Strasbourg
| Part of the series on |
| Alsace |
|---|
.svg.png) Rot un Wiss, flag of Alsace since 11th century. |
|
(including Lorraine) |
|
|
Alsace in the EU |
|
Related topics |
|
Strasbourg (/ˈstræzbɜːrɡ/, French pronunciation: [stʁaz.buʁ, stʁas.buʁ]; Alsatian: Strossburi; German: Straßburg, [ˈʃtʁaːsbʊɐ̯k]) is the capital and largest city of the Grand Est region of France and is the official seat of the European Parliament. Located close to the border with Germany in the historic region of Alsace, it is the capital of the Bas-Rhin département. In 2013, the city proper had 275,718 inhabitants, the Eurométropole de Strasbourg (Greater Strasbourg) had 475,934 inhabitants, the Arrondissement of Strasbourg had 482,384 inhabitants and Strasbourg's metropolitan area had a population of 773,347 (not counting the section across the border in Germany), making it the ninth largest metro area in France and home to 13% of the Grand Est region's inhabitants. The transnational Eurodistrict Strasbourg-Ortenau had a population of 915,000 inhabitants in 2014.[5]
Strasbourg is the seat of several European institutions, such as the Council of Europe (with its European Court of Human Rights, its European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines and its European Audiovisual Observatory) and the Eurocorps, as well as the European Parliament and the European Ombudsman of the European Union. The city is also the seat of the Central Commission for Navigation on the Rhine and the International Institute of Human Rights.[6]
Strasbourg's historic city centre, the Grande Île (Grand Island), was classified a World Heritage site by UNESCO in 1988, the first time such an honour was placed on an entire city centre. Strasbourg is immersed in the Franco-German culture and although violently disputed throughout history, has been a bridge of unity between France and Germany for centuries, especially through the University of Strasbourg, currently the second largest in France, and the coexistence of Catholic and Protestant culture. The largest Islamic place of worship in France, the Strasbourg Grand Mosque, was inaugurated by French Interior Minister Manuel Valls on 27 September 2012.[7]
Economically, Strasbourg is an important centre of manufacturing and engineering, as well as a hub of road, rail, and river transportation. The port of Strasbourg is the second largest on the Rhine after Duisburg, Germany.[8]
Etymology and names
The city's Gallicized name (Lower Alsatian: Strossburi, [ˈʃd̥rɔːsb̥uri]; German: Straßburg, [ˈʃtʁaːsbʊɐ̯k]) is of Germanic origin and means "Town (at the crossing) of roads". The modern Stras- is cognate to the German Straße and English street, all of which are derived from Latin strata ("paved road"), while -bourg is cognate to the German Burg and English borough, all of which are derived from Proto-Germanic *burgz ("hill fort, fortress").
Geography
Location

Strasbourg is situated on the eastern border of France with Germany. This border is formed by the River Rhine, which also forms the eastern border of the modern city, facing across the river to the German town Kehl. The historic core of Strasbourg however lies on the Grande Île in the River Ill, which here flows parallel to, and roughly 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) from, the Rhine. The natural courses of the two rivers eventually join some distance downstream of Strasbourg, although several artificial waterways now connect them within the city.
The city lies in the Upper Rhine Plain, at between 132 metres (433 ft) and 151 metres (495 ft) above sea level, with the upland areas of the Vosges Mountains some 20 km (12 mi) to the west and the Black Forest 25 km (16 mi) to the east. This section of the Rhine valley is a major axis of north-south travel, with river traffic on the Rhine itself, and major roads and railways paralleling it on both banks.
The city is some 400 kilometres (250 mi) east of Paris. The mouth of the Rhine lies approximately 450 kilometres (280 mi) to the north, or 650 kilometres (400 mi) as the river flows, whilst the head of navigation in Basel is some 100 kilometres (62 mi) to the south, or 150 kilometres (93 mi) by river.
Climate
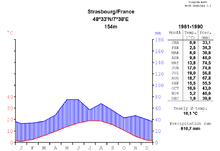
In spite of its position far inland, Strasbourg's climate is classified as Oceanic (Köppen climate classification Cfb), with warm, relatively sunny summers and cold, overcast winters. Precipitation is elevated from mid-spring to the end of summer, but remains largely constant throughout the year, totaling 631.4 mm (24.9 in) annually. On average, snow falls 30 days per year.
The highest temperature ever recorded was 38.5 °C (101.3 °F) in August 2003, during the 2003 European heat wave. The lowest temperature ever recorded was −23.4 °C (−10.1 °F) in December 1938.
Strasbourg's location in the Rhine valley, sheltered from the dominant winds by the Vosges and Black Forest mountains, results in poor natural ventilation, making Strasbourg one of the most atmospherically polluted cities of France.[9][10] Nonetheless, the progressive disappearance of heavy industry on both banks of the Rhine, as well as effective measures of traffic regulation in and around the city have reduced air pollution.[11]
| Climate data for Strasbourg, Bas-Rhin, France (1981–2010 averages) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.5 (63.5) |
21.1 (70) |
25.7 (78.3) |
30.0 (86) |
33.4 (92.1) |
37.0 (98.6) |
38.3 (100.9) |
38.5 (101.3) |
33.4 (92.1) |
29.1 (84.4) |
22.1 (71.8) |
18.3 (64.9) |
38.5 (101.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 4.5 (40.1) |
6.4 (43.5) |
11.4 (52.5) |
15.7 (60.3) |
20.2 (68.4) |
23.4 (74.1) |
25.7 (78.3) |
25.4 (77.7) |
21.0 (69.8) |
15.3 (59.5) |
8.8 (47.8) |
5.2 (41.4) |
15.3 (59.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.8 (35.2) |
2.9 (37.2) |
7 (45) |
10.5 (50.9) |
15 (59) |
18.1 (64.6) |
20.1 (68.2) |
19.8 (67.6) |
15.8 (60.4) |
11.2 (52.2) |
5.8 (42.4) |
2.8 (37) |
11 (52) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −0.8 (30.6) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
2.5 (36.5) |
5.2 (41.4) |
9.8 (49.6) |
12.8 (55) |
14.5 (58.1) |
14.1 (57.4) |
10.6 (51.1) |
7.1 (44.8) |
2.8 (37) |
0.3 (32.5) |
6.6 (43.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −23.6 (−10.5) |
−22.3 (−8.1) |
−16.7 (1.9) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
1.1 (34) |
4.9 (40.8) |
4.8 (40.6) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
−7.6 (18.3) |
−10.8 (12.6) |
−23.4 (−10.1) |
−23.6 (−10.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 32.2 (1.268) |
34.5 (1.358) |
42.8 (1.685) |
45.9 (1.807) |
81.9 (3.224) |
71.6 (2.819) |
72.7 (2.862) |
61.4 (2.417) |
63.5 (2.5) |
61.5 (2.421) |
47.0 (1.85) |
50.0 (1.969) |
665.0 (26.181) |
| Average precipitation days | 8.4 | 8.1 | 9.1 | 9.2 | 11.5 | 10.7 | 10.8 | 9.9 | 8.6 | 9.5 | 9.3 | 9.8 | 114.9 |
| Average snowy days | 7.8 | 6.7 | 4.0 | 1.5 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.4 | 6.3 | 29.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 86 | 82 | 76 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 72 | 76 | 80 | 85 | 86 | 86 | 79 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 58.1 | 83.8 | 134.8 | 180.0 | 202.5 | 223.8 | 228.6 | 219.6 | 164.5 | 98.7 | 55.3 | 43.1 | 1,692.7 |
| Source #1: Meteo France[12][13] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: Infoclimat.fr (humidity, snowy days 1961–1990)[14] | |||||||||||||
History
Prehistory
The human occupation of the environs of Strasbourg goes back many thousands of years.[15] Neolithic, bronze age and iron age artifacts have been uncovered by archeological excavations. It was permanently settled by proto-Celts around 1300 BC. Towards the end of the third century BC, it developed into a Celtic township with a market called "Argentorate". Drainage works converted the stilthouses to houses built on dry land.[16]
From Romans to Renaissance
Argentoratum
The Romans under Nero Claudius Drusus established a military outpost belonging to the Germania Superior Roman province at Strasbourg's current location, and named it Argentoratum. (Hence the town is commonly called Argentina in medieval Latin.[17]) The name "Argentoratum" was first mentioned in 12 BC and the city celebrated its 2,000th birthday in 1988. "Argentorate" as the toponym of the Gaulish settlement preceded it before being Latinized, but it is not known by how long. The Roman camp was destroyed by fire and rebuilt six times between the first and the fifth centuries AD: in 70, 97, 235, 355, in the last quarter of the fourth century, and in the early years of the fifth century. It was under Trajan and after the fire of 97 that Argentoratum received its most extended and fortified shape. From the year 90 on, the Legio VIII Augusta was permanently stationed in the Roman camp of Argentoratum. It then included a cavalry section and covered an area of approximately 20 hectares. Other Roman legions temporarily stationed in Argentoratum were the Legio XIV Gemina and the Legio XXI Rapax, the latter during the reign of Nero.
The centre of Argentoratum proper was situated on the Grande Île (Cardo: current Rue du Dôme, Decumanus: current Rue des Hallebardes). The outline of the Roman "castrum" is visible in the street pattern in the Grande Ile. Many Roman artifacts have also been found along the current Route des Romains, the road that led to Argentoratum, in the suburb of Kœnigshoffen. This was where the largest burial places were situated, as well as the densest concentration of civilian dwelling places and commerces next to the camp. Among the most outstanding finds in Kœnigshoffen were (found in 1911–12) the fragments of a grand Mithraeum that had been shattered by early Christians in the fourth century. From the fourth century, Strasbourg was the seat of the Bishopric of Strasbourg (made an Archbishopric in 1988). Archaeological excavations below the current Église Saint-Étienne in 1948 and 1956 unearthed the apse of a church dating back to the late fourth or early fifth century, considered to be the oldest church in Alsace. It is supposed that this was the first seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Strasbourg.
The Alemanni fought the Battle of Argentoratum against Rome in 357. They were defeated by Julian, later Emperor of Rome, and their King Chonodomarius was taken prisoner. On 2 January 366, the Alemanni crossed the frozen Rhine in large numbers to invade the Roman Empire. Early in the fifth century, the Alemanni appear to have crossed the Rhine, conquered, and then settled what is today Alsace and a large part of Switzerland.
Imperial city
| Imperial City of Strasbourg | ||||||||||
| Reichsstadt Straßburg (de) Ville libre de Strasbourg (fr) | ||||||||||
| Free Imperial City of the Holy Roman Empire | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Capital | Strasbourg | |||||||||
| Government | Republic | |||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | |||||||||
| • | City founded | 12 BC | ||||||||
| • | Acquired by the Empire | 923 1262 | ||||||||
| • | Gained Reichsfreiheit | 1262 | ||||||||
| • | Straßburger Revolution | 1332 | ||||||||
| • | Annexed by France | 1681 | ||||||||
| • | Annexation recognised by the Holy Roman Empire | 1697 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||



In the fifth century Strasbourg was occupied successively by Alemanni, Huns, and Franks. In the ninth century it was commonly known as Strazburg in the local language, as documented in 842 by the Oaths of Strasbourg. This trilingual text contains, alongside texts in Latin and Old High German (teudisca lingua), the oldest written variety of Gallo-Romance (lingua romana) clearly distinct from Latin, the ancestor of Old French. The town was also called Stratisburgum or Strateburgus in Latin, from which later came Strossburi in Alsatian and Straßburg in Standard German, and then Strasbourg in French. The Oaths of Strasbourg is considered as marking the birth of the two countries of France and Germany with the division of the Carolingian Empire.[18]
A major commercial centre, the town came under the control of the Holy Roman Empire in 923, through the homage paid by the Duke of Lorraine to German King Henry I. The early history of Strasbourg consists of a long conflict between its bishop and its citizens. The citizens emerged victorious after the Battle of Oberhausbergen in 1262, when King Philip of Swabia granted the city the status of an Imperial Free City.
Around 1200, Gottfried von Straßburg wrote the Middle High German courtly romance Tristan, which is regarded, alongside Wolfram von Eschenbach's Parzival and the Nibelungenlied, as one of great narrative masterpieces of the German Middle Ages.
A revolution in 1332 resulted in a broad-based city government with participation of the guilds, and Strasbourg declared itself a free republic. The deadly bubonic plague of 1348 was followed on 14 February 1349 by one of the first and worst pogroms in pre-modern history: over a thousand Jews were publicly burnt to death, with the remainder of the Jewish population being expelled from the city.[19] Until the end of the 18th century, Jews were forbidden to remain in town after 10 pm. The time to leave the city was signalled by a municipal herald blowing the Grüselhorn (see below, Museums, Musée historique);.[20] A special tax, the Pflastergeld (pavement money), was furthermore to be paid for any horse that a Jew would ride or bring into the city while allowed to.[21]
Construction on Strasbourg Cathedral began in the twelfth century, and it was completed in 1439 (though, of the towers, only the north tower was built), becoming the World's Tallest Building, surpassing the Great Pyramid of Giza. A few years later, Johannes Gutenberg created the first European moveable type printing press in Strasbourg.
In July 1518, an incident known as the Dancing Plague of 1518 struck residents of Strasbourg. Around 400 people were afflicted with dancing mania and danced constantly for weeks, most of them eventually dying from heart attack, stroke or exhaustion.
In the 1520s during the Protestant Reformation, the city, under the political guidance of Jacob Sturm von Sturmeck and the spiritual guidance of Martin Bucer embraced the religious teachings of Martin Luther. Their adherents established a Gymnasium, headed by Johannes Sturm, made into a University in the following century. The city first followed the Tetrapolitan Confession, and then the Augsburg Confession. Protestant iconoclasm caused much destruction to churches and cloisters, notwithstanding that Luther himself opposed such a practice. Strasbourg was a centre of humanist scholarship and early book-printing in the Holy Roman Empire, and its intellectual and political influence contributed much to the establishment of Protestantism as an accepted denomination in the southwest of Germany. (John Calvin spent several years as a political refugee in the city). The Strasbourg Councillor Sturm and guildmaster Matthias represented the city at the Imperial Diet of Speyer (1529), where their protest led to the schism of the Catholic Church and the evolution of Protestantism. Together with four other free cities, Strasbourg presented the confessio tetrapolitana as its Protestant book of faith at the Imperial Diet of Augsburg in 1530, where the slightly different Augsburg Confession was also handed over to Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor.
After the reform of the Imperial constitution in the early sixteenth century and the establishment of Imperial Circles, Strasbourg was part of the Upper Rhenish Circle, a corporation of Imperial estates in the southwest of Holy Roman Empire, mainly responsible for maintaining troops, supervising coining, and ensuring public security.
After the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg around 1440, the first printing offices outside the inventor's hometown Mainz were established around 1460 in Strasbourg by pioneers Johannes Mentelin and Heinrich Eggestein. Subsequently, the first modern newspaper was published in Strasbourg in 1605, when Johann Carolus received the permission by the City of Strasbourg to print and distribute a weekly journal written in German by reporters from several central European cities.

From Thirty Years' War to First World War
The Free City of Strasbourg remained neutral during the Thirty Years' War (1618-1648), and retained its status as a Free Imperial City. However, the city was later annexed by Louis XIV of France to extend the borders of his kingdom.
Louis' advisors believed that, as long as Strasbourg remained independent, it would endanger the King's newly annexed territories in Alsace, and, that to defend these large rural lands effectively, a garrison had to be placed in towns such as Strasbourg.[22] Indeed, the bridge over the Rhine at Strasbourg had been used repeatedly by Imperial (Holy Roman Empire) forces,[23] and three times during the Franco-Dutch War Strasbourg had served as a gateway for Imperial invasions into Alsace.[24] In September 1681 Louis' forces, though lacking a clear casus belli, surrounded the city with overwhelming force. After some negotiation, Louis marched into the city unopposed on 30 September 1681 and proclaimed its annexation.[25]
This annexation was one of the direct causes of the brief and bloody War of the Reunions whose outcome left the French in possession. The French annexation was recognized by the Treaty of Ryswick (1697). The official policy of religious intolerance which drove most Protestants from France after the revocation of the Edict of Nantes in 1685 was not applied in Strasbourg and in Alsace, because both had a special status as a province à l'instar de l'étranger effectif (a kind of foreign province of the king of France). Strasbourg Cathedral, however, was taken from the Lutherans to be returned to the Catholics as the French authorities tried to promote Catholicism wherever they could (some other historic churches remained in Protestant hands). Its language also remained overwhelmingly German: the German Lutheran university persisted until the French Revolution. Famous students included Goethe and Herder. The world's first school for midwives was opened in Strasbourg in 1728.[26]

During a dinner in Strasbourg organized by Mayor Frédéric de Dietrich on 25 April 1792, Claude Joseph Rouget de Lisle composed "La Marseillaise". The same year François Christophe Kellermann, a child of Strasbourg was appointed the head of the Mosel Army. He led his company to victory at the battle of Valmy and saved the young French republic. He was later appointed Duke of Valmy by Napoléon in 1808.
During this period Jean-Baptiste Kléber, also born in Strasbourg, led the French army to win several decisive victories. A statue of Kléber now stands in the centre of the city, at Place Kléber, and he is still one of the most famous French officers.
.jpg)
Strasbourg's status as a free city was revoked by the French Revolution. Enragés, most notoriously Eulogius Schneider, ruled the city with an increasingly iron hand. During this time, many churches and monasteries were either destroyed or severely damaged. The cathedral lost hundreds of its statues (later replaced by copies in the 19th century) and in April 1794, there was talk of tearing its spire down, on the grounds that it was against the principle of equality. The tower was saved, however, when in May of the same year citizens of Strasbourg crowned it with a giant tin Phrygian cap. This artifact was later kept in the historical collections of the city until it was destroyed in 1870 during the Franco-Prussian war.[27]
In 1805, 1806 and 1809, Napoléon Bonaparte and his first wife, Joséphine stayed in Strasbourg.[28] In 1810, his second wife Marie Louise, Duchess of Parma spent her first night on French soil in the palace. Another royal guest was King Charles X of France in 1828.[29] In 1836, Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte unsuccessfully tried to lead his first Bonapartist coup in Strasbourg.
With the growth of industry and commerce, the city's population tripled in the 19th century to 150,000.
During the Franco-Prussian War and the Siege of Strasbourg, the city was heavily bombarded by the Prussian army. The bombardment of the city was meant to break the morale of the people of Strasbourg.[30] On 24 and 26 August 1870, the Museum of Fine Arts was destroyed by fire, as was the Municipal Library housed in the Gothic former Dominican church, with its unique collection of medieval manuscripts (most famously the Hortus deliciarum), rare Renaissance books, archeological finds and historical artifacts. The gothic cathedral was damaged as well as the medieval church of Temple Neuf, the theatre, the city hall, the court of justice and many houses. At the end of the siege 10,000 inhabitants were left without shelter; over 600 died, including 261 civilians, and 3200 were injured, including 1,100 civilians.[31]
In 1871, after the end of the war, the city was transferred to the newly established German Empire as part of the Reichsland Elsass-Lothringen under the terms of the Treaty of Frankfurt. As part of Imperial Germany, Strasbourg was rebuilt and developed on a grand and representative scale, such as the Neue Stadt, or "new city" around the present Place de la République. Historian Rodolphe Reuss and Art historian Wilhelm von Bode were in charge of rebuilding the municipal archives, libraries and museums. The University, founded in 1567 and suppressed during the French Revolution as a stronghold of German sentiment, was reopened in 1872 under the name Kaiser-Wilhelms-Universität.
.jpg)
A belt of massive fortifications was established around the city, most of which still stands today, renamed after French generals and generally classified as Monuments historiques; most notably Fort Roon (now Fort Desaix) and Fort Podbielski (now Fort Ducrot) in Mundolsheim, Fort von Moltke (now Fort Rapp) in Reichstett, Fort Bismarck (now Fort Kléber) in Wolfisheim, Fort Kronprinz (now Fort Foch) in Niederhausbergen, Fort Kronprinz von Sachsen (now Fort Joffre) in Holtzheim and Fort Großherzog von Baden (now Fort Frère) in Oberhausbergen.[32]
Those forts subsequently served the French army (Fort Podbielski/Ducrot for instance was integrated into the Maginot Line[33]), and were used as POW-camps in 1918 and 1945.
Two garrison churches were also erected for the members of the Imperial German army, the Lutheran Église Saint-Paul and the Roman Catholic Église Saint-Maurice.
1918 to the present



Following the defeat of the German empire in World War I and the abdication of the German Emperor, some revolutionary insurgents declared Alsace-Lorraine as an independent Republic, without preliminary referendum or vote. On 11 November 1918 (Armistice Day), communist insurgents proclaimed a "soviet government" in Strasbourg, following the example of Kurt Eisner in Munich as well as other German towns. French troops commanded by French general Henri Gouraud entered triumphantly in the city on 22 November. A major street of the city now bears the name of that date (Rue du 22 Novembre) which celebrates the entry of the French in the city.[34][35][36] Viewing the massive cheering crowd gathered under the balcony of Strasbourg's town hall, French President Raymond Poincaré stated that "the plebiscite is done".[37]
In 1919, following the Treaty of Versailles, the city was annexed by France in accordance with U.S. President Woodrow Wilson's "Fourteen Points" without a referendum. The date of the assignment was retroactively established on Armistice Day. It is doubtful whether a referendum in Strasbourg would have ended in France's favour since the political parties striving for an autonomous Alsace or a connection to France accounted only for a small proportion of votes in the last Reichstag as well as in the local elections.[38] The Alsatian autonomists who were pro French had won many votes in the more rural parts of the region and other towns since the annexation of the region by Germany in 1871. The movement started with the first election for the Reichstag; those elected were called "les députés protestataires", and until the fall of Bismarck in 1890, they were the only deputies elected by the Alsatians to the German parliament demanding the return of those territories to France.[39] At the last Reichstag election in Strasbourg and its periphery, the clear winners were the Social Democrats; the city was the administrative capital of the region, was inhabited by many Germans appointed by the central government in Berlin and its flourishing economy attracted many Germans. This could explain the difference between the rural vote and the one in Strasbourg. After the war, many Germans left Strasbourg and went back to Germany; some of them were denounced by the locals or expelled by the newly appointed authorities. The Saverne Affair was vivid in the memory among the Alsatians.
In 1920, Strasbourg became the seat of the Central Commission for Navigation on the Rhine, previously located in Mannheim, one of the oldest European institutions. It moved into the former Imperial Palace.
When the Maginot Line was built, the Sous-secteur fortifié de Strasbourg (fortified sub-sector of Strasbourg) was laid out on the city's territory as a part of the Secteur fortifié du Bas-Rhin, one of the sections of the Line. Blockhouses and casemates were built along the Grand Canal d'Alsace and the Rhine in the Robertsau forest and the port.[40]
Between the German invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939 and the Anglo-French declaration of War against the German Reich on 3 September 1939, the entire city (a total of 120,000 people) was evacuated, like other border towns as well. Until the arrival of the Wehrmacht troops mid-June 1940, the city was, for ten months, completely empty, with the exception of the garrisoned soldiers. The Jews of Strasbourg had been evacuated to Périgueux and Limoges, the University had been evacuated to Clermont-Ferrand.
After the ceasefire following the Fall of France in June 1940, Alsace was annexed by Germany and a rigorous policy of Germanisation was imposed upon it by the Gauleiter Robert Heinrich Wagner. When, in July 1940, the first evacuees were allowed to return, only residents of Alsatian origin were admitted. The last Jews were deported on 15 July 1940 and the main synagogue, a huge Romanesque revival building that had been a major architectural landmark with its 54-metre-high dome since its completion in 1897, was set ablaze, then razed.[41]

In September 1940 the first Alsatian resistance movement led by Marcel Weinum called La main noire (The black hand) was created. It was composed by a group of 25 young men aged from 14 to 18 years old who led several attacks against the German occupation. The actions culminated with the attack on the Gauleiter Robert Wagner, the highest commander of Alsace directly under the order of Hitler. In March 1942, Marcel Weinum was prosecuted by the Gestapo and sentenced to be beheaded at the age of 18 in April 1942 in Stuttgart, Germany. His last words will be: "If I have to die, I shall die but with a pure heart". From 1943 the city was bombarded by Allied aircraft. While the First World War had not notably damaged the city, Anglo-American bombing caused extensive destruction in raids of which at least one was allegedly carried out by mistake.[42] In August 1944, several buildings in the Old Town were damaged by bombs, particularly the Palais Rohan, the Old Customs House (Ancienne Douane) and the Cathedral.[43] On 23 November 1944, the city was officially liberated by the 2nd French Armoured Division under General Leclerc. He achieved the oath that he made with his soldiers, after the decisive Capture of Kufra. With the Oath of Kuffra, they swore to keep up the fight until the French flag flew over the Cathedral of Strasbourg.
Many people from Strasbourg were incorporated in the German Army against their will, and were sent to the eastern front, those young men and women were called Malgré-nous. Many tried to escape from the incorporation, join the French Resistance, or desert the Wehrmacht but many couldn't because they were running the risk of having their families sent to work or concentration camps by the Germans. Many of these men, especially those who did not answer the call immediately, were pressured to "volunteer" for service with the SS, often by direct threats on their families. This threat obliged the majority of them to remain in the German army. After the war, the few that survived were often accused of being traitors or collaborationists, because this tough situation was not known in the rest of France, and they had to face the incomprehension of many. In July 1944, 1500 malgré-nous were released from Soviet captivity and sent to Algiers, where they joined the Free French Forces. Nowadays history recognizes the suffering of those people, and museums, public discussions and memorials have been built to commemorate this terrible period of history of this part of Eastern France (Alsace and Moselle). Liberation of Strasbourg took place on 23 November 1944.
In 1947, a fire broke out in the Musée des Beaux-Arts and devastated a significant part of the collections. This fire was an indirect consequence of the bombing raids of 1944: because of the destruction inflicted on the Palais Rohan, humidity had infiltrated the building, and moisture had to be fought. This was done with welding torches, and a bad handling of these caused the fire.[44]
In the 1950s and 1960s the city was enlarged by new residential areas meant to solve both the problem of housing shortage due to war damage and that of the strong growth of population due to the baby boom and immigration from North Africa: Cité Rotterdam in the North-East, Quartier de l'Esplanade in the South-East, Hautepierre in the North-West. Between 1995 and 2010, a new district has been built in the same vein, the Quartier des Poteries, south of Hautepierre.
In 1958, a violent hailstorm destroyed most of the historical greenhouses of the Botanical Garden and many of the stained glass windows of St. Paul's Church.
In 1949, the city was chosen to be the seat of the Council of Europe with its European Court of Human Rights and European Pharmacopoeia. Since 1952, the European Parliament has met in Strasbourg, which was formally designated its official 'seat' at the Edinburgh meeting of the European Council of EU heads of state and government in December 1992. (This position was reconfirmed and given treaty status in the 1997 Treaty of Amsterdam). However, only the (four-day) plenary sessions of the Parliament are held in Strasbourg each month, with all other business being conducted in Brussels and Luxembourg. Those sessions take place in the Immeuble Louise Weiss, inaugurated in 1999, which houses the largest parliamentary assembly room in Europe and of any democratic institution in the world. Before that, the EP sessions had to take place in the main Council of Europe building, the Palace of Europe, whose unusual inner architecture had become a familiar sight to European TV audiences.[45] In 1992, Strasbourg became the seat of the Franco-German TV channel and movie-production society Arte.
In 2000, a terrorist plot to blow up the cathedral was prevented thanks to the cooperation between French and German police that led to the arrest in late 2000 of a Frankfurt-based group of terrorists.
On 6 July 2001, during an open-air concert in the Parc de Pourtalès, a single falling Platanus tree killed thirteen people and injured 97. On 27 March 2007, the city was found guilty of neglect over the accident and fined €150,000.[46]
In 2006, after a long and careful restoration, the inner decoration of the Aubette, made in the 1920s by Hans Arp, Theo van Doesburg, and Sophie Taeuber-Arp and destroyed in the 1930s, was made accessible to the public again. The work of the three artists had been called "the Sistine Chapel of abstract art".[47]
Districts
Strasbourg is divided into the following districts:[48]
- Bourse, Esplanade, Krutenau
- Centre République
- Centre Gare
- Conseil des XV, Rotterdam
- Cronenbourg, Hautepierre, Poteries, Hohberg
- Koenigshoffen, Montagne-Verte, Elsau
- Meinau
- Neudorf, Schluthfeld, Port du Rhin, Musau
- Neuhof, Stockfeld, Ganzau
- Robertsau, Wacken
Main sights

Architecture
The city is chiefly known for its sandstone Gothic Cathedral with its famous astronomical clock, and for its medieval cityscape of Rhineland black and white timber-framed buildings, particularly in the Petite France district or Gerberviertel ("tanners' district") alongside the Ill and in the streets and squares surrounding the cathedral, where the renowned Maison Kammerzell stands out.
Notable medieval streets include Rue Mercière, Rue des Dentelles, Rue du Bain aux Plantes, Rue des Juifs, Rue des Frères, Rue des Tonneliers, Rue du Maroquin, Rue des Charpentiers, Rue des Serruriers, Grand' Rue, Quai des Bateliers, Quai Saint-Nicolas and Quai Saint-Thomas. Notable medieval squares include Place de la Cathédrale, Place du Marché Gayot, Place Saint-Étienne, Place du Marché aux Cochons de Lait and Place Benjamin Zix.


In addition to the cathedral, Strasbourg houses several other medieval churches that have survived the many wars and destructions that have plagued the city: the Romanesque Église Saint-Étienne, partly destroyed in 1944 by Allied bombing raids, the part Romanesque, part Gothic, very large Église Saint-Thomas with its Silbermann organ on which Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and Albert Schweitzer played,[49] the Gothic Église protestante Saint-Pierre-le-Jeune with its crypt dating back to the seventh century and its cloister partly from the eleventh century, the Gothic Église Saint-Guillaume with its fine early-Renaissance stained glass and furniture, the Gothic Église Saint-Jean, the part Gothic, part Art Nouveau Église Sainte-Madeleine, etc. The Neo-Gothic church Saint-Pierre-le-Vieux Catholique (there is also an adjacent church Saint-Pierre-le-Vieux Protestant) serves as a shrine for several 15th-century wood worked and painted altars coming from other, now destroyed churches and installed there for public display. Among the numerous secular medieval buildings, the monumental Ancienne Douane (old custom-house) stands out.
The German Renaissance has bequeathed the city some noteworthy buildings (especially the current Chambre de commerce et d'industrie, former town hall, on Place Gutenberg), as did the French Baroque and Classicism with several hôtels particuliers (i.e. palaces), among which the Palais Rohan (1742, now housing three museums) is the most spectacular. Other buildings of its kind are the "Hôtel de Hanau" (1736, now the city hall), the Hôtel de Klinglin (1736, now residence of the préfet), the Hôtel des Deux-Ponts (1755, now residence of the military governor), the Hôtel d'Andlau-Klinglin (1725, now seat of the administration of the Port autonome de Strasbourg) etc. The largest baroque building of Strasbourg though is the 150 m (490 ft) long 1720s main building of the Hôpital civil. As for French Neo-classicism, it is the Opera House on Place Broglie that most prestigiously represents this style.
Strasbourg also offers high-class eclecticist buildings in its very extended German district, the Neustadt, being the main memory of Wilhelmian architecture since most of the major cities in Germany proper suffered intensive damage during World War II. Streets, boulevards and avenues are homogeneous, surprisingly high (up to seven stories) and broad examples of German urban lay-out and of this architectural style that summons and mixes up five centuries of European architecture as well as Neo-Egyptian, Neo-Greek and Neo-Babylonian styles. The former imperial palace Palais du Rhin, the most political and thus heavily criticized of all German Strasbourg buildings epitomizes the grand scale and stylistic sturdiness of this period. But the two most handsome and ornate buildings of these times are the École internationale des Pontonniers (the former Höhere Mädchenschule, girls college) with its towers, turrets and multiple round and square angles[50] and the École des Arts décoratifs with its lavishly ornate façade of painted bricks, woodwork and majolica.[51]

Notable streets of the German district include: Avenue de la Forêt Noire, Avenue des Vosges, Avenue d'Alsace, Avenue de la Marseillaise, Avenue de la Liberté, Boulevard de la Victoire, Rue Sellénick, Rue du Général de Castelnau, Rue du Maréchal Foch, and Rue du Maréchal Joffre. Notable squares of the German district include: Place de la République, Place de l'Université, Place Brant, and Place Arnold
Impressive examples of Prussian military architecture of the 1880s can be found along the newly reopened Rue du Rempart, displaying large-scale fortifications among which the aptly named Kriegstor (war gate).
As for modern and contemporary architecture, Strasbourg possesses some fine Art Nouveau buildings (such as the huge Palais des Fêtes and houses and villas like Villa Schutzenberger and Hôtel Brion), good examples of post-World War II functional architecture (the Cité Rotterdam, for which Le Corbusier did not succeed in the architectural contest) and, in the very extended Quartier Européen, some spectacular administrative buildings of sometimes utterly large size, among which the European Court of Human Rights building by Richard Rogers is arguably the finest. Other noticeable contemporary buildings are the new Music school Cité de la Musique et de la Danse, the Musée d'Art moderne et contemporain and the Hôtel du Département facing it, as well as, in the outskirts, the tramway-station Hoenheim-Nord designed by Zaha Hadid.
The city has many bridges, including the medieval and four-towered Ponts Couverts that, despite their name, are no longer covered. Next to the Ponts Couverts is the Barrage Vauban, a part of Vauban's 17th-century fortifications, that does include a covered bridge. Other bridges are the ornate 19th-century Pont de la Fonderie (1893, stone) and Pont d'Auvergne (1892, iron), as well as architect Marc Mimram's futuristic Passerelle over the Rhine, opened in 2004.
The largest square at the centre of the city of Strasbourg is the Place Kléber. Located in the heart of the city's commercial area, it was named after general Jean-Baptiste Kléber, born in Strasbourg in 1753 and assassinated in 1800 in Cairo. In the square is a statue of Kléber, under which is a vault containing his remains. On the north side of the square is the Aubette (Orderly Room), built by Jacques François Blondel, architect of the king, in 1765–1772.
Parks

Strasbourg features a number of prominent parks, of which several are of cultural and historical interest: the Parc de l'Orangerie, laid out as a French garden by André le Nôtre and remodeled as an English garden on behalf of Joséphine de Beauharnais, now displaying noteworthy French gardens, a neo-classical castle and a small zoo; the Parc de la Citadelle, built around impressive remains of the 17th-century fortress erected close to the Rhine by Vauban;[52] the Parc de Pourtalès, laid out in English style around a baroque castle (heavily restored in the 19th century) that now houses a small three-star hotel,[53] and featuring an open-air museum of international contemporary sculpture.[54] The Jardin botanique de l'Université de Strasbourg (botanical garden) was created under the German administration next to the Observatory of Strasbourg, built in 1881, and still owns some greenhouses of those times. The Parc des Contades, although the oldest park of the city, was completely remodeled after World War II. The futuristic Parc des Poteries is an example of European park-conception in the late 1990s. The Jardin des deux Rives, spread over Strasbourg and Kehl on both sides of the Rhine opened in 2004 and is the most extended (60-hectare) park of the agglomeration. The most recent park is Parc du Heyritz (8,7 ha), opened in 2014 along a canal facing the hôpital civil.
Museums
For a city of comparatively small size, Strasbourg displays a large quantity and variety of museums:
Fine art museums

Unlike most other cities, Strasbourg's collections of European art are divided into several museums according not only to type and area, but also to epoch. Old master paintings from the Germanic Rhenish territories and until 1681 are displayed in the Musée de l'Œuvre Notre-Dame, old master paintings from all the rest of Europe (including the Dutch Rhenish territories) and until 1871 as well as old master paintings from the Germanic Rhenish territories between 1681 and 1871 are displayed in the Musée des Beaux-Arts. Old master graphic arts until 1871 is displayed in the Cabinet des estampes et dessins. Decorative arts until 1681 ("German period") are displayed in the Musée de l'Œuvre Notre-Dame, decorative arts from 1681 to 1871 ("French period") are displayed in the Musée des Arts décoratifs. International art (painting, sculpture, graphic arts) and decorative art since 1871 is displayed in the Musée d'art moderne et contemporain. The latter museum also displays the city's photographic library.
- The Musée des Beaux-Arts owns paintings by Hans Memling, Francisco de Goya, Tintoretto, Paolo Veronese, Giotto di Bondone, Sandro Botticelli, Peter Paul Rubens, Anthony van Dyck, El Greco, Correggio, Cima da Conegliano and Piero di Cosimo, among others.
- The Musée de l'Œuvre Notre-Dame (located in a part-Gothic, part-Renaissance building next to the Cathedral) houses a large and renowned collection of medieval and Renaissance upper-Rhenish art, among which original sculptures, plans and stained glass from the Cathedral and paintings by Hans Baldung and Sebastian Stoskopff.
- The Musée d'Art moderne et contemporain is among the largest museums of its kind in France.
- The Musée des Arts décoratifs, located in the sumptuous former residence of the cardinals of Rohan, the Palais Rohan displays a reputable collection of 18th century furniture and china.
- The Cabinet des estampes et des dessins displays five centuries of engravings and drawings, but also woodcuts and lithographies.
- The Musée Tomi Ungerer/Centre international de l'illustration, located in a large former villa next to the Theatre, displays original works by Ungerer and other artists (Saul Steinberg, Ronald Searle...) as well as Ungerer's large collection of ancient toys.
Other museums
- The Musée archéologique presents a large display of regional findings from the first ages of man to the sixth century, focussing especially on the Roman and Celtic period.
- The Musée alsacien is dedicated to traditional Alsatian daily life.
- Le Vaisseau ("The vessel") is a science and technology centre, especially designed for children.
- The Musée historique (historical museum) is dedicated to the tumultuous history of the city and displays many artifacts of the times, among which the 'Grüselhorn, the horn that was blown every evening at 10:00, during medieval times, to order the Jews out of the city.
- The Musée de la Navigation sur le Rhin, also going by the name of Naviscope, located in an old ship, is dedicated to the history of commercial navigation on the Rhine.
- The Musée vodou (Vodou museum) opened its doors on 28 November 2013. Displaying a private collection of artefacts from Haiti, it is located in a former water tower (château d'eau) built in 1883 and classified as a Monument historique.
University museums
The Université de Strasbourg is in charge of a number of permanent public displays of its collections of scientific artefacts and products of all kinds of exploration and research.[55]
- The Musée zoologique is one of the oldest in France and is especially famous for its collection of birds. The museum is co-administrated by the municipality.
- The Gypsothèque (also known as Musée des moulages) is France's second largest cast collection and the largest university cast collection in France.
- The Musée de Sismologie et Magnétisme terrestre displays antique instruments of measure
- The Musée Pasteur is a collection of medical curiosities
- The Musée de minéralogie is dedicated to minerals
- The Musée d'Égyptologie houses a collections of archaeological findings made in and brought from Egypt and Sudan
- The Crypte aux étoiles ("star crypt") is situated in the vaulted basement below the Observatory of Strasbourg and displays old telescopes and other antique astronomical devices such as clocks and theodolites.
Demographics
The metropolitan area of Strasbourg had a population of 768,868 inhabitants in 2012 (French side of the border only), while the transnational Eurodistrict had a population of 915,000 inhabitants in 2014.
Population growth
| 1684 | 1789 | 1851 | 1871 | 1890 | 1910 | 1921 | 1936 | 1946 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22,000 | 49,943 | 75,565 | 85,654 | 123,500 | 178,891 | 166,767 | 193,119 | 175,515 |
| 1954 | 1962 | 1968 | 1975 | 1982 | 1990 | 1999 | 2006 | 2013 |
| 200,921 | 228,971 | 249,396 | 253,384 | 248,712 | 252,338 | 263,941 | 272,975 | 275,718 |

Population composition
| 2012 | % | 2007 | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Population | 274,394 | 100 | 272,123 | 100 |
| 0–14 years | 47,473 | 17.3 | 46,263 | 17.0 |
| 15–29 years | 77,719 | 28.3 | 78,291 | 28.8 |
| 30–44 years | 54,514 | 19.9 | 54,850 | 20.2 |
| 45–59 years | 45,436 | 16.6 | 47,236 | 17.4 |
| 60–74 years | 30,321 | 11.1 | 27,060 | 9.9 |
| 75+ years | 18,931 | 6.9 | 18,424 | 6.8 |
Culture
Strasbourg is the seat of internationally renowned institutions of music and drama:
- The Orchestre philharmonique de Strasbourg, founded in 1855, one of the oldest symphonic orchestras in western Europe. Based since 1975 in the Palais de la musique et des congrès.
- The Opéra national du Rhin
- The Théâtre national de Strasbourg
- The Percussions de Strasbourg
- The Théâtre du Maillon
- The "Laiterie"
- Joshy's house - a venue for performance poetry and freestyle urban music.
- Au Zénith
Other theatres are the Théâtre jeune public, the TAPS Scala, the Kafteur...
Events
- Musica, international festival of contemporary classical music (autumn)
- Festival international de Strasbourg (founded in 1932), festival of classical music and jazz (summer)
- Festival des Artefacts, festival of contemporary non-classical music
- Les Nuits électroniques de l'Ososphère
- The Spectre Film Festival is an annual film festival that is devoted to science fiction, horror and fantasy.
- The Strasbourg International Film Festival is an annual film festival focusing on new and emerging independent filmmakers from around the world.
Education
Universities and tertiary education
Strasbourg, well known as centre of humanism, has a long history of excellence in higher-education, at the crossroads of French and German intellectual traditions. Although Strasbourg had been annexed by the Kingdom of France in 1683, it still remained connected to the German-speaking intellectual world throughout the 18th century and the university attracted numerous students from the Holy Roman Empire, including Goethe, Metternich and Montgelas, who studied law in Strasbourg, among the most prominent. Nowadays, Strasbourg is known to offer among the best university courses in France, after Paris.
Up until January 2009 there were three universities in Strasbourg, with an approximate total of 48,500 students as of 2007 (another 4,500 students are being taught at one of the diverse post-graduate schools):[56]
- Strasbourg I – Louis Pasteur University
- Strasbourg II – Marc Bloch University
- Strasbourg III – Robert Schuman University
Since 1 January 2009, those three universities have merged and constitute now the Université de Strasbourg. Schools part of the Université de Strasbourg include:
- The IEP (Institut d'études politiques de Strasbourg), the University of Strasbourg's political science & international studies center.
- The EMS (École de management Strasbourg), the University of Strasbourg's Business School.
- The INSA (Institut national des sciences appliquées), the University of Strasbourg's Engineering School.
- The ENA (École nationale d'administration). ENA trains most of the nation's high-ranking civil servants. The relocation to Strasbourg was meant to give a European vocation to the school and to implement the French government's "décentralisation" plan.
- The ESAD (École supérieure des arts décoratifs) is an art school of European reputation.
- The ISEG Group (Institut supérieur européen de gestion group).
- The ISU (International Space University) is located in the south of Strasbourg (Illkirch-Graffenstaden).
- The ECPM (École européenne de chimie, polymères et matériaux).
- The EPITECH (École pour l'informatique et les nouvelles technologies).
- The INET (Institut national des études territoriales).
- The IIEF (Institut international d'études françaises).
- The ENGEES (École nationale du génie de l'eau et de l'environnement de Strasbourg).
- The CUEJ (Centre universitaire d'enseignement du journalisme).
- TÉLÉCOM Physique Strasbourg,(École nationale supérieure de physique de Strasbourg), Institute of Technology, located in the South of Strasbourg (Illkirch-Graffenstaden).
Primary and secondary education
International schools include:
Multiple levels:
For elementary education:[57]
- École Internationale Robert Schuman
- Strasbourg International School
- International School at Lucie Berger
- Russian Mission School in Strasbourg[58]
For middle school/junior high school education:[57]
- Collège Internationale de l'Esplenade
For senior high school/sixth form college:[57]
- Lycée international des Pontonniers (FR)
Libraries

The Bibliothèque nationale et universitaire (BNU) is, with its collection of more than 3,000,000 titles,[59] the second largest library in France after the Bibliothèque nationale de France. It was founded by the German administration after the complete destruction of the previous municipal library in 1871 and holds the unique status of being simultaneously a students' and a national library. The Strasbourg municipal library had been marked erroneously as "City Hall" in a French commercial map, which had been captured and used by the German artillery to lay their guns. A librarian from Munich later pointed out "...that the destruction of the precious collection was not the fault of a German artillery officer, who used the French map, but of the slovenly and inaccurate scholarship of a Frenchman."[60]
The municipal library Bibliothèque municipale de Strasbourg (BMS) administrates a network of ten medium-sized librairies in different areas of the town. A six stories high "Grande bibliothèque", the Médiathèque André Malraux, was inaugurated on 19 September 2008 and is considered the largest in Eastern France.[61]
Incunabula
As one of the earliest centers of book-printing in Europe (see above: History), Strasbourg for a long time held a large number of incunabula—documents printed before 1500—in her library as one of her most precious heritages. After the total destruction of this institution in 1870, however, a new collection had to be reassembled from scratch. Today, Strasbourg's different public and institutional libraries again display a sizable total number of incunabula, distributed as follows: Bibliothèque nationale et universitaire, ca. 2 098[62] Médiathèque de la ville et de la communauté urbaine de Strasbourg, 394[63] Bibliothèque du Grand Séminaire, 238[64] Médiathèque protestante, 94[65] and Bibliothèque alsatique du Crédit Mutuel, 5.[66]
Transportation
Train services operate from the Gare de Strasbourg, the city's main station in the city centre, eastward to Offenburg and Karlsruhe in Germany, westward to Metz and Paris, and southward to Basel. Strasbourg's links with the rest of France have improved due to its recent connection to the TGV network, with the first phase of the TGV Est (Paris–Strasbourg) in 2007, the TGV Rhin-Rhône (Strasbourg-Lyon) in 2012, and the second phase of the TGV Est in July 2016.
Strasbourg also has its own airport, serving major domestic destinations as well as international destinations in Europe and northern Africa. The airport is linked to the Gare de Strasbourg by a frequent train service.[67][68]
City transportation in Strasbourg includes the futurist-looking Strasbourg tramway that opened in 1994 and is operated by the regional transit company Compagnie des Transports Strasbourgeois (CTS), consisting of 6 lines with a total length of 55.8 km (34.7 mi). The CTS also operates a comprehensive bus network throughout the city that is integrated with the trams. With more than 500 km (311 mi) of bicycle paths, biking in the city is convenient and the CTS operates a cheap bike-sharing scheme named Vélhop'. The CTS, and its predecessors, also operated a previous generation of tram system between 1878 and 1960, complemented by trolleybus routes between 1939 and 1962.
Being a city on the Ill and close to the Rhine, Strasbourg has always been an important centre of fluvial navigation, as is attested by archeological findings. In 1682 the Canal de la Bruche was added to the river navigations, initially to provide transport for sandstone from quarries in the Vosges for use in the fortification of the city. That canal has since closed, but the subsequent Canal du Rhone au Rhine, Canal de la Marne au Rhin and Grand Canal d'Alsace are still in use, as is the important activity of the Port autonome de Strasbourg. Water tourism inside the city proper attracts hundreds of thousands of tourists yearly.
The tram system that now criss-crosses the historic city centre complements walking and biking in it. The centre has been transformed into a pedestrian priority zone that enables and invites walking and biking by making these active modes of transport comfortable, safe and enjoyable. These attributes are accomplished by applying the principle of "filtered permeability" to the existing irregular network of streets. It means that the network adaptations favour active transportation and, selectively, "filter out" the car by reducing the number of streets that run through the centre. While certain streets are discontinuous for cars, they connect to a network of pedestrian and bike paths which permeate the entire centre. In addition, these paths go through public squares and open spaces increasing the enjoyment of the trip. This logic of filtering a mode of transport is fully expressed in a comprehensive model for laying out neighbourhoods and districts – the Fused Grid.
At present the A35 autoroute, which parallels the Rhine between Karlsruhe and Basel, and the A4 autoroute, which links Paris with Strasbourg, penetrate close to the centre of the city. The Grand contournement ouest (GCO) project, programmed since 1999, plans to construct a 24 km (15 mi) long highway connection between the junctions of the A4 and the A35 autoroutes in the north and of the A35 and A352 autoroutes in the south. This routes well to the west of the city and is meant to divest a significant portion of motorized traffic from the unité urbaine.[69]
European role
Institutions
Strasbourg is the seat of over twenty international institutions,[70] most famously of the Council of Europe and of the European Parliament, of which it is the official seat. Strasbourg is considered the legislative and democratic capital of the European Union, while Brussels is considered the executive and administrative capital and Luxembourg the judiciary and financial capital. [71]
Strasbourg is the seat of the following organisations, among others:
- Central Commission for Navigation on the Rhine (since 1920)
- Council of Europe with all the bodies and organisations affiliated to this institution (since 1949)
- European Parliament (since 1952)
- European Ombudsman
- Eurocorps headquarters,
- Franco-German television channel Arte
- European Science Foundation
- International Institute of Human Rights
- Human Frontier Science Program
- International Commission on Civil Status
- Assembly of European Regions
- Centre for European Studies (French: Centre d'études européennes de Strasbourg)
- Sakharov Prize
Eurodistrict
France and Germany have created a Eurodistrict straddling the Rhine, combining the Greater Strasbourg and the Ortenau district of Baden-Württemberg, with some common administration. It was established in 2005 and is fully functional since 2010.
Sports
Internationally renowned teams from Strasbourg are the Racing Club de Strasbourg (football), Strasbourg IG (basketball) and the Étoile Noire (ice hockey).[72] The women's tennis Internationaux de Strasbourg is one of the most important French tournaments of its kind outside Roland-Garros. In 1922, Strasbourg was the venue for the XVI Grand Prix de l’A.C.F. which saw Fiat battle Bugatti, Ballot, Rolland Pilain, and Britain's Aston Martin and Sunbeam.
Honours
Honours associated with the city of Strasbourg.
- The Medal of Honor Strasbourg
- Sakharov Prize seated in Strasbourg
- City of Strasbourg Silver (gilt) Medal, a former medal with City Coat of Arms and Ten Arms of the Cities of the Dekapolis[73]
Notable people
In chronological order, notable people born in Strasbourg include: Eric of Friuli, Johannes Tauler, Sebastian Brant, Jean Baptiste Kléber, Louis Ramond de Carbonnières, François Christophe Kellermann, Marie Tussaud, Ludwig I of Bavaria, Charles Frédéric Gerhardt, Louis-Frédéric Schützenberger, Gustave Doré, Émile Waldteufel, Jean/Hans Arp, Charles Münch, Hans Bethe, Maurice Kriegel-Valrimont, Marcel Marceau, Tomi Ungerer, Arsène Wenger, Petit and Matt Pokora.
In chronological order, notable residents of Strasbourg include: Johannes Gutenberg, Hans Baldung, Martin Bucer, John Calvin, Joachim Meyer, Johann Carolus, Johann Wolfgang Goethe, Jakob Michael Reinhold Lenz, Klemens Wenzel von Metternich, Georg Büchner, Louis Pasteur, Ferdinand Braun, Albrecht Kossel, Georg Simmel, Albert Schweitzer, Otto Klemperer, Marc Bloch, Alberto Fujimori, Marjane Satrapi, Paul Ricoeur and Jean-Marie Lehn.
Twin towns and sister cities
Strasbourg is twinned with:[74]
 Boston, United States, since 1960[74][75]
Boston, United States, since 1960[74][75] Leicester, Great Britain, since 1960[74][76][77]
Leicester, Great Britain, since 1960[74][76][77] Stuttgart, Germany, since 1962[74][78]
Stuttgart, Germany, since 1962[74][78] Dresden, Germany, since 1990[74][79]
Dresden, Germany, since 1990[74][79] Ramat Gan, Israel, since 1991[74][80]
Ramat Gan, Israel, since 1991[74][80]
Strasbourg has cooperative agreements with:
- Jacmel, Haiti, since 1996 (Coopération décentralisée)
- Veliky Novgorod, Russia, since 1997 (Coopération décentralisée)
- Fes, Morocco (Coopération décentralisée)
- Douala, Cameroon (Coopération décentralisée)
- Bamako, Mali (Coopération décentralisée)
In popular culture
In film
- The opening scenes of the 1977 Ridley Scott film The Duellists take place in Strasbourg in 1800.
- The 2007 film In the City of Sylvia is set in Strasbourg.
- Early February 2011, principal photography for Sherlock Holmes: A Game of Shadows (2011) moved for two days to Strasbourg. Shooting took place on, around, and inside the Strasbourg Cathedral. The opening scene of the movie covers an assassination-bombing in the city.
In literature
- One of the longest chapters of Laurence Sterne's novel Tristram Shandy (1759–1767), "Slawkenbergius' tale", takes place in Strasbourg.[81]
- An episode of Matthew Gregory Lewis' novel The Monk (1796) takes place in the forests then surrounding Strasbourg.
In music
- Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart called his Third violin concerto (1775) Straßburger Konzert because of one of its most prominent motives, based on a local, minuet-like dance that had already appeared as a tune in a symphony by Carl Ditters von Dittersdorf.[82] It is not related to Mozart's ulterior stay in Strasbourg (1778), where he gave three concert performances on the piano.
- Havergal Brian's Symphony No.7 was inspired by passages in Goethe's memoirs recalling his time spent at Strasbourg University. The work ends with an orchestral bell sounding the note E, the strike-note of the bell of Strasbourg Cathedral.
- British art-punk band The Rakes had a minor hit in 2005 with their song "Strasbourg". This song features witty lyrics with themes of espionage and vodka and includes a cleverly placed count of 'eins, zwei, drei, vier!!', even though Strasbourg's spoken language is French.
- On their 1974 album Hamburger Concerto, Dutch progressive band Focus included a track called "La Cathédrale de Strasbourg", which included chimes from a cathedral-like bell.
- Strasbourg pie, a dish containing foie gras, is mentioned in the finale of the Andrew Lloyd Webber musical Cats.
- Several works have specifically been dedicated to Strasbourg Cathedral, notably ad hoc compositions (masses, motets etc.) by Kapellmeisters Franz Xaver Richter and Ignaz Pleyel and, more recently, It is Finished by John Tavener and Details on the Strasbourg Rosace by Spencer Topel.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Only the part of the urban area on French territory.
- ↑ "67482-Strasbourg". insee.fr. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- ↑ "AUnité urbaine de Strasbourg (partie française) (67701)". insee.fr. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- ↑ "Aire urbaine de Strasbourg (partie française) (009)". insee.fr. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
- ↑ "Données relatives à l'Eurodistrict". eurodistrict.eu. Retrieved 31 December 2015.
- ↑ "The international institute of Human Rights".
- ↑ France Vows to Kick out Islamic Troublemakers.
- ↑ "Figures on the port's website". Web.archive.org. Archived from the original on 20 April 2008. Retrieved 5 April 2011.
- ↑ "Daily measurements for Strasbourg and Alsace". Atmo-alsace.net. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ Measurements made on 18 and 19 October 2005
- ↑ "Outlines of the urban transportation policy led by the urban community of Strasbourg". Epe.be. 29 March 2010. Archived from the original on 11 December 2008. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ "Données climatiques de la station de Strasbourg" (in French). Meteo France. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ↑ "Climat Alsace" (in French). Meteo France. Retrieved 10 December 2014.
- ↑ "Normes et records 1961-1990: Strasbourg-Entzheim (67) - altitude 150m" (in French). Infoclimat. Retrieved 16 December 2014.
- ↑ Racontez-moi Strasbourg Guy Trendel, Édition La Nuée Bleue, p.10
- ↑ Histoire secrète de Strasbourg, Michel Bertrand, Édition Albin Michel, p.11 et p.12
- ↑ Grässe, J. G. Th. (1909) [1861]. "A". Orbis Latinus; oder, Verzeichnis der wichtigsten lateinischen orts- und ländernamen [Orbis Latinus; or, Index of the important Latin place and land-names] (Lexicon) (in German) (2nd ed.). Berlin: Schmidt. OCLC 1301238 – via Columbia University.
- ↑ Matthias von Hellfeld. "Die Geburt zweier Staaten – Die Straßburger Eide vom 14. Februar 842 , Wir Europäer , Deutsche Welle". Dw-world.de. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ (French) The "Valentine's day massacre" of 1349
- ↑ (French) The Jews of Strasbourg and the Great Plague
- ↑ (French) The Jews of Strasbourg until the French Revolution
- ↑ John A. Lynn, The Wars of Louis XIV: 1667–1714, p. 164.
- ↑ John A. Lynn, The Wars of Louis XIV: 1667–1714, pp. 163–164.
- ↑ John A. Lynn, The Wars of Louis XIV: 1667–1714, p. 169.
- ↑ John A. Lynn, The Wars of Louis XIV: 1667–1714, p. 163.
- ↑ Grimberg, Michel (2003). Recherches sur le monde germanique. Presses de l'Université Paris-Sorbonne. p. 425. ISBN 2-84050-303-4. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
- ↑ "Strasbourg Cathedral and the French Revolution (1789–1802)". Inlibroveritas.net. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ "The Napoleon room" (in French). Ameliefr.club.fr. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ Recht, Roland; Foessel, Georges; Klein, Jean-Pierre: Connaître Strasbourg, 1988, ISBN 2-7032-0185-0 (French)
- ↑ Pierre Jacob, Histoire-Géographie - Alsachroniques - Strasbourg bombardé, in Lycée Marcel Rudloff, Strasbourg 2013, quoting "Illustrierte Geschichte des Krieges 1870/71, Stuttgart, Berlin, Leipzig"; Raymond BONGRAND, 1870, Alsace, Metz-Sedan, Strasbourg, 1970. Sur le siège de Strasbourg: p. 332 & seq.;François UBERFILL, La société strasbourgeoise entre France et Allemagne (1871-1924), Collection « Recherches et documents », Tome 67, Publications de la Société Savante d'Alsace, 2001, p. 63 & seq.; Raymond OBERLE, Alsace: 1870, l'année terrible, Strasbourg, 2000.
- ↑ Le siège de Strasbourg en 1870, Fort Frère, Strasbourg 2013; http://www.fort-frere.fr/la-place-forte-de-strasbourg/son-histoire/10-le-siege-de-strasbourg-en-1870.
- ↑ "La place forte de Strasbourg – Découverte des ouvrages" (in French). fort-frere.fr. Retrieved 25 July 2010.
- ↑ Festen incorporées, dans la Ligne, www.ligne-maginot.fr (French)
- ↑ "Architecture et photos à Strasbourg".
- ↑ Didier Daeninckx: 11 Novembre 1918: le drapeau rouge flotte sur Strasbourg
- ↑ Ballade strasbourgeoise, INA.fr (French)
- ↑ Jean-Noël Grandhomme, « Le retour de l'Alsace-Lorraine », L'Histoire, no 336, Novembre 2008, p. 60-63.
- ↑ As can be seen here
- ↑ Les députés « protestataires » d'Alsace-Lorraine sur assemblee-nationale.fr.
- ↑ Secteur fortifié du Bas-Rhin (French)
- ↑ La Synagogue Consistoriale du quai Kléber: de la pose de la première pierre à sa destruction (1896–1940) (French); Daltroff, Jean: 1898–1940, La synagogue consistoriale de Strasbourg, Éditions Ronald Hirlé, 1996, ISBN 2-910048-35-7
- ↑ "Civilians on the frontline ? Allied aerial bombings in north-eastern France, 1940–1945" (PDF). Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ "Pictures of Strasbourg in ruins after the 1944 bombing raids". Witzgilles.com. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ Peintures flamandes et hollandaises du Musée des Beaux-Arts de Strasbourg, Éditions des Musées de Strasbourg, February 2009, ISBN 978-2-35125-030-3 (French) – page 14
- ↑ "The former hemicycle of the European Parliament in Strasbourg (1999)". CVCE. Retrieved 16 January 2015.
- ↑ "City of Strasbourg fined in storm death". News.monstersandcritics.com. 27 March 2007. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ "Reopening of the restored rooms". Batiactu.com. 13 April 2006. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ "Les quartiers".
- ↑ "History and description of the instrument". Perso.wanadoo.fr. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ "Pictures". Archi-strasbourg.org. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ Views
- ↑ "Parc de la Citadelle with remains of the Vauban fortress". Archi-strasbourg.org. 26 August 2007. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ "Overview". chateau-pourtales.eu. Retrieved 12 December 2010.
- ↑ "Overview". Ceaac.org. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ "Overview of the collections". Collections.u-strasbg.fr. Retrieved 9 December 2013.
- ↑ "Internet Archive Wayback Machine". Web.archive.org. 12 October 2007. Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 3 June 2011.
- 1 2 3 "International schooling in Strasbourg" (Archive). City of Strasbourg. Retrieved on 28 March 2016. p. 1.
- ↑ "Контакты." Russian Mission School in Strasbourg. Retrieved on March 28, 2016. "6, alle'e de la Robertsau, 67000, Strasbourg"
- ↑ "Figures". Bnu.fr. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ Butler, Pierce. 1945. Books and libraries in wartime. Chicago, Ill: University of Chicago Press. Page 15.
- ↑ Strasbourg ouvre une grande médiathèque sur le port in L'Express (French)
- ↑ "Les incunables" (in French). Bibliothèque nationale et universitaire de Strasbourg. Retrieved 12 December 2014.
- ↑ "Strasbourg - Médiathèque André Malraux" (in French). Catalogue collectif de France (CCFr). Retrieved 12 December 2014.
- ↑ "La bibliothèque ancienne du Grand Séminaire" (in French). Séminaire Sainte Marie Majeure - Diocèse de Strasbourg. Retrieved 12 December 2014.
- ↑ "Catalogue de la Médiathèque protestante". Médiathèque protestante. Retrieved 15 December 2014.
- ↑ "Général". Bacm.creditmutuel.fr. Retrieved 16 June 2009.
- ↑ "Destination map". Aéroport Strasbourg. Archived from the original on 18 September 2015. Retrieved 18 September 2015.
- ↑ "Shuttle train". Aéroport Strasbourg. Archived from the original on 18 September 2015. Retrieved 18 September 2015.
- ↑ Grand Contournement Ouest de Strasbourg(French)
- ↑ "List of international institutions in Strasbourg". Investir-strasbourg.com. 15 January 2003. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ "Comparative Law Academy: the ECHR and the FCC". The Brief. 2011-05-24. Retrieved 2016-10-13.
- ↑ "Etoile Noire de Strasbourg". Etoile-noire.fr. 31 May 2009. Retrieved 16 June 2009.
- ↑ http://www.cachecoins.org/strasbourg.htm
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Strasbourg, Twin City". Strasbourg.eu & Communauté Urbaine. Archived from the original on 28 July 2013. Retrieved 21 August 2013.
- ↑ "Boston Sister Cities". The City of Boston. Archived from the original on 8 February 2009. Retrieved 5 April 2009.
- ↑ "British towns twinned with French towns". Archant Community Media Ltd. Retrieved 11 July 2013.
- ↑ "Twinning". Leicester City council. Retrieved 5 February 2010.
- ↑ "Stuttgart Städtepartnerschaften". Landeshauptstadt Stuttgart, Abteilung Außenbeziehungen (in German). Retrieved 27 July 2013.
- ↑ "Dresden – Partner Cities". 2008 Landeshauptstadt Dresden. Archived from the original on 16 October 2008. Retrieved 29 December 2008.
- ↑ "Ramat Gan Sister Cities". Archived from the original on 7 March 2008. Retrieved 6 April 2008.
- ↑ "Full text". Tristramshandyweb.it. Retrieved 15 April 2010.
- ↑ Lempfrid, Wolfgang. "Wolfgng Amadeus Mozart: Konzert für Violine und Orchester in D-Dur, KV 218". koelnklavier.de. Retrieved 5 April 2016.
Sources
- Connaître Strasbourg by Roland Recht, Georges Foessel and Jean-Pierre Klein, 1988, ISBN 2-7032-0185-0
- Histoire de Strasbourg des origines à nos jours, four volumes (ca. 2000 pages) by a collective of historians under the guidance of Georges Livet and Francis Rapp, 1982, ISBN 2-7165-0041-X
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Strasbourg. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Strasbourg. |
- Strasbourg municipality website
- Tourist office of Strasbourg
- CTS – Compagnie des transports strasbourgeois
- The museums of Strasbourg
- The city archives of Strasbourg (French)





.jpg)
.jpg)