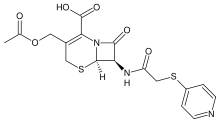
Cefapirin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a601206 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous, intramuscular |
| ATC code | J01DB08 (WHO) QG51AA05 (WHO) QJ51DB08 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
21593-23-7 |
| PubChem (CID) | 30699 |
| DrugBank |
DB01139 |
| ChemSpider |
28486 |
| UNII |
89B59H32VN |
| KEGG |
D07636 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:554446 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1599 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.409 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H17N3O6S2 |
| Molar mass | 423.466 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Cefapirin (INN, also spelled cephapirin) is an injectable, first-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. It is marketed under the trade name Cefadyl. Production for use in humans has been discontinued in the United States.[1]
It also has a role in veterinary medicine as Metricure, an intrauterine preparation, and combined with prednisolone in Mastiplan, an intramammary preparation. Both are licensed in cattle.
Synthesis
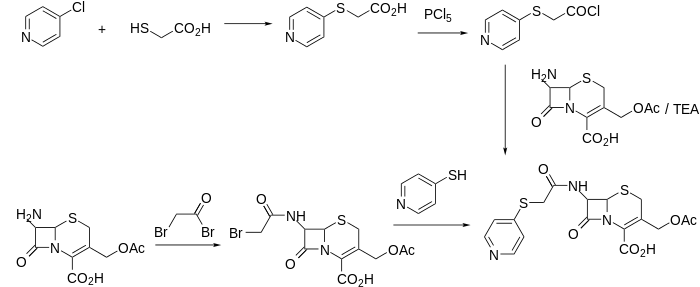
In one of the syntheses, 7-aminocephalosporanic acid (7-ACA) is reacted with bromoacetyl chloride to give the amide. The halo group is then displaced by 4-thiopyridine.[2]
References
- ↑ http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm?fuseaction=Search.Overview&DrugName=CEFADYL
- 1 2 Crast, L. B.; Graham, R. G.; Cheney, L. C. (1973). "Synthesis of cephapirin and related cephalosporins from 7-(.alpha.-bromoacetamido)cephalosporanic acid". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 16 (12): 1413. doi:10.1021/jm00270a025.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.