Additional Articles of the Constitution of the Republic of China
|
Additional Articles of the Constitution of the Republic of China | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese |
中華民國憲法 增修條文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese |
中华民国宪法 增修条文 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of the Republic of China |
|---|
 |
| Commonly known as Taiwan |
|
Leadership |
|
|
|
Other branches 
|
|
Related topics |
|
Taiwan portal |
The Additional Articles of the Constitution of the Republic of China (Chinese: 中華民國憲法增修條文) are the revisions and constitutional amendments to the original constitution to meet the requisites of the nation and the political status of Taiwan.
The Additional Articles are the fundamental law of the present government of the Republic of China on Taiwan since 1991.
Articles
- Article 1: About the procedure of the amendment of the Constitution and alteration of the national territory.
- Article 2: About the president and the vice president.
- Article 3: About the premier and the Executive Yuan.
- Article 4: About the Legislative Yuan.
- Article 5: About the Judicial Yuan.
- Article 6: About the Examination Yuan.
- Article 7: About the Control Yuan.
- Article 8: About the remuneration and pay of the members of the Legislative Yuan.
- Article 9: About the local governments.
- Article 10: About the basic national policy.
- Article 11: About the Cross-Strait relations (rights and obligations between the free area and mainland China).
- Article 12: About the amendment of the Constitution.
Comparison of the governmental structure
The present structure of government are regulated by the Additional Articles in 2005.[1]
| Governmental structure | Original Constitution (1947) | Additional Articles (2005) |
|---|---|---|
| Head of state | The president and the vice president are elected separately by the National Assembly for a duration of 6 years | The president and the vice president are elected in a group by the citizens of the Free area for a duration of 4 years, renewable once. |
| Head of government | The premier is nominated by the president, and consented by the Legislative Yuan. | The premier is appointed by the president. |
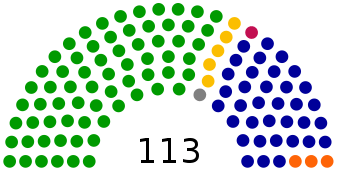
| Parliament | Tricameralism: National Assembly, Legislative Yuan and Control Yuan. The members of the National Assembly are elected for a duration of 6 years. The members of the Legislative Yuan are elected for a duration of 3 years. The members of the Control Yuan are elected by provincial legislators for a duration of 6 years. | Unicameralism: Legislative Yuan. The 113 members of the Legislative Yuan are elected for a duration of 4 years. |
| Judiciary | The justices are nominated by the president, and consented by the Control Yuan. The justices are tenure. | The 15 justices are nominated by the president, and consented by the Legislative Yuan for a duration of 8 years, non-renewable. |
| Local government | Two level system: provincial Level, county Level | The provinces are streamlined. Counties and cities under provinces are directly led by the central government. |
See also
- Constitution of the Republic of China
- Temporary Provisions Effective During the Period of Communist Rebellion
- Politics of the Republic of China
References
External links
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
| Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Annotated Republic of China Laws/Additional Articles of the Constitution of the Republic of China |
- Additional Articles of the Constitution by the Office of the President, Republic of China (Taiwan)
- English translation of the Additional Articles of the Constitution (2005 reform)
- English translation of the Constitution by the Taiwan Documents Project.
- Constitution day and constitutional government
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/1/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.