VisSim
|
| |
| Paradigm | Modular, Visual Programming, Simulation language |
|---|---|
| Developer | Visual Solutions |
| First appeared | 1989 |
| Stable release |
Version 9
/ january 2015 |
| OS | Windows |
| License | Proprietary software |
| Filename extensions | .VSM |
| Website | http://www.vissim.com |
| Influenced by | |
| C, Laboratory Workbench, AVS (Advanced Visualization System) | |
VisSim is a visual block diagram language for simulation of dynamical systems and model based design of embedded systems. It is developed by Visual Solutions of Westford, Massachusetts. It uses a graphical data flow paradigm to implement dynamic systems based on differential equations. Version 8 adds interactive UML OMG 2 compliant state chart graphs that are placed in VisSim diagrams. This allows easy modeling of state based systems like startup sequencing of process plants or serial protocol decoding.
Applications
VisSim is widely used in control system design and digital signal processing for multidomain simulation and design.[1] It includes blocks for arithmetic, Boolean, and transcendental functions, as well as digital filters, transfer functions, numerical integration and interactive plotting.[2] The most commonly modeled systems are aeronautical, biological/medical, digital power, electric motor, electrical, hydraulic, mechanical, process, thermal/HVAC and econometric.[1]
Academic use
Accredited educational institutions are allowed to site license VisSim v3.0 at no cost. The latest versions of VisSim and add-ons are also available to students and academic institutions at greatly reduced pricing.[2]
Distributing VisSim models
A read-only version of the software, VisSim Viewer, is available free of charge and provides a way for people not licensed to use VisSim to run VisSim models.[3] This program is intended to allow models to be more widely shared while preserving the model in its published form.[3] The viewer will execute any VisSim model, and only allows changes to block and simulation parameters to illustrate different design scenarios. Sliders and buttons may be activated if included in the model.
Code generation
The "VisSim/C-Code" add-on generates ANSI C code for the model, and generates target specific code for on-chip devices like PWM, ADC, encoder, GPIO, I2C etc. This is useful for development of embedded systems. After the behavior of the controller has been simulated, C-code can be generated, compiled and run on the target. For debugging, VisSim supports an interactive JTAG linkage, called "Hotlink", that allows interactive gain change and plotting of on-target variables. The VisSim generated code has been called efficient and readable, making it well suited for development of embedded systems.[4] VisSim's author served on the X3J11 ANSI C committee and wrote several C compilers, in addition to co-authoring a book on C.[5] This deep understanding of ANSI C, and the nature of the resulting machine code when compiled, is the key to the code generator's efficiency. VisSim can target small 16-bit fixed point systems like the Texas Instruments MSP430, using only 740 bytes flash and 64 bytes of RAM for a small closed-loop Pulse-width modulation (PWM) actuated system, as well as allowing very high control sample rates over 500 kHz on larger 32-bit floating point processors like the Texas Instruments 150 MHz F28335.
Use of model-based development
The technique of simulating system performance off-line, and then generating code from the simulation is known as "model-based development". Model-based development for embedded systems is becoming widely adopted for production systems because it shortens development cycles for hardware development in the same way that Model-driven architecture shortens production cycles for software development.[6]
Model building is a visual way of describing a situation. In an engineering context, instead of writing and solving a system of equations, model building involves using visual "blocks" to solve the problem. The advantage of using models is that in some cases problems which appear difficult if expressed mathematically may be easier to understand when represented pictorially.
VisSim uses a hierarchical composition to create nested block diagrams. A typical model would consist of "virtual plants" composed of various VisSim "layers", combined if necessary with custom blocks written in C or FORTRAN. A virtual controller can be added and tuned to give desired overall system response. Graphical control element such as sliders and buttons allow control of what-if analysis for operator training or controller tuning.
Although VisSim was originally designed for use by control engineers, it can be used for any type of mathematical model. An example is work done by Steve Keen, an economist.[7]
Optional features
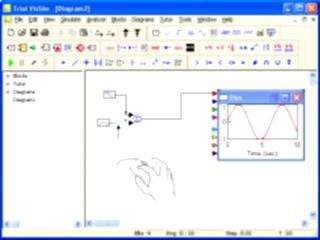 |
|
Screenshots show the simulation of a sine function in VisSim. Noise is added to the model, then filtered out using a Butterworth filter. The signal traces of the sine function with noise and filtered noise are first shown together, and then shown in separate windows in the plot block. |
| This video size: 50% (320x240 pixels) |
| Other size: 100% (640x480 pixels) |
- CAN bus (Controller-area network) packet read and write
- Communication system Physical layer simulation (modulators, encoders, PLLs, Costas Loop, BPSK, QPSK, DQPSK, QAM, Bit Error Rate (BER), Eye Diagram, Viterbi algorithm, Reed-Solomon, etc.)
- C code generation - Generates executable C code directly from the block diagram
- Electric motor simulation library for AC induction, Brushless DC, and Stepper motors
- Embedded system targeting for Texas Instruments C2000 and MSP430, ARM Cortex-M chips. Supports on-chip peripherals like serial ports, CAN, PWM, Quadrature Encoder Pulse (QEP), Event Capture, Serial Peripheral Interface Bus (SPI), I²C, Analog-to-digital converter (ADC), Digital-to-analog converter (DAC), and GPIO.
- Fixed-point arithmetic blockset for bit-true simulation and code generation
- Frequency domain analysis (Bode plot, Root locus, Nyquist plot)
- Global optimization of system parameters
- Neural networks
- OPC (OLE for process control) client gives read and write of OPC tags for real-time simulation of SCADA/HMI virtual plants
- Real-time analog signal and digital I/O under Windows
- Serial(RS-232/RS-485) serial data read and write. Allows real-time reading and writing of serial data from the VisSim diagram. It supports pattern matching, string based transmit, and simulated data streams.
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol) packet read and write. Allows real-time reading and writing of ethernet based UDP packets from the VisSim diagram
See also
References
- 1 2 Books on wide variety of technical subjects referencing VisSim on the Google Books Library Project
- 1 2 Visual simulation with student VisSim, by Karen Darnell, 1996, PWS Pub. Co., Boston, ISBN 0-534-95485-5
- 1 2 Viewer page on company website
- ↑ Graphical Environment for Modeling Control Systems in Full Scope Training Simulators
- ↑ Books on C by Peter A. Darnell and Philip E. Margolis
- ↑ Principles of model-driven architecture, Stephen J. Mellor, Addison-Wesley, 2004
- ↑ VisSim models by Steve Keen
- Texas Instruments MSP430 spotlight article published in IEEE magazine.
- VisSim web site
- Mechatronics System Design, by Devdas Shetty, Richard A. Kolk, Edition 2, Cengage Learning, 2011, ISBN 143906198X, ISBN 9781439061985
- C: A Software Engineering Approach, by Peter A Darnell, Philip E Margolis, 3rd edition, 1996, ISBN 978-0-387-94675-7
External links
- A Simulation-Aided Introduction with VisSim/Comm Digital Transmission Series: Signals and Communication Technology, Guimaraes, Dayan Adionel, 2010, ISBN 978-3-642-01358-4
- Dynamics of Energy Supply and Conversion Dr Perez-Blanco, Horacio, 2009, CRC Press, ISBN 978-1-4200-7688-2
- System Dynamics Exercises Dr Juan Martin Garcia, ISBN 84-609-9804-5
- Hybrid Intelligent Aircraft Landing Controller and Its Hardware Implementation, by Jih-gau Juang and Bo-Shian Lin in Advances in Natural Computation: Second International Conference, ICNC 2006, ISBN 978-3-540-45907-1