United States Army Alaska
| United States Army Alaska | |
|---|---|
|
United States Army Alaska | |
| Active | 1994 – present |
| Country |
|
| Branch |
|
| Part of | United States Army Pacific |
| Garrison/HQ | Fort Richardson |
| Nickname(s) | America's Arctic Warriors (Special Designation)[1] |
| Commanders | |
| Current Commander | Major General Bryan R. Owens |
| Command Sergeant Major | Command Sergeant Major Michael A. Ferrusi |
| Insignia | |
| Distinctive Unit Insignia |
 |
United States Army Alaska (USARAK or "America's Arctic Warriors"[1]) is a military command of the United States Army located in the U.S. state of Alaska. A subordinate command of the United States Army Pacific, USARAK is the ground element of the Alaskan Command. USARAK is headquartered at Fort Richardson and commanded by a major general.
Early Army involvement in Alaska

The U.S. Army's important history in the Great Land began at the very moment Alaska became American soil on October 18, 1867. Elements of the 9th Infantry were on hand as the Russian Golden Eagle was lowered and the Stars and Stripes were raised in Sitka, which then became headquarters for the Alaska Military District.
Charged with maintaining law and order in the new territory, U.S. Army soldiers helped quell uprisings and built new forts at Wrangell, St. Paul Canal, Kodiak Island, and on the Kenai Peninsula. They also enforced regulations regarding the killing of fur seals, whose population had been severely depleted during the Russian reign.
The Army relinquished control of Alaska to the U.S. Treasury Department in 1877, but did not entirely leave the territory. The Signal Corps operated weather stations, and a number of officers led small geographic explorations to learn more about the territory. These expeditions into various parts of Alaska continued through the turn of the 20th Century, as mapmaking and road and bridge building expanded the frontier. The Klondike Gold Rush in Yukon Territory, Canada, and later gold rushes in Alaska helped that expansion, as thousands of people poured into Alaska.
Early 20th Century
Although the Royal Canadian Mounted Police maintained law and order in the Yukon during the Gold Rush, the U.S. government, after sending Captain Patrick H. Ray and First Lieutenant Wilds P. Richardson to study the situation, did not deem it necessary to send the Army into Alaska as peacekeepers. As more and more people came into Alaska and northwestern Canada, the need for better communications with the lower 48 states became critical. The Washington-Alaska Military Cable and Telegraph System (WAMCATS) connected all the forts in the territory with Seattle. By 1903, the line stretched from Seattle to southeastern Alaska, Valdez, the interior, and Nome. The project fell under the direction of Brigadier General Adolphus W. Greely. Lieutenant William "Billy" Mitchell, another officer who would later achieve military fame, also worked on the four-year project.
While Greely and his men struggled to complete the WAMCATS project, Richardson, on his third tour of duty in Alaska, headed the Alaska Road Commission, building garrisons and trails in south-central Alaska. The Army in Alaska saw a decline in activity from 1908 to 1939, with a brief surge during World War I. Work continued building roads and bridges and improving trails during this period.
Alaska during World War II
Military construction in Alaska accelerated in 1940 as the world prepared for another great war. Ladd Field, near Fairbanks, was built as a cold-weather test station and Fort Richardson, named for Wilds P. Richardson, was built near Anchorage. Colonel Simon B. Buckner assumed command of the Alaska Defense Force in 1940, achieving the rank of Major General during his following three-year tenure in what evolved into the Alaska Department.
Through the Lend-Lease Program, the United States transferred nearly 8,000 aircraft to the Soviet Union at Ladd Field, which later became Fort Wainwright. The aircraft were flown from Great Falls, Montana, to Ladd Field by American crews. Russian crews then flew the planes to Siberia and on to the Russian Front. The pilots leaving Great Falls followed a series of small airfields that became known as the Northwest Staging Route. One of those airfields, Big Delta Airfield, later became Fort Greely, providing ample acreage large scale training exercises, northern warfare training and extreme cold weather testing.
Following the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941, Army and Navy engineers began building airstrips in the Aleutian Islands to defend against possible Japanese attacks. U.S. Army units also built an initial pioneer road in 1942 for the Alaska-Canada (ALCAN) Highway in less than eight months. In 1943, civilian contractors followed and constructed a more permanent, all-weather highway. The 1,420-mile road was built as an overland supply route to get personnel and equipment to Alaska. The ALCAN Highway complimented military infrastructure that was built throughout Alaska than ensured Allied forces could defend the territory and carry the fight to the enemy, if necessary.
Main Article: Aleutian Islands Campaign Alaska was the only American soil on which ground fighting occurred during World War II, this following the Japanese bombing of Dutch Harbor and seizure of Attu and Kiska islands in the Aleutian Chain in June, 1942. The successful battle by the U.S. to retake Attu Island in May, 1943, was proportionately one of the most costly amphibious assaults of World War II in the Pacific in terms of American casualties suffered. The Japanese secretly evacuated Kiska in late-July, 1943, several weeks prior to U.S. and Canadian forces seizing the island in mid-August, 1943. At the end of the war, most Army installations throughout the state closed permanently or transferred to other agencies. Postwar emphasis turned to training.
Post World War II: USARAL
The Alaskan Command (ALCOM) was created in January, 1947. As the first Unified Command under the Department of Defense, ALCOM was headquartered at Elmendorf Air Force Base near Anchorage where it controlled all military forces in Alaska.
The Alaskan Department changed its name again in 1947. The new name for the headquarters for all Army personnel in Alaska became U.S. Army Alaska, or USARAL. Military missions assigned to USARAL included ground and air defense of Alaska, with priority to the Anchorage and Fairbanks areas; development of cold-weather and mountain-warfare doctrines; conducting a cold-weather and mountain school at Fort Greely; providing logistical support to Air Force and Navy elements in Alaska; conducting National Guard and U.S. Army Reserve training; supervising Reserve Officer Training Corps activities; and, providing internal security, including plans for recovery from nuclear attack. By 1959, several Nike Hercules missile battalions were activated in the Anchorage and Fairbanks areas which operated under the last unit inactivated in 1979.
The Army established the Yukon Command at Ladd Air Force Base as a component of the U.S. Army Alaska (USARAL) with the mission of point defense of U.S. military installations north of the Alaska Range. Consequently, infantry and anti-aircraft units comprised most of the Army presence at Ladd AFB during the 1950s. Elements of the 4th Regimental Combat Team arrived at Ladd AFB in 1950, and the 1st Battle Group, 9th "Manchu" Infantry Regiment took its place in 1956. At some time by December, 1957, the 1st Battle Group, 9th "Manchu" Infantry was split between Ladd AFB and Eielson AFB, with the headquarters being at Eielson AFB and some of the line companies (C Company, for one) remaining at Ladd AFB. That configuration remained until at least December, 1959. The 4th AAA Group was stationed at Ladd until 1958. In 1959, a NIKE battalion equipped with nuclear-capable Nike Hercules surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) took over the interior defense mission.
Later two battalions of Nike missiles were stationed in Alaska: 4th Battalion (later 1st Battalion), 43rd Air Defense Artillery Regiment, and 2d Battalion, 562nd Air Defense Artillery Regiment. The two battalions and their direct support ordnance companies fell under the command of the USARAL Artillery Group, headquartered at Fort Richardson.[2] The Group was directly responsible to the USARAL Commanding General for Army participation in the air defense of Alaska, which involved Nike Hercules batteries, fighter interceptors, and the associated early warning radars and communications systems.
In 1964 the USARAL Air Defense Artillery Group, composed of two Nike-Hercules missile battalions, was activated and moved its offices from Building 1 to building 656, Fort Richardson. The USARAL Air Defense Artillery Group was renamed the 87th Artillery Group (Air Defense) in January 1968.[3] 4-43 ADA defended Anchorage while 2-562 ADA provided area defense around Fairbanks. The 4/43 was redesignated as the 1st Battalion, 43rd Air Defense Artillery in 1971. It was at that time that the 2/562 ADA was deactivated. In March 1971 the Department of the Army announced its decision to close the remaining Fairbanks area missile sites of the 2/562 Artillery, the 166th Ordinance, and the 87th Artillery Group by the end of June 1971.
USARAL's combat units officially reorganized in July, 1963, into the 172nd Infantry Brigade Mechanized) at Fort Richardson and the 171st Infantry Brigade (Mechanized) at Fort Wainwright. The two brigades were re-designated as Light Infantry Brigades in 1969.
Home of the 6th Infantry Division
USARAL was discontinued as a major subordinate command on December 31, 1972, and the 172nd Infantry Brigade (Alaska), headquartered at Fort Richardson, assumed command and control, reporting to U.S. Army Forces Command at Fort McPherson, Georgia. The 171st Infantry Brigade was inactivated in 1973 leaving the reorganized 172nd Infantry Brigade (Separate) as the principal combat formation, split-stationed at both Fort Richardson and Fort Wainwright
The 6th Infantry Division (Light), headquartered at Fort Richardson, was activated in 1986, replacing 172nd Infantry Brigade (Separate). The 6th ID (L) Division headquarters moved to Fort Wainwright in 1990. The 6th 1D (L) maintained an Arctic focus in its unit training and was actively involved in training exercises in Japan and Thailand, at the Joint Readiness Training Center in Arkansas and Louisiana, and throughout Alaska until its inactivation in July 1994. At that time, Army forces in Alaska reorganized under the command of U.S. Army Alaska (USARAK), headquartered at Fort Richardson, with the 172nd Infantry Brigade as the principal combat formation, split-stationed at both Fort Richardson and Fort Wainwright.
1993 onwards: USARAK
The command was activated after the Department of the Army's decision in March 1993 to inactivate the 6th Infantry Division (Light), which was then the principal Army unit in Alaska.
Current Structure
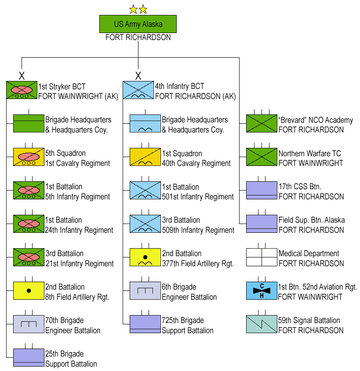

United States Army Alaska commands two brigade combat teams, an NCO Academy, the US Army's Northern Warfare Training Center (NWTC), and the United States Army garrisons in Alaska, as well as tenant organizations and Reserve Component units.[4]
Major units under the United States Army Alaska command are:
- based at Fort Wainwright
- 1st Stryker Brigade Combat Team, 25th Infantry Division
- Northern Warfare Training Center at Fort Wainwright
- based at Fort Richardson
- 4th Airborne Brigade Combat Team, 25th Infantry Division
- Noncommissioned Officer Academy
- 17th Combat Sustainment Support Battalion
- Army Field Support Battalion-Alaska
- 59th Signal Battalion (part of 516th Signal Brigade)
The reserve component units located throughout the state include:
- Alaska Army National Guard:
- 297th Battlefield Surveillance Brigade (formed from the 207th Infantry Group (Scout) in 2008)
- 1st Battalion, 207th Aviation Regiment
- United States Army Reserve:
- 2nd Battalion, 196th Infantry Brigade
- Company B, 411th Engineer Battalion
See also
- List of Nike missile locations - for USARAL missile locations in 1950s
References
- 1 2 "Special Unit Designations". United States Army Center of Military History. 21 April 2010. Retrieved 12 July 2010.
- ↑ U.S. Army Alaska, 'Nike Operations in Alaska,' Chapter 4
- ↑ Woodman, Duty Station Northwest, Vol. 111, p. 154, cited at http://nikealaska.org/87th/87th.html
- ↑ "USARAK Media Page". US Army. 16 March 2016. Archived from the original on 9 August 2016. Retrieved 2016-08-09.
External links
- United States Army Alaska, Official homepage
- United States Army Alaska, Nike Operations in Alaska


