Siuslaw National Forest
| Siuslaw National Forest | |
|---|---|
|
IUCN category V (protected landscape/seascape) | |
|
Cape Perpetua on the Lincoln County coast | |
 | |
| Location | Oregon, United States |
| Nearest city | Corvallis, Oregon |
| Coordinates | 44°20′00″N 123°55′00″W / 44.33333°N 123.91667°WCoordinates: 44°20′00″N 123°55′00″W / 44.33333°N 123.91667°W |
| Area | 634,207 acres (2,566.54 km2)[1] |
| Established | July 1, 1908[2] |
| Visitors | 1,856,000[3] (in 2006) |
| Governing body | United States Forest Service |
| Website | Siuslaw National Forest |
The Siuslaw National Forest (/saɪˈjuːslɔː/ sy-EW-slaw)[4] is a national forest in western Oregon in the United States. Established in 1908, the Siuslaw is made up of a wide variety of ecosystems, ranging from coastal forests to sand dunes.
Geography

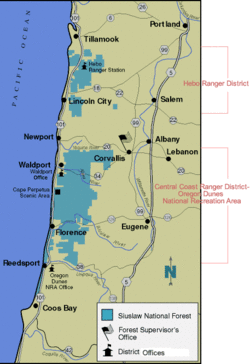
The Siuslaw National Forest encompasses more than 630,000 acres (2,500 km2) along the central Oregon Coast between Coos Bay and Tillamook, and in some places extends east from the ocean, beyond the crest of the Oregon Coast Range, almost reaching the Willamette Valley. The forest lies primarily in Lane County (39% of the forest) and Lincoln County (27% of the forest); the rest in descending order of land area are Tillamook, Douglas, Yamhill, Benton, Coos, and Polk counties. It includes the Sand Lake Recreation Area and the Oregon Dunes National Recreation Area. The Forest Supervisor's office is located in Corvallis, and the Siuslaw is broken up into two ranger districts—the Hebo Ranger District, with approximately 151,000 acres (610 km2), and the Central Coast Ranger District, with approximately 479,000 acres (1,940 km2).[5]
The forest contains Marys Peak, the highest point in the Oregon Coast Range at 4,097 feet (1,249 m). Numerous aquatic habitats are found in the forest: marine shore, rivers and streams—1,200 miles (1,900 km), including the Alsea, Nestucca, Siuslaw, and Umpqua rivers—and 30 lakes. The terrestrial environment can be regarded as two major vegetation zones, one near the coast dominated by Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis), and the other dominated by western hemlock (Tsuga heterophylla) and Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii). Western hemlock often grows in the shade under Douglas fir. Other major tree species in the forest are western red cedar (Thuja plicata), red alder (Alnus rubra), and bigleaf maple (Acer macrophyllum).[5] A 1993 Forest Service study estimated that the extent of old growth in the forest was 33,800 acres (13,700 ha).[6] The Cummins Creek Wilderness and the Rock Creek Wilderness preserve some of this old growth.
Recreational activities
Recreational activities in the Siuslaw National Forest include fishing, camping, hiking, horseback riding, mountain biking, exploring tide pools, and riding off highway vehicles.
Wilderness areas
There are three officially designated wilderness areas within the Siuslaw National Forest that are part of the National Wilderness Preservation System, all established in 1984:
- Drift Creek Wilderness - Lincoln County
- Cummins Creek Wilderness - Lane County
- Rock Creek Wilderness - Lane County
References
- ↑ "Land Areas of the National Forest System" (PDF). U.S. Forest Service. January 2012. Retrieved 2012-06-30.
- ↑ "The National Forests of the United States" (PDF). ForestHistory.org. Retrieved 2012-07-30.
- ↑ Revised Visitation Estimates (PDF) - U.S. Forest Service
- ↑ "FAQ 18: How do you pronounce Siuslaw?". U.S. Forest Service. Retrieved 2007-11-10.
- 1 2 "About the Forest". U.S. Forest Service. Retrieved 2014-08-03.
- ↑ Bolsinger, Charles L.; Waddell, Karen L. (December 1993). "Area of Old-Growth Forests in California, Oregon, and Washington" (PDF). U.S. Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station. p. 14. Resource Bulletin PNW-RB-197. Retrieved 2014-08-05.
External links
- Siuslaw National Forest official website
-
 Media related to Siuslaw National Forest at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Siuslaw National Forest at Wikimedia Commons
