1965 in spaceflight
For launches in the first quarter of the year, see 1965 in spaceflight (January–March), for launches in the second quarter, see 1965 in spaceflight (April–June), for the third quarter see 1965 in spaceflight (July–September) and for the fourth quarter see 1965 in spaceflight (October–December).
|
Launch of a Delta D rocket carrying the first commercial geosynchronous communications satellite, Intelsat I F1 | |
| Orbital launches | |
|---|---|
| First | 11 January |
| Last | 28 December |
| Total | 124 |
| Successes | 108 |
| Failures | 15 |
| Partial failures | 1 |
| Catalogued | 112 |
| National firsts | |
| Satellite |
|
| Orbital launch |
|
| Rockets | |
| Maiden flights |
Atlas LV-3C Centaur-D Delta E Diamant-A Kosmos-2M Scout A Scout B Soyuz/Vostok 11A510 Thor LV-2D Burner-1 Thor LV-2D MG-18 Titan IIIC UR-500 (Proton) |
| Retirements |
Atlas LV-3A Agena-B Atlas LV-3C Centaur-C Delta D Kosmos-1 Molniya 8K78 Molniya-L 8K78L Saturn I Scout X-4 Thor DSV-2A Ablestar Thor LV-2D MG-18 Thor SLV-2 Agena-B Titan IIIA |
| Manned flights | |
| Orbital | 6 |
| Total travellers | 13 |
Deep Space Rendezvous
| Date (UTC) | Spacecraft | Event | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 February | Ranger 8 | Lunar impact | Impacted Mare Tranquillitatis at 09:57:37, returned 7,137 images |
| 24 March | Ranger 9 | Lunar impact | Impacted Alphonsus Crater at 14:08:20, returned 5,814 images |
| 12 May | Luna 5 | Lunar impact | Failed lander, impacted at 19:10 |
| 11 June | Luna 6 | Lunar flyby | Failed lander, closest approach: 160,000 kilometres (99,000 mi) |
| 15 July | Mariner 4 | Flyby of Mars | Returned 21 images |
| 20 July | Zond 3 | Lunar flyby | Returned 25 images |
| 6 August | Zond 4 | Flyby of Mars | Communications system failed before flyby |
| 7 October | Luna 7 | Lunar impact | Failed lander, impacted at 22:08 |
| 6 December | Luna 8 | Lunar impact | Failed lander, impacted at 21:51:30 |
EVAs
| Start Date/Time | Duration | End Time | Spacecraft | Crew | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 March 08:34 |
12 minutes | 08:47 | Voskhod 2 | First EVA in history.[1] Leonov had difficulty fitting back into the spacecraft due to spacesuit stiffness in vacuum. He vented air from his spacesuit to bend back into the capsule.[2] | |
| 3 June 19:46 |
20 minutes | 20:06 | Gemini IV | First US EVA.[3] White also had difficulty returning to the Gemini spacecraft. Although very fit, the effort left White exhausted.[4] |
Orbital launch summary
By country
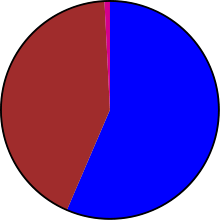 |
| |||||||
| Orbital launch attempts by country in 1965 | ||||||||
| Country | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | First orbital launch |
| | 53 | 46 | 7 | 0 | |
| | 70 | 61 | 8 | 1 |
By rocket
| Rocket | Country | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atlas D | | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | Suborbital component of one failed launch was successful |
| Atlas LV-3A Agena-B | | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Retired |
| Atlas LV-3A Agena-D | | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Atlas SLV-3 Agena-D | | 11 | 9 | 2 | 0 | |
| Atlas LV-3C Centaur-C | | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Retired |
| Atlas LV-3C Centaur-D | | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight |
| Delta C | | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0 | |
| Delta D | | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Retired |
| Delta E | | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight |
| Diamant A | | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight |
| Kosmos-1 63S3 | | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | Retired |
| Kosmos-2I 63S1 | | 7 | 4 | 3 | 0 | |
| Kosmos-2M 63S1M | | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight |
| Molniya 8K78 | | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 | Retired |
| Molniya-L 8K78L | | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Retired |
| Molniya-M 8K78M | | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0 | |
| Saturn I | | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | Retired |
| Scout A | | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight |
| Scout B | | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight |
| Scout X-4 | | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | Retired |
| Soyuz/Vostok 11A510 | | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight |
| Thor DSV-2A Ablestar | | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | Retired |
| Thor LV-2D Burner-1 | | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight |
| Thor LV-2D MG-18 | | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Only flights |
| Thor SLV-2 Agena-B | | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | Retired |
| Thor SLV-2 Agena-D | | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| Thrust Augmented Thor SLV-2A Agena-D | | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0 | |
| Titan II GLV | | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | Also made one suborbital launch |
| Titan IIIA | | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Retired |
| Titan IIIC | | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Maiden flight |
| Voskhod 11A57 | | 12 | 12 | 0 | 0 | |
| Vostok-2 8A92 | | 8 | 7 | 1 | 0 | |
| Vostok-2M 8A92M | | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| UR-500 (Proton) 8K72 | | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | Maiden flight |
By orbit
| Orbital regime | Launches | Achieved | Not Achieved | Accidentally Achieved |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Earth | 96 | 85 | 9 | 2 | |
| Medium Earth | 7 | 6 | 1 | 0 | |
| High Earth | 13 | 11 | 2 | 0 | Including Highly elliptical and Molniya orbits |
| Geosynchronous/transfer | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1* | * - One launch to geosynchronous orbit reached geosynchronous transfer orbit |
| Heliocentric | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
References
|
Generic references:
|
Footnotes
- ↑ Alexander Anikeev (2008). "Spacecraft "Voskhod-2" web page". Manned Astronautics: Figures and Facts website. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ Mark Wade (2008). "Leonov web page". Encyclopedia Astronautica web site. Archived from the original on 23 December 2008. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- ↑ David R. Williams (2004). "The First U.S. Spacewalk - Gemini 4". Lunar and Planetary Science. NASA. Retrieved 2009-12-28.
- ↑ Cernan, Eugene; Don Davis (1999). The Last Man on the Moon. New York: St. Martin's Press. p. 83. ISBN 0-312-19906-6.
| Timeline of spaceflight | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1940s | 1944 | 1945 | 1946 | 1947 | 1948 | 1949 | ||||
| 1950s | 1950 | 1951 | 1952 | 1953 | 1954 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 |
| 1960s | 1960 | 1961 | 1962 | 1963 | 1964 | 1965 | 1966 | 1967 | 1968 | 1969 |
| 1970s | 1970 | 1971 | 1972 | 1973 | 1974 | 1975 | 1976 | 1977 | 1978 | 1979 |
| 1980s | 1980 | 1981 | 1982 | 1983 | 1984 | 1985 | 1986 | 1987 | 1988 | 1989 |
| 1990s | 1990 | 1991 | 1992 | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 |
| 2000s | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 |
| 2010s | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/8/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
