Hexahydroxybenzene trisoxalate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hexahydroxybenzene trisoxalate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2,3,6,7,10,11-hexahydro-1,4,5,8,9,12-hexaoxatriphenylene-2,3,6,7,10,11-hexone | |
| Other names
1,4,5,8,9,12-hexaoxatriphenylene-2,3,6,7,10,11-hexone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 28426725 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12O12 | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
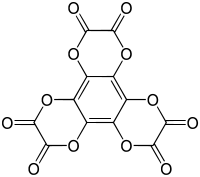
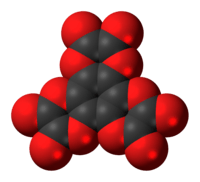
Hexahydroxybenzene trisoxalate is a chemical compound, an oxide of carbon with formula C
12O
12. Its molecule consists of a benzene core with the six hydrogen atoms replaced by three oxalate groups. It can be seen as a sixfold ester of benzenehexol and oxalic acid.
The compound was first described by H. S. Verter and R. Dominic in 1967.[1]
See also
- Tetrahydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone bisoxalate
- Tetrahydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone biscarbonate
- Hexahydroxybenzene triscarbonate
References
- ↑ H. S. Verter, R. Dominic (1967), A new carbon oxide: synthesis of hexahydroxybenzene tris oxalate. Tetrahedron, Volume 23, Issue 10, , Pages 3863-3864 doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)97894-9
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/20/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.