Lesogaberan
Lesogaberan
 |
 |
| Names |
| IUPAC name
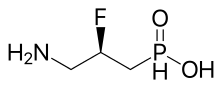
((R)-3-Amino-2-fluoropropyl)phosphinic acid |
| Other names
AZD-3355 |
| Identifiers |
| |
344413-67-8  Y= Y=  Y Y |
| 3D model (Jmol) |
Interactive image |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL448343  N N |
| ChemSpider |
23254384  N N |
| ECHA InfoCard |
100.133.162 |
| |
7705 |
| PubChem |
9833984 |
| UNII |
4D6Q6HGC7Z  Y Y |
InChI=1S/C3H9FNO2P/c4-3(1-5)2-8(6)7/h3,8H,1-2,5H2,(H,6,7)/t3-/m1/s1  N NKey: LJNUIEQATDYXJH-GSVOUGTGSA-N  N NInChI=1/C3H9FNO2P/c4-3(1-5)2-8(6)7/h3,8H,1-2,5H2,(H,6,7)/t3-/m1/s1 Key: LJNUIEQATDYXJH-GSVOUGTGBQ
|
| |
| Properties |
| |
C3H9FNO2P |
| Molar mass |
141.08 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
 N verify (what is N verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) |
| Infobox references |
|
|
Lesogaberan (AZD-3355) was[1] an experimental drug candidate developed by AstraZeneca for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).[2] As a GABAB receptor agonist,[3] it has the same mechanism of action as baclofen, but is anticipated to have fewer of the central nervous system side effects that limit the clinical use of baclofen for the treatment of GERD.[4]
References
- ↑ AstraZeneca. "AZD3355". Retrieved 30 December 2011.
- ↑ Bredenoord, Albert J. (2009). "Lesogaberan, a GABAB agonist for the potential treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease". IDrugs. 12 (9): 576–584. PMID 19697277.
- ↑ Alstermark; Amin, K; Dinn, SR; Elebring, T; Fjellström, O; Fitzpatrick, K; Geiss, WB; Gottfries, J; et al. (2008). "Synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation of Novel γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type B (GABAB) Receptor Agonists as Gastroesophageal Reflux Inhibitors". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 51 (14): 4315–4320. doi:10.1021/jm701425k. PMID 18578471.
- ↑ Brian E. Lacy; Robert Chehade; Michael D. Crowell (2010). "Lesogaberan". Drugs of the Future. 35 (12): 987–992. doi:10.1358/dof.2010.035.012.1540661.
|
|---|
|
Receptor
(ligands) | | Agonists | |
|---|
| PAMs |
- (Abridged; see here for a full list): α-EMTBL
- Alcohols (e.g., ethanol)
- Anabolic steroids
- Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin)
- Barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital)
- Benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam)
- Bromide compounds (e.g., potassium bromide)
- Carbamates (e.g., meprobamate)
- Carbamazepine
- Chloralose
- Chlormezanone
- Clomethiazole
- Dihydroergolines (e.g., ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine))
- Etazepine
- Etifoxine
- Fenamates (e.g., mefenamic acid)
- Flavonoids (e.g., apigenin, hispidulin)
- Fluoxetine
- Flupirtine
- Imidazoles (e.g., etomidate)
- Kava constituents (e.g., kavain)
- Lanthanum
- Loreclezole
- Monastrol
- Neuroactive steroids (e.g., allopregnanolone, cholesterol)
- Niacin
- Nicotinamide (niacinamide)
- Nonbenzodiazepines (e.g., β-carbolines (e.g., abecarnil), cyclopyrrolones (e.g., zopiclone), imidazopyridines (e.g., zolpidem), pyrazolopyrimidines (e.g., zaleplon))
- Norfluoxetine
- Petrichloral
- Phenols (e.g., propofol)
- Phenytoin
- Piperidinediones (e.g., glutethimide)
- Propanidid
- Pyrazolopyridines (e.g., etazolate)
- Quinazolinones (e.g., methaqualone)
- Retigabine (ezogabine)
- ROD-188
- Skullcap constituents (e.g., baicalin)
- Stiripentol
- Sulfonylalkanes (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal))
- Topiramate
- Valerian constituents (e.g., valerenic acid)
- Volatiles/gases (e.g., chloral hydrate, chloroform, diethyl ether, paraldehyde, sevoflurane)
|
|---|
| Antagonists | |
|---|
| NAMs |
- 1,3M1B
- 3M2B
- 17-Phenylandrostenol
- α5IA (LS-193,268)
- β-CCB
- β-CCE
- β-CCM
- β-CCP
- β-EMGBL
- Anabolic steroids
- Amiloride
- Anisatin
- β-Lactams (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems)
- Basmisanil
- Bemegride
- Bilobalide
- CHEB
- Cicutoxin
- Cloflubicyne
- Cyclothiazide
- DHEA
- DHEA-S
- Dieldrin
- (+)-DMBB
- DMCM
- DMPC
- EBOB
- Etbicyphat
- FG-7142 (ZK-31906)
- Fiproles (e.g., fipronil)
- Flavonoids (e.g., amentoflavone, oroxylin A)
- Flumazenil
- Fluoroquinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin)
- Flurothyl
- Furosemide
- Iomazenil (123I)
- Isoallopregnanolone
- Isopregnanolone (sepranolone)
- L-655,708
- Laudanosine
- Leptazol
- Lindane
- MaxiPost
- Morphine
- Morphine-3-glucuronide
- MRK-016
- Naloxone
- Naltrexone
- Nicardipine
- Non-steroidal antiandrogens (e.g., apalutamide, bicalutamide, enzalutamide, flutamide, nilutamide)
- Oenanthotoxin
- Pentetrazol (metrazol)
- Phenylsilatrane
- Picrotoxin (i.e., picrotin and picrotoxinin)
- Pregnenolone sulfate
- Propybicyphat
- PWZ-029
- Radequinil
- Ro 15-4513
- Ro 19-4603
- RO4882224
- RO4938581
- Sarmazenil
- SCS
- Suritozole
- TB-21007
- TBOB
- TBPS
- TCS-1105
- Terbequinil
- TETS
- Thujone
- U-93631
- Zinc
- ZK-93426
|
|---|
|
|---|
| | Agonists | |
|---|
| PAMs | |
|---|
| Antagonists | |
|---|
| NAMs | |
|---|
|
|---|
| | Agonists | |
|---|
| Antagonists | |
|---|
| NAMs | |
|---|
| PAMs | |
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
|
Transporter
(blockers) | |
|---|
|
Enzyme
(inhibitors) | |
|---|
|
| Others | Precursors | |
|---|
| Analogues | |
|---|
| Others | |
|---|
|
|---|
|
See also: GHBergics • Glutamatergics • Glycinergics |

