Solar eclipse of February 5, 2000
| Solar eclipse of February 5, 2000 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Partial |
| Gamma | -1.2233 |
| Magnitude | 0.5795 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 70°12′S 134°06′E / 70.2°S 134.1°E |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 12:50:27 |
| References | |
| Saros | 150 (16 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9507 |
A partial solar eclipse occurred on February 5, 2000. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. It was only visible over Antarctica.
Images
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1997-2000
Each member in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1997 to 2000 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Saros | Map | |||
120 Chita, Russia | March 9, 1997 Total |
125 | September 2, 1997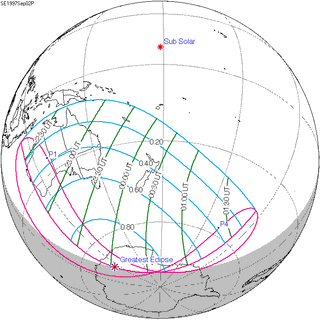 Partial | |||
| 130 | February 26, 1998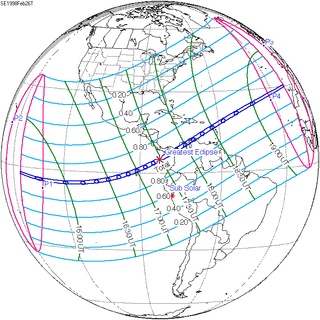 Total |
135 | August 22, 1998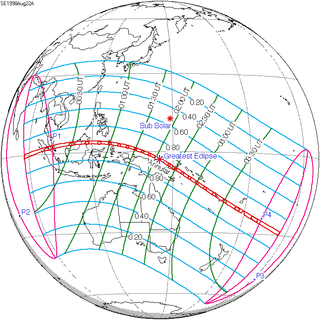 Annular | |||
| 140 | February 16, 1999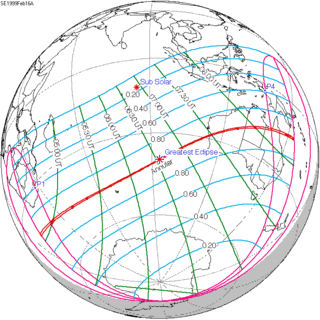 Annular |
145 Totality from France | August 11, 1999 Total | |||
| 150 | February 5, 2000 Partial |
155 | July 31, 2000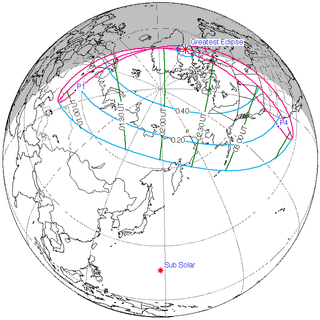 Partial | |||
| Partial solar eclipses on July 1, 2000 and December 25, 2000 occur in the next lunar year eclipse set. | ||||||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
| 22 eclipse events between September 12, 1931 and July 1, 2011. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| September 11-12 | June 30-July 1 | April 18-19 | February 4-5 | November 22-23 |
| 114 | 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 |
 September 12, 1931 |
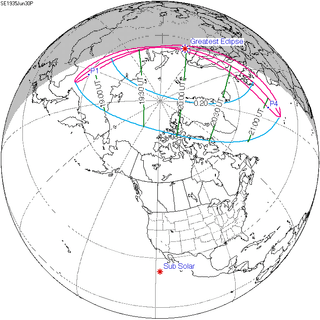 June 30, 1935 |
 April 19, 1939 |
 February 4, 1943 |
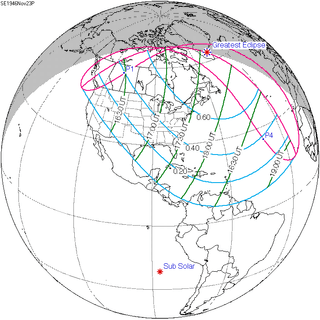 November 23, 1946 |
| 124 | 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 |
 September 12, 1950 |
 June 30, 1954 |
 April 19, 1958 |
 February 5, 1962 |
 November 23, 1965 |
| 134 | 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 |
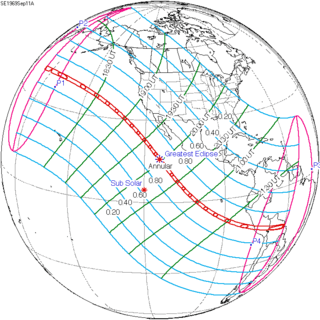 September 11, 1969 |
 June 30, 1973 |
 April 18, 1977 |
 February 4, 1981 |
 November 22, 1984 |
| 144 | 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 |
 September 11, 1988 |
 June 30, 1992 |
 April 17, 1996 |
 February 5, 2000 |
 November 23, 2003 |
| 154 | 156 | |||
 September 11, 2007 |
 July 1, 2011 | |||
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 2000 February 5. |
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/19/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
