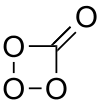
Carbon tetroxide
"CO4" redirects here. For the Colchester postal district, see CO postcode area.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2,3-Trioxetan-4-one | |||
| Other names
4-Trioxetanone | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 853179-44-9 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CO4 | |||
| Molar mass | 76.01 g·mol−1 | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Carbon tetroxide is a highly unstable oxide of carbon with formula CO
4. It was proposed as an intermediate in the O-atom exchange between carbon dioxide (CO
2) and oxygen (O
2) at high temperatures.[1]
References
- ↑ Yeung, L. Y.; Okumura, M.; Paci, J. T.; Schatz, G. C.; Zhang, J.; Minton, T. K. (2009). "Hyperthermal O-Atom Exchange Reaction O2 + CO2 through a CO4 Intermediate". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 131 (39): 13940–13942. doi:10.1021/ja903944k.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/28/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.