Pantetheine
Not to be confused with pantethine.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
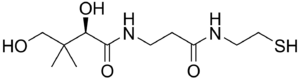
| IUPAC name
2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-N-[2-(2-sulfanylethylcarbamoyl)ethyl]butanamide | |
| Other names
Pantetheine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 496-65-1 R | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| 3DMet | B00185 |
| 1714196 R | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:16753 |
| ChemSpider | 466 388453 R |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.114 |
| EC Number | 207-824-1 |
| KEGG | C00831 |
| MeSH | Pantetheine |
| PubChem | 479 439322 R |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H22N2O4S | |
| Molar mass | 278.37 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Pantethine |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Pantetheine is the cysteamine amide analog of pantothenic acid (vitamin B5). The dimer of this compound, pantethine is more commonly known, and is considered to be a more potent form of vitamin B5 than pantothenic acid. Pantetheine is an intermediate in the production of coenzyme A by the body.[1]
References
- ↑ MB Hoagland, GD Novelli (1954). "Biosynthesis of coenzyme A from phosphopantetheine and of pantetheine from pantothenate". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 207: 767–773.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/26/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
