Stratified Morse theory
In mathematics, stratified Morse theory is an analogue to Morse theory for general stratified spaces, originally developed by Mark Goresky and Robert MacPherson. The main point of the theory is to consider functions 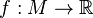 and consider how the stratified space
and consider how the stratified space ![f^{-1}(-\infty,c]](../I/m/72b1b322ce9ce2a7d3a9bdd543226368.png) changes as the real number
changes as the real number 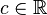 changes. Morse theory of stratified spaces has uses everywhere from pure mathematics topics such as braid groups and representations to robot motion planning and potential theory. A popular application in pure mathematics is Morse theory on manifolds with boundary, and manifolds with corners.
changes. Morse theory of stratified spaces has uses everywhere from pure mathematics topics such as braid groups and representations to robot motion planning and potential theory. A popular application in pure mathematics is Morse theory on manifolds with boundary, and manifolds with corners.
See also
References
- "Stratified Morse theory", by M. Goresky and R. MacPherson Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 1988, xiv + 272 pp. DJVU file on Goresky's page
- D. Handron, Generalized billiard paths and Morse theory on manifolds with corners. Topology and its Applications, Volume 126, Number 1, 30 November 2002, pp. 83–118(36)
- S.A. Vakhrameev, Morse lemmas for smooth functions on manifolds with corners. Dynamical systems, 8. J. Math. Sci. (New York) 100 (2000), no. 4, 2428–2445.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/14/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
