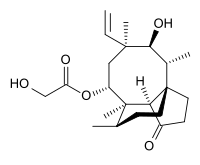
Pleuromutilin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(4R,5S,6S,8R,9aR,10R)-6-Ethenyl-5-hydroxy-4,6,9,10-tetramethyl-1-oxodecahydro-3a,9-propanocyclopenta[8]annulen-8-yl hydroxyacetate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 125-65-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL497295 |
| ChemSpider | 8061754 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.316 |
| KEGG | C09169 |
| PubChem | 9886081 |
| UNII | 3DE4A80MZ1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H34O5 | |
| Molar mass | 378.509 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Pleuromutilin and its derivatives are antibacterial drugs that inhibit protein synthesis in bacteria by binding to the peptidyl transferase component of the 50S subunit of ribosomes.[1][2]
This class of antibiotics includes the licensed drugs retapamulin (approved for topical use in humans), valnemulin and tiamulin (approved for use in animals) and the investigational drugs azamulin and lefamulin (BC-3781).
History
Pleuromutilin was first discovered as an antibiotic in 1950.[3] It is derived from the fungus Clitopilus passeckerianus (formerly Pleurotus passeckerianus), and has also been found in Drosophila subatrata, Clitopilus scyphoides, and some other Clitopilus species.[4]
References
- ↑ Long, Katherine S; Lykke H. Hansen; Lene Jakobsen; Birte Vester (April 2006). "Interaction of Pleuromutilin Derivatives with the Ribosomal Peptidyl Transferase Center" (PDF). Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 50 (4): 1458–1462. doi:10.1128/AAC.50.4.1458-1462.2006. PMC 1426994
 . PMID 16569865.
. PMID 16569865. - ↑ Lolk, L.; Pøhlsgaard, J.; Jepsen, A. S.; Hansen, L. H.; Nielsen, H.; Steffansen, S. I.; Sparving, L.; Nielsen, A. B.; Vester, B.; Nielsen, P. (2008). "A Click Chemistry Approach to Pleuromutilin Conjugates with Nucleosides or Acyclic Nucleoside Derivatives and Their Binding to the Bacterial Ribosome". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 51 (16): 4957–4967. doi:10.1021/jm800261u. PMID 18680270.
- ↑ Novak, R; Shlaes DM (February 2010). "The pleuromutilin antibiotics: a new class for human use". Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs. 11 (2): 182–91. PMID 20112168.
- ↑ Kilaru, Sreedhar; Catherine M. Collins; Amanda J. Hartley; Andy M. Bailey; Gary D. Foster (2009-09-18). "Establishing Molecular Tools for Genetic Manipulation of the Pleuromutilin-Producing Fungus Clitopilus passeckerianus". Appl Environ Microbiol. American Society for Microbiology. 75 (22): 7196–7204. doi:10.1128/AEM.01151-09. PMC 2786515
 . PMID 19767458.
. PMID 19767458.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/12/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.