Type of analysis permitted:
- Laminar flow
- Turbulent flows
- Incompressible flow
- Compressible flow
- Multiphase flow
- Fluid flow through porous media
- Scalar mass transport
- Fluid flow with rigid body movement
Thermal module
The Thermal module of SimScale uses OpenFOAM for fluid-fluid and fluid-solid thermal interaction problems. For thermo-structural analysis, SimScale uses Code Aster and CalculiX. At present, SimScale allows uncoupled thermo-mechanical simulations,[10] conjugate heat transfer[11] and convective heat transfer analysis. Both steady-state and transient simulations are possible. In addition, fluid simulations also allow usage of Turbulence models.
Other modules
The other modules of SimScale include
- Particle analysis
- Acoustics
File format
SimScale allows import of geometry in STEP, IGES, BREP and STL formats; mesh in OpenFOAM, UNV, EGC, MED, CGNS formats. In addition, the geometry can be directly imported from their partner CAD platform, namely Onshape.
A SimScale add-in for Autodesk Fusion 360 has been released to allow direct import of models from Autodesk Fusion 360 to SimScale.[12]
SimScale community
The SimScale Community Plan was announced on 2 December 2015 based on new investment round led by Union Square Ventures (USV).[13] The Community Plan is free and includes 3000 computation hours and 500 GB of storage per year for any registered user. Simulations/Projects created by a user registered under the "Community plan" is available for access, to all other users, in the SimScale public projects.[1] The SimScale public projects is a library of simulations/projects from which any registered user can use as template to modify or copy an existing simulation.[14]
SimScale outreach program
SimScale has also organized several free webinars as a part of its outreach program to make simulation technologies more popular among hobbyists and designers. Webinars organized by SimScale include
- 3D Printing Workshop[15]
- F1 Aerodynamics Workshop[16]
- Simulation in Biomedical Engineering Workshop[17]
References
- 1 2 Wasserman, Shawn (9 December 2015). "SimScale Brings the Price of Computer-Aided Engineering Down to Zero". engineering.com.
- ↑ Tara, Roopinder (16 June 2016). "Be Warned: The CAE World Is About to Shift". engineering.com.
- ↑ "SimScale". CrunchBase.
- ↑ Schmitz, Barb (26 August 2013). "Cloud-Based Simulation". engineering.com.
- ↑ "SimScale announces free access to simulation technology as a part of its new community plan" (Press release). NAFEMS. 2 December 2015.
- ↑ König, Peter (15 April 2016). "Mit SimScale und Make gratis simulieren lernen wie die Profis" (Press release). MAKE.
- ↑ "SimScale to bring simulation technology to small and medium businesses". Global Manufacturing. 8 December 2015.
- ↑ Wasserman, Shawn (30 April 2015). "Is Cloud-Based Simulation Affordable Enough to Dominate the Start-Up Market?". Engineering.com.
- ↑ Wasserman, Shawn (18 September 2015). "SimScale Update Focuses on Fluid Flow". engineering.com.
- ↑ Wasserman, Shawn (19 January 2015). "Transient Heating and Thermal Shock Analysis for Free". engineering.com.
- ↑ Wasserman, Shawn (19 May 2016). "Freemium Simulation Software Now Includes Conjugate Heat Transfer". engineering.com.
- ↑ "SimScale Integrates with Autodesk Fusion 360". Inside HPC. 22 August 2016.
- ↑ "Union Square Ventures invests in Munich-based startup SimScale". Tech.eu. 2 December 2015.
- ↑ "Public Projects". SimScale.
- ↑ "SimScale Offers Three Workshops to Teach 3D Printing". 3Dprint.com. 11 February 2016.
- ↑ "SimScale Offers Online F1 Aerodynamics Workshop". Inside HPC. 11 March 2016.
- ↑ "SimScale Offers Training on Using Simulation in Biomedical Engineering". Engineering.com. 19 August 2016.