Beta Tauri
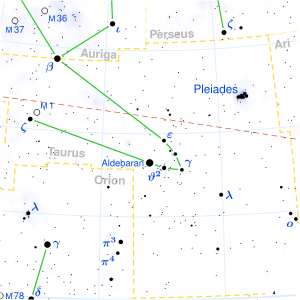 Elnath is the β star in Taurus (map: top left). | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Taurus |
| Right ascension | 05h 26m 17.5134s[1] |
| Declination | 28° 36′ 27.494″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 1.65[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B7III[1] |
| U−B color index | -0.49[2] |
| B−V color index | -0.13[2] |
| Variable type | None |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 9.2[1] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 23.28[1] mas/yr Dec.: -174.22[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 24.89 ± 0.88[1] mas |
| Distance | 131 ± 5 ly (40 ± 1 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | -1.34 |
| Details | |
| Mass | 5.0 ± 0.1[3] M☉ |
| Radius | 4.2[4] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 700[5] L☉ |
| Temperature | 13,824 ± 475[4] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | -0.10[1][6] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 82[1][7] km/s |
| Age | 100 ± 10[3] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Beta Tauri (β Tauri, abbreviated Beta Tau, β Tau), also named Elnath,[8] is the second-brightest star in the constellation of Taurus, with an apparent magnitude of 1.68.[1]
Nomenclature
Beta Tauri is the star's Bayer designation. Ptolemy considered the star to be shared by Auriga, and Johann Bayer assigned it a designation in both constellations: Beta Tauri and Gamma Aurigae (γ Aur). When the modern constellation boundaries were fixed in 1930, the latter designation dropped from use.[9]
The traditional name Elnath, variously El Nath or Alnath, comes from the Arabic word النطح an-naţħ, meaning "the butting" (i.e. the bull's horns). As in many other (but not all) Arabic star names, the article ال is transliterated literally as el, despite the fact that in Arabic pronunciation it is assimilated to the following n; it can also be omitted: Nath. In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[10] to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016[11] included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included Elnath for this star.
In Chinese, 五車 (Wǔ Chē), meaning Five Chariots, refers to an asterism consisting of β Tauri, ι Aurigae, Capella, β Aurigae and θ Aurigae.[12] Consequently, β Tauri itself is known as 五車五 (Wǔ Chē Wǔ; English: Fifth of the Five Chariots.)[13]
Properties
Elnath's absolute magnitude is -1.34, similar to another Taurean star, Maia in the Pleiadian star cluster. Like Maia, Elnath is a B-class giant with a luminosity 700 times solar.[5] However, being approximately 130 light-years distant compared to Maia's estimated 360 light-years, Elnath ranks as the second-brightest star in the constellation.
Uniquely positioned along the plane of the Milky Way Galaxy a few degrees west of the galactic anticenter, Elnath heralds a rich collection of nebulae and star clusters.[14] Relative to the Sun, β Tauri is notable for a high abundance of manganese, but little calcium and magnesium.[5][6] This star has begun to evolve away from the main sequence.
This star can be occulted by the moon. Such occultations occur when the moon's ascending node is near the vernal equinox, as was the case in 2007. Most occultations are visible only in parts of the Southern Hemisphere, because the star lies at the northern edge of the lunar occultation zone. Rarely, it may be occulted as far north as southern California.[15]
Double star
There is a faint star that appears close enough to Elnath for astronomers to consider it a double star. Its visual companion, known as BD+28 795B, has a PA of 239 degrees and is separated from the main star by 33.4 arcseconds.[16][17]
See also
- Lists of stars in the constellation Taurus
- Class B Stars
- Beta Tauri in fiction
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "SIMBAD query result: ELNATH -- Star in double system". Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2010-03-07.
- 1 2 3 Ducati, J. R. (2002). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Catalogue of Stellar Photometry in Johnson's 11-color system". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues. 2237: 0. Bibcode:2002yCat.2237....0D.
- 1 2 Janson, Markus; et al. (August 2011), "High-contrast Imaging Search for Planets and Brown Dwarfs around the Most Massive Stars in the Solar Neighborhood", The Astrophysical Journal, 736 (2): 89, arXiv:1105.2577
 , Bibcode:2011ApJ...736...89J, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/736/2/89
, Bibcode:2011ApJ...736...89J, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/736/2/89 - 1 2 Underhill, A. B.; et al. (November 1979), "Effective temperatures, angular diameters, distances and linear radii for 160 O and B stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 189 (3): 601–605, Bibcode:1979MNRAS.189..601U, doi:10.1093/mnras/189.3.601
- 1 2 3 Kaler, James B., ELNATH (Beta Tauri), University of Illinois, retrieved 2010-03-07
- 1 2 Heacox, W. D. (1979). "Chemical abundances in Hg-Mn stars". Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 41: 675. Bibcode:1979ApJS...41..675H. doi:10.1086/190637.
- ↑ Bernacca, P. L.; Perinotto, M. (1970). "A catalogue of stellar rotational velocities". Contr. Oss. Astrof. Padova in Asiago. 239. Bibcode:1970CoAsi.239....1B.
- ↑ "IAU Catalog of Star Names". Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- ↑ Bayer’s Uranometria and Bayer letters
- ↑ "IAU Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)". Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ↑ "Bulletin of the IAU Working Group on Star Names, No. 1" (PDF). Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- ↑ (Chinese) 中國星座神話, written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, ISBN 978-986-7332-25-7.
- ↑ (Chinese) 香港太空館 - 研究資源 - 亮星中英對照表, Hong Kong Space Museum. Accessed on line November 23, 2010.
- ↑ Nemiroff, R.; Bonnell, J., eds. (5 March 2010). "Deep Auriga". Astronomy Picture of the Day. NASA. Retrieved 2010-03-07.
- ↑ Abrams Planetarium - Skywatcher's Diary Archived August 30, 2007, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "CCDM (Catalog of Components of Double & Multiple stars (Dommanget+ 2002)". VizieR. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2010-03-07.
- ↑ "Al Nath". Alcyone Bright Star Catalogue. Retrieved 2010-03-07.
External links
- Jim Kaler's Stars:Elnath
- NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day: Image of Elnath (5 March 2010)
Coordinates: ![]() 05h 26m 17.5134s, +28° 36′ 27.494″
05h 26m 17.5134s, +28° 36′ 27.494″
