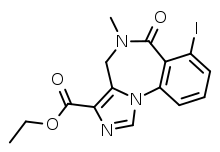
Iomazenil
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Ro 16-0154 |
| CAS Number |
127985-21-1 127396-36-5 (123I) |
| PubChem (CID) | 65959 |
| ChemSpider | 59362 |
| UNII |
7DVX185FLQ Template:UNII (123I) Template:UNII (123I) |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2105020 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H14123IN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 407.290 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Iomazenil (also known as Ro16-0154, INN, USAN; benzodine) is an antagonist and partial inverse agonist of benzodiazepine and a potential treatment for alcohol abuse. The compound was introduced in 1989 by pharmaceutical company Hoffmann-La Roche as an Iodine-123-labelled SPECT tracer for imaging benzodiazepine receptors (GABAA receptors) in the brain. Iomazenil is an analogue of flumazenil (Ro15-1788).[1]
Use in brain research
123I-labelled iomazenil can be used to image epileptic seizure foci as an alternative to 18F-fludeoxyglucose PET imaging.[2][3]
The effect of iomazenil of reducing levels of GABA in the brain was used by researchers to exacerbate symptoms in patients with schizophrenia in a laboratory study, supporting the theory that a GABA deficiency underlies that disease.[4]
Alcohol treatment
Researcher Deepak D'Souza and colleagues at Yale University and Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System are testing iomazenil as a potential treatment for drunkenness due to its ability to bind alcohol receptors in the brain.[5]
References
- ↑ Höll, K; Deisenhammer E; Dauth J; Carmann H; Schubiger PA (1989). "Imaging benzodiazepine receptors in the human brain by single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)". Int J Rad Appl Instrum B. 16 (8): 759–63.
- ↑ Kung, Hank F.; Mei-Ping Kung; Seok Rye Choi (January 2003). "Radiopharmaceuticals for single-photon emission computed tomography brain imaging". Seminars in Nuclear Medicine. 33 (1): 2–13. doi:10.1053/snuc.2003.127296. PMID 12605353.
- ↑ Goethals, I; Van de Wiele C; Boon P; Dierckx R (February 2003). "Is central benzodiazepine receptor imaging useful for the identification of epileptogenic foci in localization-related epilepsies?". Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 30 (2): 325–8.
- ↑ Ahn, Kyungheup; Gil R; Seibyl J; Sewell RA; D'Souza DC (February 2011). "Probing GABA receptor function in schizophrenia with iomazenil". Neuropsychopharmacology. Nature Publishing Group. 36 (3): 677–83. doi:10.1038/npp.2010.198. PMC 3055690
 . PMID 21068719.
. PMID 21068719. - ↑ Dobson, Roger; Jonathan Owen (13 May 2012). "Tests begin on new drink-busting drug". Independent on Sunday. Retrieved 20 May 2012.
External links
- [123I]Iomazenil, Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database, NCBI
- Effects of Delta-9-THC and Iomazenil in Healthy Humans, Clinicaltrials.gov
- Ability of Partial Inverse Agonist, Iomazenil, to Block Ethanol Effects in Humans